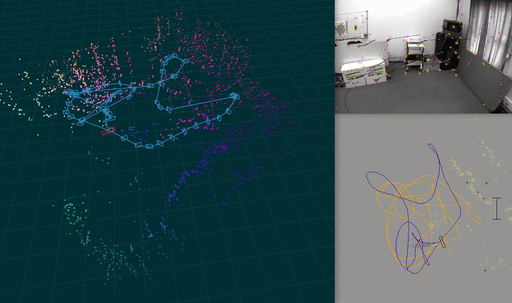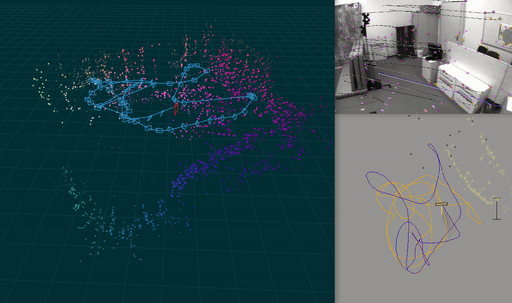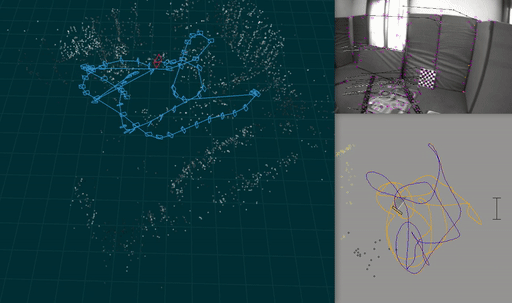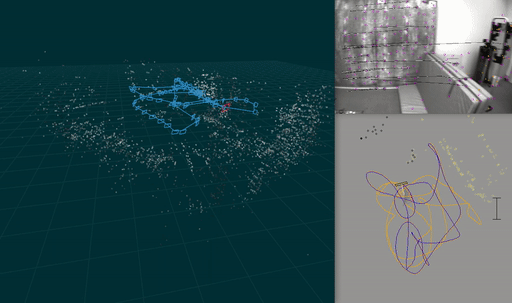
A visual-inertial odometry system with an optional SLAM module.
This is a research-oriented codebase, which has been published for the purposes of verifiability and reproducibility of the results in the paper:
- Otto Seiskari, Pekka Rantalankila, Juho Kannala, Jerry Ylilammi, Esa Rahtu, and Arno Solin (2022). HybVIO: Pushing the limits of real-time visual-inertial odometry. In IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). [arXiv pre-print] | [video]
It can also serve as a baseline in VIO and VISLAM benchmarks. The code is not intended for production use and does not represent a particularly clean or simple way of implementing the methods described in the above paper. The code contains numerous feature flags and parameters (see codegen/parameter_definitions.c) that are not used in the HybVIO but may (or may not) be relevant in other scenarios and use cases.
Here are basic instructions for setting up the project, there is some more detailed help included in the later sections (e.g., for Linux).
- Install CMake, glfw and ffmpeg, e.g., by
brew install cmake glfw ffmpeg. - Clone this repository with the
--recursiveoption (this will take a while) - Build dependencies by running
cd 3rdparty/mobile-cv-suite; ./scripts/build.sh - Make sure you are using
clangto compile the C++ sources (it's the default on Macs). If not default, like on many Linux Distros, you can control this with environment variables, e.g.,CC=clang CXX=clang++ ./scripts/build.sh - (optional) In order to be able to use the SLAM module, run
./src/slam/download_orb_vocab.sh
Then, to build the main and test binaries, perform the standard CMake routine:
mkdir target
cd target
cmake -DBUILD_VISUALIZATIONS=ON -DUSE_SLAM=ON ..
# or if not using clang by default:
# CC=clang CXX=clang++ cmake ..
make -j6Now the target folder should contain the binaries main and run-tests. After making changes to code, only run make. Tests can be run with the binary run-tests.
To compile faster, pass -j argument to make, or use a program like ccache. To run faster, check CMakeLists.txt for some options.
If you see error messages related to OpenGL or GLFW, try building without visualizations
cd 3rdparty/mobile-cv-suite && BUILD_VISUALIZATIONS=OFF ./scripts/build.sh
cd ../..; mkdir -p target; cd target
cmake -DBUILD_VISUALIZATIONS=OFF -DUSE_SLAM=ON ..or without any GPU support
cd 3rdparty/mobile-cv-suite && WITH_OPENGL=OFF BUILD_VISUALIZATIONS=OFF ./scripts/build.sh
cd ../..; mkdir -p target; cd target
cmake -DBUILD_VISUALIZATIONS=OFF -DBUILD_WITH_GPU=OFF -DUSE_SLAM=ON ..List of packages needed: clang, cmake, ffmpeg, glfw, gtk3
On Debian Stretch, had to install (some might be optional): clang, libc++-dev, libgtk2.0-dev, libgstreamer1.0-dev, libvtk6-dev, libavresample-dev.
On Raspbian (Pi 4, 8 GiB), had to install at least: libglfw3-dev and libglfw3 (for accelerated arrays) and libglew-dev and libxkbcommon-dev (for Pangolin, still had problems). Also started off with the Debian setup above.
To run benchmarks on EuRoC, TUM and SenseTime datasets and reproduce numbers published in https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.11857, please follow the instructions in https://github.com/AaltoML/vio_benchmark/tree/main/hybvio_runner.
If you want to test the software on individual datasets, e.g. to see various real-time visualizations, you can use the main binary. For example to run an EuRoC dataset, you can do the following:
- In
vio_benchmarkroot folder, runpython convert/euroc_to_benchmark.pyto download and convert the EuRoC data - Symlink that data here:
mkdir -p data && cd data && ln -s /path/to/vio_benchmark/data/benchmark .
Then inside the target/ folder use, e.g.:
./main -i=../data/benchmark/euroc-v1-02-medium -p -useStereo
In general, to run the algorithm on recorded data, use ./main -i=path/to/datafolder, where datafolder/ must at the very least contain a data.{jsonl|csv}, data.{mp4|mov|avi}, and parameters.txt (sensor data, camera data, and camera calibration). Read about the formats here. Such recordings can be created with
Some common arguments to main are:
-p: show pose visualization.-c: show video output.-useSlam: Enable SLAM module.-useStereo: Enable stereo.-s: show 3d visualization. Requires-useSlam.-gpu: Enable GPU acceleration
You can get full list of command line options with ./main -help.
These keys can be used when any of the graphical windows are focused (see commandline/command_queue.cpp for full list).
Ato pause and toggle step mode, where a key press (e.g., SPACE) processes the next frame.Qor Escape to quitRto rotate camera window- The horizontal number keys 1,2,… toggle methods drawn in the pose visualization.
When the command line is focused, Ctrl-C aborts the program.
Licensed under GPLv3. For different (commercial) licensing options, contact us at https://www.spectacularai.com/