MQTT, designed initially as a lightweight publish/subscribe messaging protocol, is now becoming essential for Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Industry 4.0. Its significance lies in facilitating the seamless connection between diverse industrial devices and the cloud, enabling the convergence of Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT).
This article compares the top 3 MQTT brokers for IIoT in 2023, including each broker's advantages, disadvantages, and use cases. It also shows how you can leverage the features of these 3 MQTT brokers to build a Unified Namespace (UNS) architecture for your IIoT solution.
We select the top open-source MQTT brokers for industrial IoT based on these two criteria:
- Community, popularity, and project activity of the open source projects.
- Compatibility with resource-constrained industrial devices and gateways.
Based on the criteria, we choose the 3 popular open-source MQTT brokers:
- EMQX: The most starred MQTT broker on GitHub, with 11.4k stars. EMQX has a booting footprint of 50M and supports clustering capabilities.
- Mosquitto: The second-most-starred but the most prevalent among MQTT brokers. In a single-threaded architecture, Mosquitto has a booting footprint of less than 1M.
- NanoMQ: The latest and one of the most active MQTT brokers available. With multi-threading and async-io support, NanoMQ has a startup space of about 2M.
Here is a summary of the 3 projects hosted on GitHub:
| EMQX | Mosquitto | NanoMQ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Official Website | EMQX | Eclipse Mosquitto | NanoMQ |
| GitHub Project | EMQX GitHub | Mosquitto GitHub | NanoMQ GitHub |
| Project Created | 2012 | 2009 | 2020 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 | EPL/EDL License | MIT License |
| Programming Language | Erlang | C/C++ | C |
| Latest Release | v5.0.23 (April 2023) | 2.0.15 (Aug 2022) | v0.17.0 (March 2023) |
| GitHub Stars | 11.5k | 7.2k | 800+ |
| GitHub Releases | 260+ | 60+ | 75+ |
| GitHub Commits | 14k+ | 2800+ | 2000+ |
| GitHub Commits (Last 12 Months) | 3000+ | 500+ | 1200+ |
| GitHub PRs | 6000+ | 600 | 780+ |
| GitHub Contributors | 100+ | 110+ | 20+ |
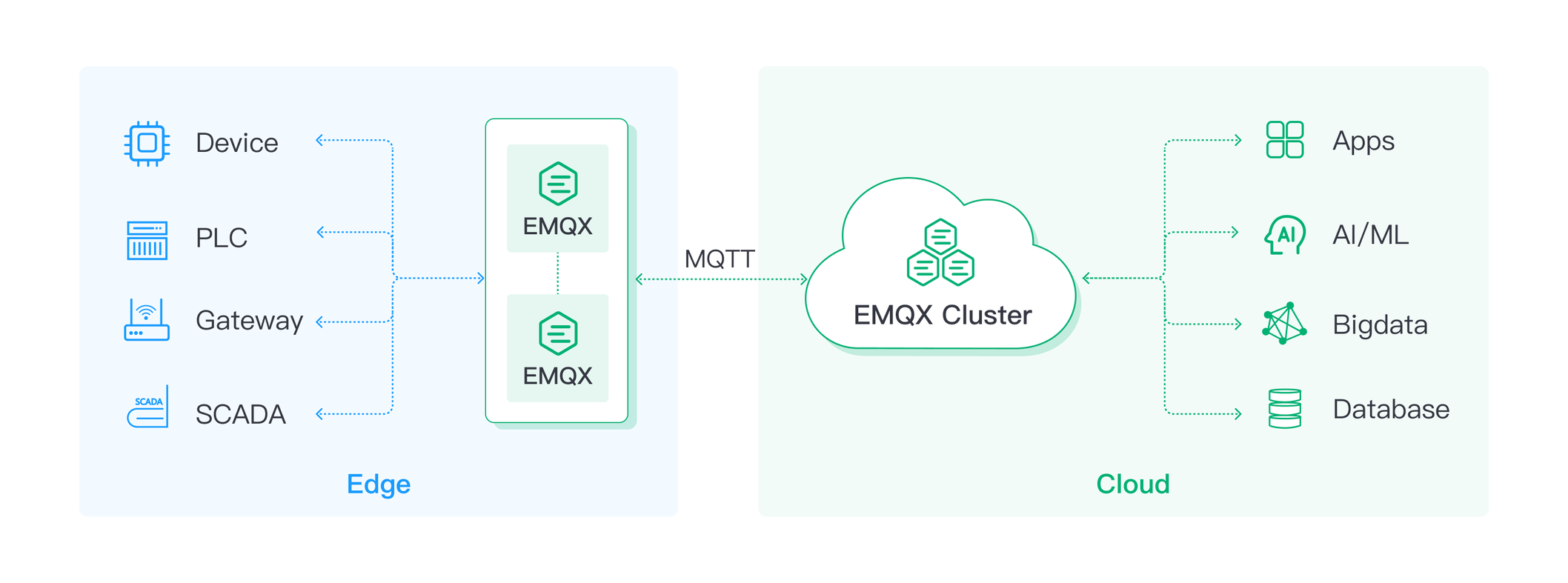
EMQX is a highly scalable, distributed MQTT broker for enterprise IIoT deployments. It offers extensive support for MQTT 5.0, MQTT-SN, SSL/TLS encryption, and MQTT over QUIC. It further enables masterless clustering to achieve high availability and horizontal scalability.
