符号表是一种存储键值对的数据结构,目的是将一个键与一个值连接起来,支持两种操作:
- 插入(put),即将一组新的键值对存入表中;
- 查找(get),即根据给定的键得到相应的值。
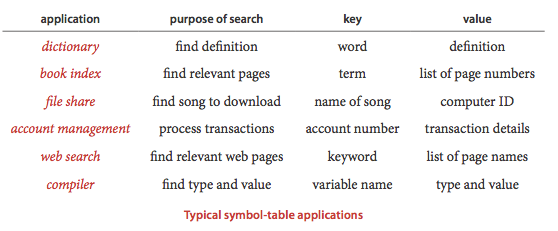
应用:
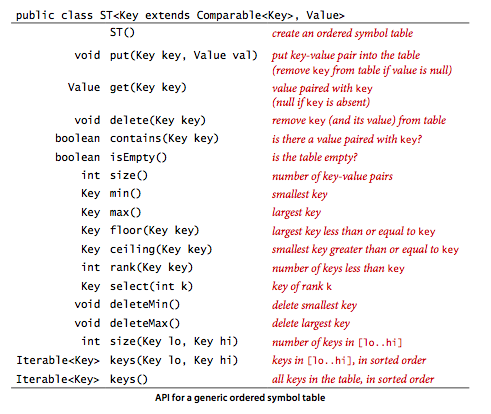
符号表分为有序和无序两种,有序符号表主要指支持 min()、max() 等根据键的大小关系来实现的操作。
-
无序符号表
public interface UnorderedST<Key, Value> { int size(); Value get(Key key); void put(Key key, Value value); void delete(Key key); }
-
有序符号表
public interface OrderedST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> { int size(); void put(Key key, Value value); Value get(Key key); Key min(); Key max(); int rank(Key key); List<Key> keys(Key l, Key h); }
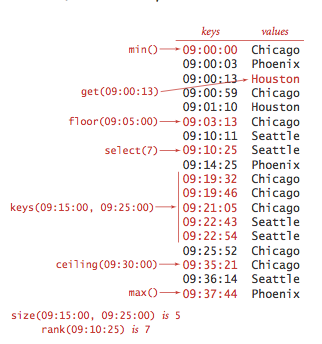
操作示例:
public class FrequencyCounter {
// Do not instantiate.
private FrequencyCounter() { }
public static void main(String[] args) {
int distinct = 0, words = 0;
int minlen = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
ST<String, Integer> st = new ST<String, Integer>();
// compute frequency counts
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
if (key.length() < minlen) continue;
words++;
if (st.contains(key)) {
st.put(key, st.get(key) + 1);
}
else {
st.put(key, 1);
distinct++;
}
}
// find a key with the highest frequency count
String max = "";
st.put(max, 0);
for (String word : st.keys()) {
if (st.get(word) > st.get(max))
max = word;
}
StdOut.println(max + " " + st.get(max));
StdOut.println("distinct = " + distinct);
StdOut.println("words = " + words);
}
}统计标准输入中各个单词出现的频率,然后将最高频率单词打印出来。
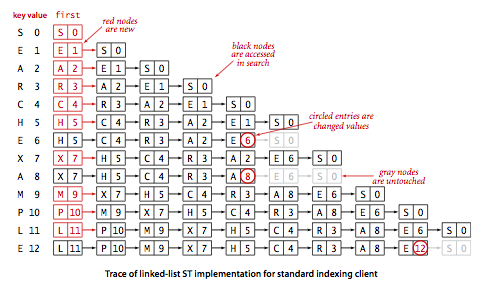
public class ListUnorderedST<Key, Value> implements UnorderedST<Key, Value> {
private Node first;
private class Node {
Key key;
Value value;
Node next;
Node(Key key, Value value, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
int cnt = 0;
Node cur = first;
while (cur != null) {
cnt++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cnt;
}
@Override
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
Node cur = first;
// 如果在链表中找到节点的键等于 key 就更新这个节点的值为 value
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key)) {
cur.value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 否则使用头插法插入一个新节点
first = new Node(key, value, first);
}
@Override
public void delete(Key key) {
if (first == null)
return;
if (first.key.equals(key))
first = first.next;
Node pre = first, cur = first.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key)) {
pre.next = cur.next;
return;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public Value get(Key key) {
