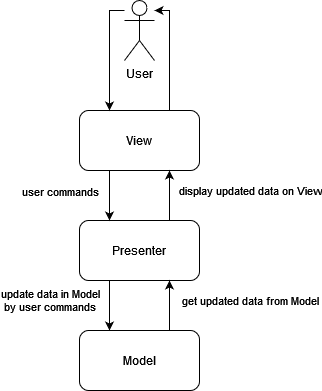
Implementation of MVP (Model-View-Presenter) architectural pattern via Unity engine.
Before to start, it's recommended to get sample project with the latest version of the package.
MVP or Model-View-Presenter is an architectural pattern, which consists of three components: Model, View and Presenter.
- Model is a data.
- View is an interface that displays data and routes user commands to Presenter.
- Presenter wires up Model and View together and thereby creates a functioning entity.
For more information about MVP, check an original source - "MVP: Model-View-Presenter. The Taligent Programming Model for C++ and Java." Mike Potel.
Implement IModel interface to create a Model -
public class CubeModel : IModel
{
// ...
}
Implement IView interface to create a View -
public class CubeView : MonoBehaviour, IView
{
// ...
}
You can also use MonoView class as an "stub" instead of MonoBehaviour -
public class CubeView : MonoView, IView
Create a CubePresenter class and derive it from Presenter<TView, TModel>. Specify types: TView and TModel. In our case TModel is CubeModel and TView is CubeView -
CubePresenter : Presenter<CubeView, CubeModel>
public class CubePresenter : Presenter<CubeView, CubeModel>
{
public CubePresenter(CubeView cubeView, CubeModel cubeModel) : base(cubeView, cubeModel)
{
// ...
}
}
At this point we're done with the main components of MVP - CubeModel, CubeView and CubePresenter!
To create an instance of a Presenter use Create<TPresenter>() method in PresenterFactory -
[SerializeField]
private CubeView cubeView;
// ...
private CubePresenter cubePresenter;
// ...
void Start()
{
cubePresenter = presenterFactory.Create<CubePresenter>(cubeView, new CubeModel());
}
PresenterFactory is built-in implementation of IPresenterFactory interface -
public interface IPresenterFactory
{
public TPresenter Create<TPresenter>(params object[] data) where TPresenter : IPresenter;
}
But you can implement your own factory.
Each Presenter should interact with another Presenter. One possible way to do it is to use messages. MessageDispatcher is a class which provides needed functionality for messaging.
But to receive a Message we need a Subscriber.
Implement IMessageSubscriber interface to make some class available for message receiving -
public interface IMessageSubscriber
{
void ReceiveMessage<TMessage>(TMessage message);
}
In the example we have UIPresenter -
public class UIPresenter : Presenter<UIView, UIModel>, IMessageSubscriber
{
// ...
void IMessageSubscriber.ReceiveMessage<TMessage>(TMessage message)
{
switch (message)
{
case CubeColorMessage cubeColorMessage:
model.ColorText = cubeColorMessage.Color.ToString();
break;
}
}
}
Switch-case is used here as a way to handle a message from CubePresenter.
To send a Message to some Presenter use DispatchMessageTo<TSubscriber, TMessage>(TMessage message) method in MessageDispatcher -
MessageDispatcher.DispatchMessageTo<UIPresenter, CubeColorData>(new CubeColorData(color))
In the example where CubePresenter class is -
public class CubePresenter : Presenter<CubeView, CubeModel>
{
// ...
private void OnModelColorChanged(Color color)
{
view.Color = color;
messageDispatcher.DispatchMessageTo<UIPresenter, CubeColorMessage>(new CubeColorMessage { Color = color });
}
}
To clear a Presenter (or some class) you can use built-in IClearable interface -
public interface IClearable
{
public void Clear();
}
Base Presenter class implements IClearable interface -
Presenter<TView, TModel> : IPresenter, IClearable
In the example, inside of EntryPoint.OnDestroy() method Clear is used to free up resources -
public class EntryPoint : MonoBehaviour
{
// ...
private CubePresenter cubePresenter;
private UIPresenter UIPresenter;
// ...
private void OnDestroy()
{
cubePresenter.Clear();
UIPresenter.Clear();
}
{