- This dive 👉 『Geometric optics』in『Discrete mathematics』
- Described by .ppt ⊊ 👉「1.『Multiple Euclidean algorithm』runs automatically in『Dewar bottle』=『pure-reflection non-absorbing notched blackbody』.pptx」
- Utilizes simulator ⊷ 👉 2D ray-optics simulation
- Utilized by .ppt ⊶ 👉「A_guided_tour_to_Ray_&_Wave_Optics_Simulation.pptx」
- Links to model ✉ 👉 NLAST-vector model (Private)
- Contains paper ⊋ 👉 Berry-Mcleod paper (Private)
- 『Wave Optics』in『Partial Differential Equations (PDEs)』
- Links to model ✉ 👉 NLAST-vector model (Private)
- Utilized by .ppt ⊶ 👉「A_guided_tour_to_Ray_&_Wave_Optics_Simulation.pptx」
- Involved in book ⊊ 👉 Illusions_of_Illustrations_·_Zodiac
- Contained by books ⊂ 👉 three e-books
- Belongs to Career ⊊ 👉 PhD activities
- Linked to ✉ 👉「Penrose's room」that「cannot be illuminated by a single point」
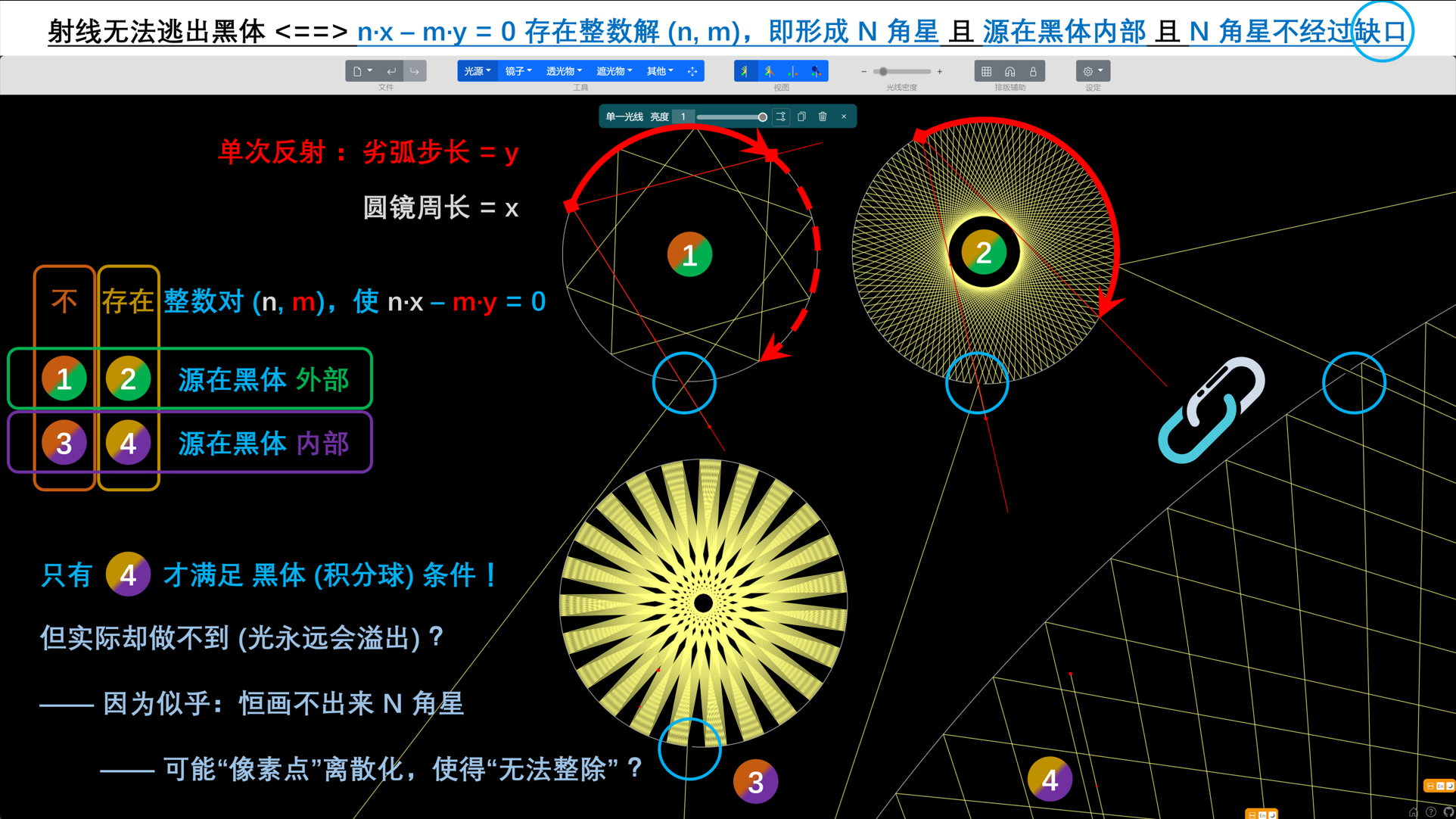
- 中文「自述文档」㊥ 👉 几何光学 in 离散数学
- 『This exploration process』is one of『the examples of the second book』
- Using『Euclidean algorithm』to understand the『Multiple reflections』of light from the『Inner wall of the silver mirror』in the unsealed『Dewar bottle』
- Discussed the application of algebra (mathematics) in geometry (optics)
- External light source: when it enters the『pure reflection blackbody』from the outside, the light will eventually come out from the gap. Why?