Node cur = first;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key))
return cur.value;
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
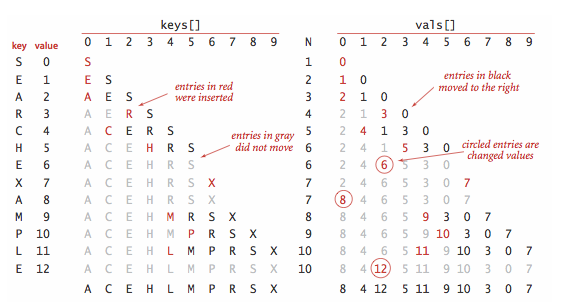
}使用一对平行数组,一个存储键一个存储值。
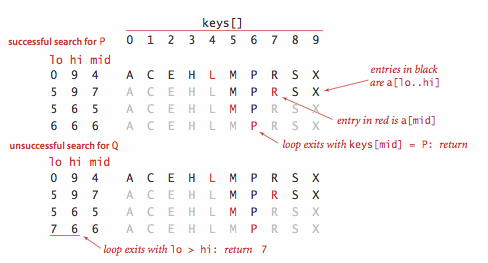
二分查找的 rank() 方法至关重要,当键在表中时,它能够知道该键的位置;当键不在表中时,它也能知道在何处插入新键。
二分查找最多需要 logN+1 次比较,使用二分查找实现的符号表的查找操作所需要的时间最多是对数级别的。但是插入操作需要移动数组元素,是线性级别的。
public class BinarySearchOrderedST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> implements OrderedST<Key, Value> {
private Key[] keys;
private Value[] values;
private int N = 0;
public BinarySearchOrderedST(int capacity) {
keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity];
values = (Value[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public int size() {
return N;
}
@Override
public int rank(Key key) {
int l = 0, h = N - 1;
while (l <= h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[m]);
if (cmp == 0)
return m;
else if (cmp < 0)
h = m - 1;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return l;
}
@Override
public List<Key> keys(Key l, Key h) {
int index = rank(l);
List<Key> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (keys[index].compareTo(h) <= 0) {
list.add(keys[index]);
index++;
}
return list;
}
@Override
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
int index = rank(key);
// 如果找到已经存在的节点键为 key,就更新这个节点的值为 value
if (index < N && keys[index].compareTo(key) == 0) {
values[index] = value;
return;
}
// 否则在数组中插入新的节点,需要先将插入位置之后的元素都向后移动一个位置
for (int j = N; j > index; j--) {
keys[j] = keys[j - 1];
values[j] = values[j - 1];
}
keys[index] = key;
values[index] = value;
N++;
}
@Override
public Value get(Key key) {
int index = rank(key);
if (index < N && keys[index].compareTo(key) == 0)
return values[index];
return null;
}
@Override
public Key min() {
return keys[0];
}
@Override
public Key max() {
return keys[N - 1];
}
}递归实现:
public int rank(Key key, int lo, int hi) {
if (lo > hi) return lo;
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
int cmp = key.compareTo(key[mid]);
if (cmp > 0) return rank(key, mid + 1, hi);
else if (cmp < 0) return rank(key, lo, mid-1);
else return mid;
}非递归实现:
public int rank(Key key) {
int l = 0, h = N - 1;
while (l <= h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[m]);
if (cmp == 0)
return m;
else if (cmp < 0)
h = m - 1;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return l;
}在 N 个键的有序数组中进行二分查找最多需要 (lgN+1) 次比较(无论是否成功)。
向大小为 N 的有序数组中插入一个新的元素在最坏情况下需要访问 ~2N 次数组,因此向一个空符号表中插入 N 个元素在最坏情况下需要访问 ~N^2 次数组。