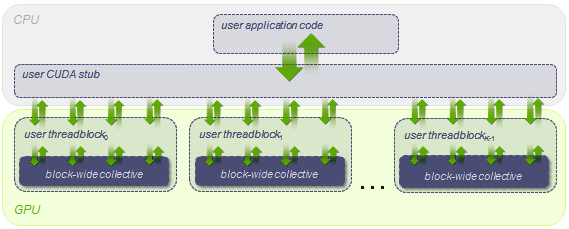
CUB provides state-of-the-art, reusable software components for every layer of the CUDA programming model:
- Device-wide primitives
- Sort, prefix scan, reduction, histogram, etc.
- Compatible with CUDA dynamic parallelism
- Block-wide "collective" primitives
- I/O, sort, prefix scan, reduction, histogram, etc.
- Compatible with arbitrary thread block sizes and types
- Warp-wide "collective" primitives
- Warp-wide prefix scan, reduction, etc.
- Safe and architecture-specific
- Thread and resource utilities
- PTX intrinsics, device reflection, texture-caching iterators, caching memory allocators, etc.
CUB is included in the NVIDIA HPC SDK and the CUDA Toolkit.
We recommend the CUB Project Website for further information and examples.
#include <cub/cub.cuh>
// Block-sorting CUDA kernel
__global__ void BlockSortKernel(int *d_in, int *d_out)
{
using namespace cub;
// Specialize BlockRadixSort, BlockLoad, and BlockStore for 128 threads
// owning 16 integer items each
using BlockRadixSort = BlockRadixSort<int, 128, 16>;
using BlockLoad = BlockLoad<int, 128, 16, BLOCK_LOAD_TRANSPOSE>;
using BlockStore = BlockStore<int, 128, 16, BLOCK_STORE_TRANSPOSE>;
// Allocate shared memory
__shared__ union {
typename BlockRadixSort::TempStorage sort;
typename BlockLoad::TempStorage load;
typename BlockStore::TempStorage store;
} temp_storage;
int block_offset = blockIdx.x * (128 * 16); // OffsetT for this block's ment
// Obtain a segment of 2048 consecutive keys that are blocked across threads
int thread_keys[16];
BlockLoad(temp_storage.load).Load(d_in + block_offset, thread_keys);
__syncthreads();
// Collectively sort the keys
BlockRadixSort(temp_storage.sort).Sort(thread_keys);
__syncthreads();
// Store the sorted segment
BlockStore(temp_storage.store).Store(d_out + block_offset, thread_keys);
}Each thread block uses cub::BlockRadixSort to collectively sort
its own input segment. The class is specialized by the
data type being sorted, by the number of threads per block, by the number of
keys per thread, and implicitly by the targeted compilation architecture.
The cub::BlockLoad and cub::BlockStore classes are similarly specialized.
Furthermore, to provide coalesced accesses to device memory, these primitives are
configured to access memory using a striped access pattern (where consecutive threads
simultaneously access consecutive items) and then transpose the keys into
a blocked arrangement of elements across threads.
Once specialized, these classes expose opaque TempStorage member types.
The thread block uses these storage types to statically allocate the union of
shared memory needed by the thread block. (Alternatively these storage types
could be aliased to global memory allocations).
CUB is regularly tested using the specified versions of the following compilers. Unsupported versions may emit deprecation warnings, which can be silenced by defining CUB_IGNORE_DEPRECATED_COMPILER during compilation.
- NVCC 11.0+
- GCC 5+
- Clang 7+
- MSVC 2019+ (19.20/16.0/14.20)
CUB is distributed with the NVIDIA HPC SDK and the CUDA Toolkit in addition to GitHub.
See the changelog for details about specific releases.
| CUB Release | Included In |
|---|---|
| 2.0.1 | CUDA Toolkit 12.0 |
| 2.0.0 | TBD |
| 1.17.2 | TBD |
| 1.17.1 | TBD |
| 1.17.0 | TBD |
| 1.16.0 | TBD |
| 1.15.0 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 22.1 & CUDA Toolkit 11.6 |
| 1.14.0 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 21.9 |
| 1.13.1 | CUDA Toolkit 11.5 |
| 1.13.0 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 21.7 |
| 1.12.1 | CUDA Toolkit 11.4 |
| 1.12.0 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 21.3 |
| 1.11.0 | CUDA Toolkit 11.3 |
| 1.10.0 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 20.9 & CUDA Toolkit 11.2 |
| 1.9.10-1 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 20.7 & CUDA Toolkit 11.1 |
| 1.9.10 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 20.5 |
| 1.9.9 | CUDA Toolkit 11.0 |
| 1.9.8-1 | NVIDIA HPC SDK 20.3 |
| 1.9.8 | CUDA Toolkit 11.0 Early Access |
| 1.9.8 | CUDA 11.0 Early Access |
| 1.8.0 | |
| 1.7.5 | Thrust 1.9.2 |
| 1.7.4 | Thrust 1.9.1-2 |
| 1.7.3 | |
| 1.7.2 | |
| 1.7.1 | |
| 1.7.0 | Thrust 1.9.0-5 |
| 1.6.4 | |
| 1.6.3 | |
| 1.6.2 (previously 1.5.5) | |
| 1.6.1 (previously 1.5.4) | |
| 1.6.0 (previously 1.5.3) | |
| 1.5.2 | |
| 1.5.1 | |
| 1.5.0 | |
| 1.4.1 | |
| 1.4.0 | |
| 1.3.2 | |
| 1.3.1 | |
| 1.3.0 | |
| 1.2.3 | |
| 1.2.2 | |
| 1.2.0 | |
| 1.1.1 | |
| 1.0.2 | |
| 1.0.1 | |
| 0.9.4 | |
| 0.9.2 | |
| 0.9.1 | |
| 0.9.0 |
CUB and Thrust depend on each other. It is recommended to clone Thrust and build CUB as a component of Thrust.
CUB uses the CMake build system to build unit tests, examples, and header tests. To build CUB as a developer, the following recipe should be followed:
# Clone Thrust and CUB from Github. CUB is located in Thrust's
# `dependencies/cub` submodule.
git clone --recursive https://github.com/NVIDIA/thrust.git
cd thrust
# Create build directory:
mkdir build
cd build
# Configure -- use one of the following:
cmake -DTHRUST_INCLUDE_CUB_CMAKE=ON .. # Command line interface.
ccmake -DTHRUST_INCLUDE_CUB_CMAKE=ON .. # ncurses GUI (Linux only)
cmake-gui # Graphical UI, set source/build directories and options in the app
# Build:
cmake --build . -j <num jobs> # invokes make (or ninja, etc)
# Run tests and examples:
ctestBy default, the C++14 standard is targeted, but this can be changed in CMake. More information on configuring your CUB build and creating a pull request is found in CONTRIBUTING.md.
CUB is available under the "New BSD" open-source license:
Copyright (c) 2010-2011, Duane Merrill. All rights reserved.
Copyright (c) 2011-2018, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* Neither the name of the NVIDIA CORPORATION nor the
names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products
derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL NVIDIA CORPORATION BE LIABLE FOR ANY
DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND
ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.