In the last chapter, we discussed object composition, where complex classes are constructed from simpler classes and types. Object composition is perfect for building new objects that have a “has-a” relationship with their parts. However, object composition is just one of the two major ways that C++ lets you construct complex classes. The second way is through inheritance, which models an “is-a” relationship between two objects.
在上一章中我们讨论了对象组合,一种通过组合简单对象形成复杂对象的过程。对象组合非常好,能建立一种"has-a"的关系模型。然而对象组合仅仅是C++给你提供的构造复杂对象的两种之中的一种方法。另一种方法是继承,继承在两个对象之间建立了一种"is-a"的关系。
Unlike object composition, which involves creating new objects by combining and connecting other objects, inheritance involves creating new objects by directly acquiring the attributes and behaviors of other objects and then extending or specializing them. Like object composition, inheritance is everywhere in real life. When you were conceived, you inherited your parents genes, and acquired physical attributes from both of them -- but then you added your own personality on top. Technological products (computers, cell phones, etc…) inherit features from their predecessors (often used for backwards compatibility). For example, the Intel Pentium processor inherited many of the features defined by the Intel 486 processor, which itself inherited features from earlier processors. C++ inherited many features from C, the language upon which it is based, and C inherited many of its features from the programming languages that came before it.
不像对象组合,对象组合是通过组合和连接其他对象来实现的。继承通过直接获取别的对象的属性和行为创建新的对象,然后再扩展功能和特例化他们的功能。像组合一样,继承也存在于我们现实生活的每个方面。你继承了你父母的属性,然后你又在其上建立了自己的个性。技术产品继承了他们前代产品的特点(通常是为了后向兼容,后向兼容的意思是事物向前发展,如果同时还能兼容自己身后的东西,就叫后向兼容)。举个例子,因特尔的奔腾处理器从前代因特尔486处理器中继承了许多特性,而Inter486他自己也从前代处理器中继承了许多特性。C++从C语言中继承了许多特性。C也从它之前的语言中继承了许多特性。
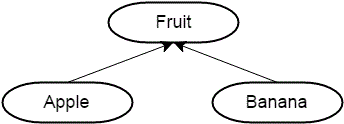
Consider apples and bananas. Although apples and bananas are different fruits, both have in common that they are fruits. And because apples and bananas are fruits, simple logic tells us that anything that is true of fruits is also true of apples and bananas. For example, all fruits have a name, a color, and a size. Therefore, apples and bananas also have a name, a color, and a size. We can say that apples and bananas inherit (acquire) these all of the properties of fruit because they are fruit. We also know that fruit undergoes a ripening process, by which it becomes edible. Because apples and bananas are fruit, we also know that apples and bananas will inherit the behavior of ripening.
思考一下苹果和香蕉的关系。尽管苹果和香蕉是不同的水果。两者都有共同点是水果。然后因为苹果和香蕉是水果,所以简单逻辑告诉我们对于水果是来说是真的事情,对于苹果和香蕉来说也是真的。举个例子,所有的苹果都有名字,颜色和大小。所以苹果和香蕉也有名字颜色和大小。我们可以说啊苹果和香蕉从水果身上继承了所有的属性,因为他们是水果。我们知道苹果要经历一个成熟过程,然后它变得可以使用,因为苹果和香蕉是水果,我们也知道苹果和香蕉会继承变得成熟这样的行为。
Put into a diagram, the relationship between apples, bananas, and fruit might look something like this:
画成图的话,就是下面这个样子。
This diagram defines a hierarchy.
这张图定义了一种层级结果。
Hierarchies
A hierarchy is a diagram that shows how various objects are related. Most hierarchies either show a progression over time (386 -> 486 -> Pentium), or categorize things in a way that moves from general to specific (fruit -> apple -> red delicious). If you’ve ever taken biology, the famous domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species ordering defines a hierarchy (from general to specific).
hierarchy是一种表明不同对象之间是怎么联系的图。大部分层级图显示一种时间上,或者种类上从普遍到具体的的过程。如果你学过生物的话,你就会知道生物里面是怎么划分层级的。
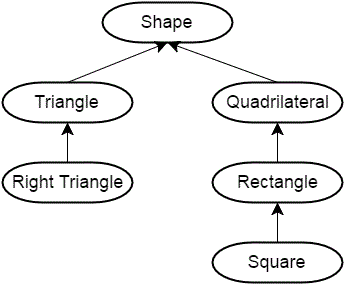
Here’s another example of a hierarchy: a square is a rectangle, which is a quadrilateral, which is a shape. A right triangle is a triangle, which is also a shape. Put into a hierarchy diagram, that would look like this:
这里有另一个hierarchy ,一个方形是一个矩形,也是一个四边形,是一个形状。一个右三角形是一个三角形。也是一个形状。画成图会是下面的这个样子。
This diagram goes from general (top) to specific (bottom), with each item in the hierarchy inheriting the properties and behaviors of the item above it.
这张图从普通到具体,从上到下,下面的对象继承了上面对象的属性和行为。
A look ahead
In this chapter, we’ll explore the basics of how inheritance works in C++.
Next chapter, we’ll explore how inheritance enables polymorphism (one of object-oriented programming’s big buzzwords) through virtual functions.
在下一章中,我们将会学习继承怎么通过虚函数来是使多态成为可能。
As we progress, we’ll also talk about inheritance’s key benefits, as well as some of the downsides.
随着我们的进步,我们会探讨一些关于继承的益处和一些缺点。