- Internal light source: when the source is inside the『pure reflection blackbody』,light may not necessarily come out from the gap. What are the corresponding conditions?
- Ideological perspective: Abstract the『optical process』in『concave mirror』into『mathematical process』
- See the animation in file「Multiple Euclidean algorithm runs automatically in『Dewar bottle』=『pure-reflection non-absorbing notched blackbody』.pptx」
- See the content『The origin of the circular vector』on page 8 of「2.『Illusions_of_Illustrations_·_Zodiac』.pdf」
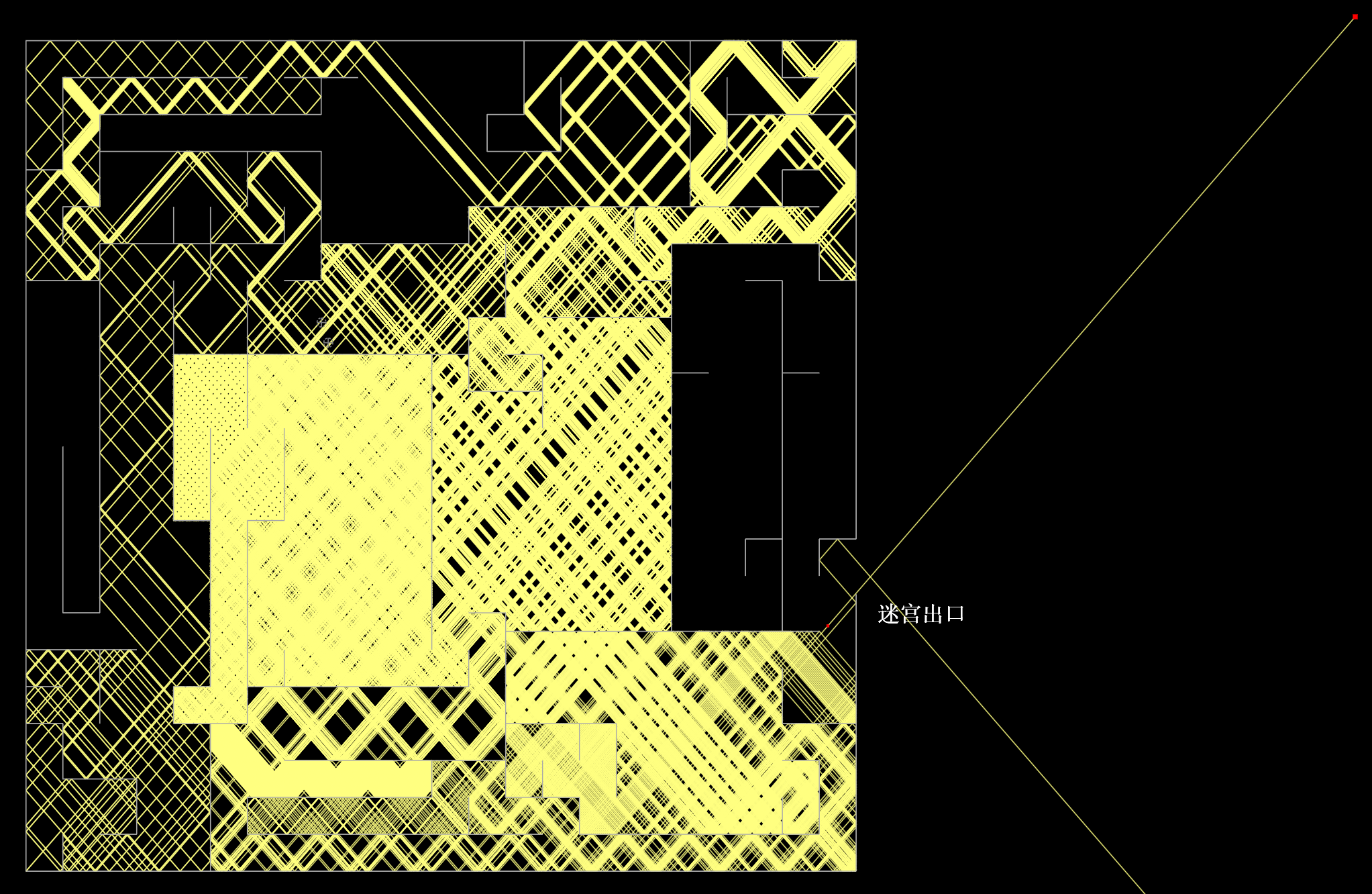
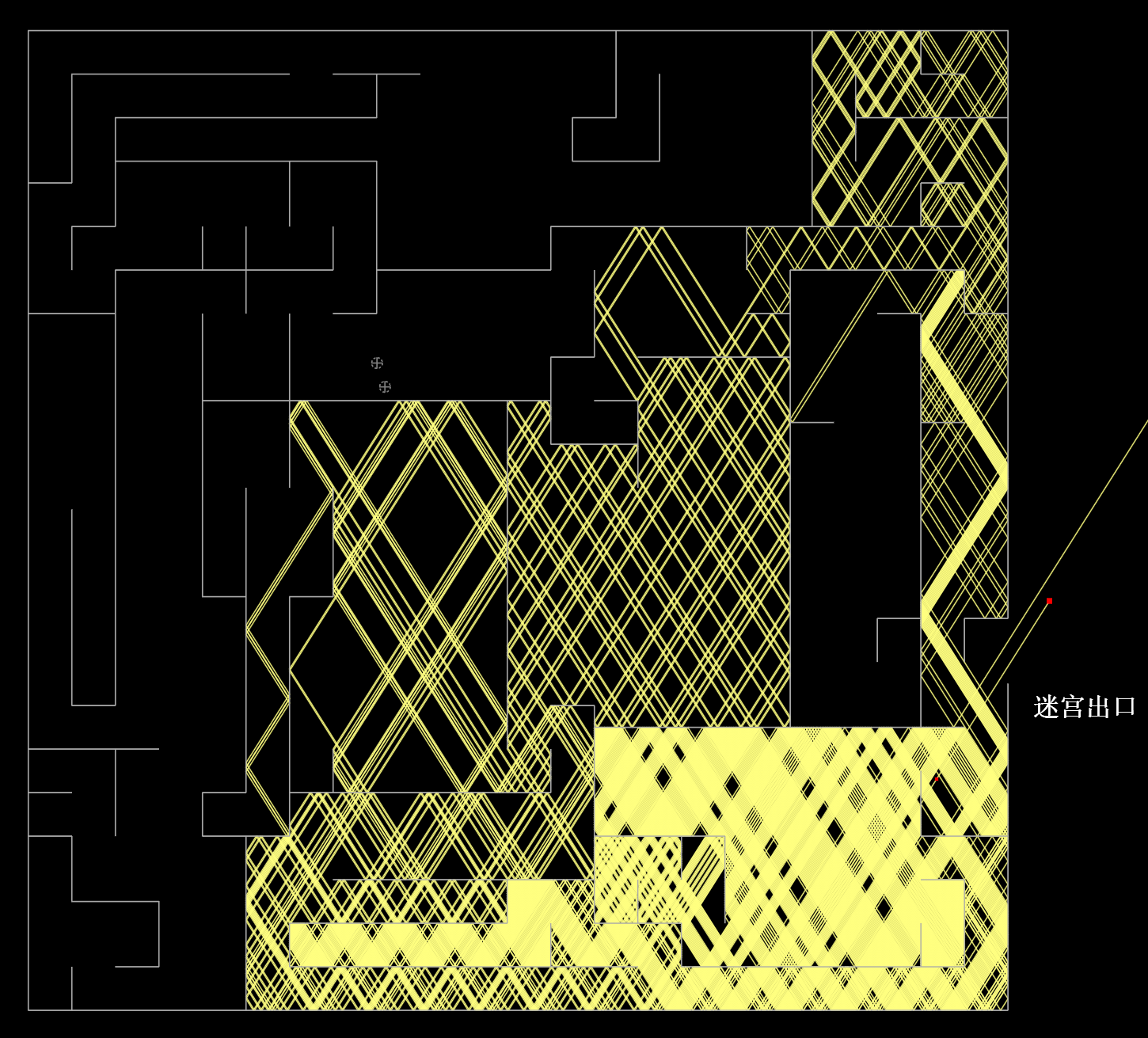
- Optical Expansion:『Integral Sphere with Notches』➞『Maze with Exits』
- The same conclusion applies to『any other shape』, such as a『labyrinth-shaped cavity』
- That is to say, the shape of a blackbody may not necessarily be spherical
- If the light source is『inside the maze』, the light『may not be able to solve/escape the maze』
- See the case『Maze solution』
- If the light source is『outside the maze』, then the light『can definitely come out of the maze again』
- Mathematical Expansion:『Bivariate』to『Multivariate』linear indeterminate equation ('s Special/General solution)
- Open the folder "cpp_codes_for_book2『Illusions_of_Illustrations_·_Zodiac』".
- Run「12.第10个程序的改良版(2+5+8b).cpp」inside using Visual C++ 6.0, or rather,
- using
Microsoft Visual Studio C++ 6.0\Common\MSDev98\Bin\MSDEV.EXE. - VC6.0 Download & Setup ; Higher version of C++ is recommended, but may not be able to run this project?
- using
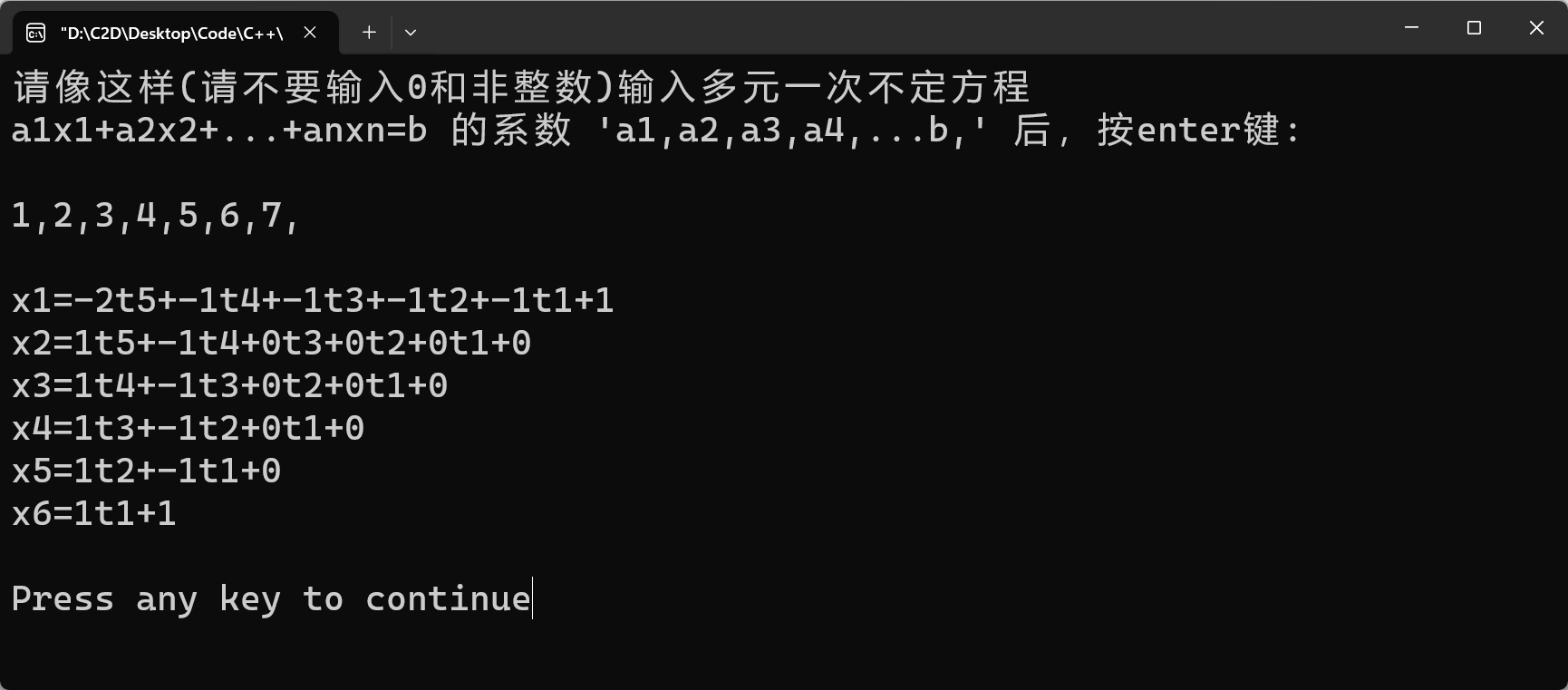
- See page 10 of「2.『Illusions_of_Illustrations_·_Zodiac』.pdf」
- This dive 👉 『Geometric optics』in『Discrete mathematics』
- (Personal time) 25-year_10-month-old
- (Personal stage) Ph.D. 2nd Grade Winter Vacation (1.5 / 3.0)
- (World time) 2024.02