With an impressive 11.5k stars on GitHub, EMQX has established itself as one of the most popular MQTT brokers available. The EMQX project was launched in 2012 and is licensed under Apache version 2.0. EMQX is written in Erlang/OTP, a programming language for building massively scalable soft real-time systems.
EMQX is suitable for deployment in the cloud and on the edge. At the edge, it can integrate with various industrial gateways such as N3uron, Neuron, and Kepware. In cloud environments, EMQX offers seamless integration with a range of technologies, including Kafka, databases, and cloud services, on leading public cloud platforms like AWS, GCP, and Azure.
With comprehensive enterprise-grade features, data integration capabilities, cloud hosting services, and commercial support from EMQ Technologies Inc, EMQX is widely used for mission-critical applications in the IIoT domain. See more in Use Cases.
- Masterless clustering and high availability
- High-performance and low latency
- Rich authentication mechanism
- Edge-to-cloud deployment
- Pioneering MQTT over QUIC
- Complex to set up and configure
- High CPU/Mem usage
- Automotive manufacturing
- Iron and steel manufacturing
- Oil & Gas
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Water supplies
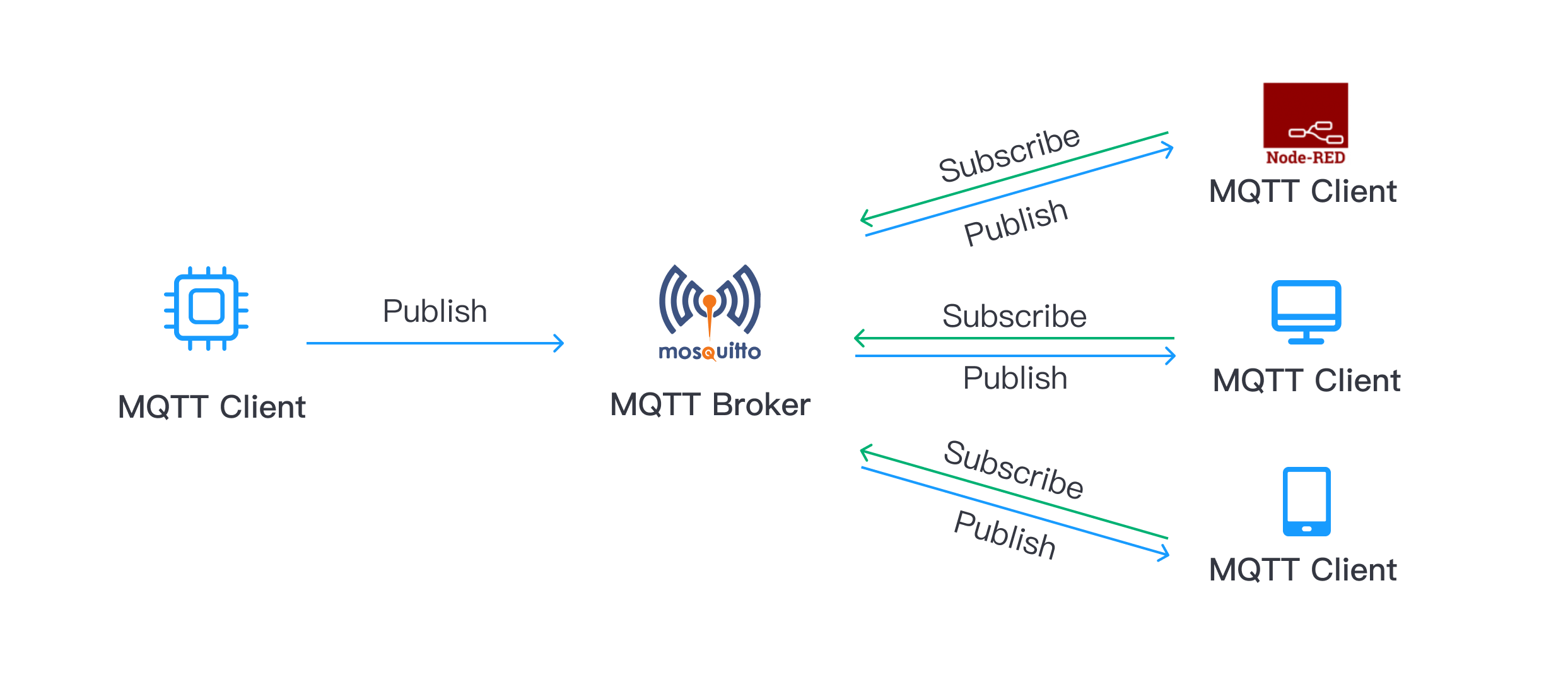
Mosquitto is a widely used open-source MQTT broker under the Eclipse Foundation, licensed under the Eclipse Public License (EPL/EDL license). As of March 2023, it has over 7k stars on GitHub. It implements MQTT protocol versions 5.0, 3.1.1, and 3.1 and supports SSL/TLS and WebSocket.
Mosquitto is written in C/C++ and uses a single-threaded architecture. Its lightweight design makes Mosquitto suitable for deployment on embedded devices or industrial gateways with limited resources. Mosquitto is cross-platform and can run on various platforms, including Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- Lightweight and small footprint
- Simplicity and easy to use
- Without multi-threading and clustering support
- Not suitable deployment in the cloud
- Factory Automation
- Smart Manufacturing
- Smart Hardware
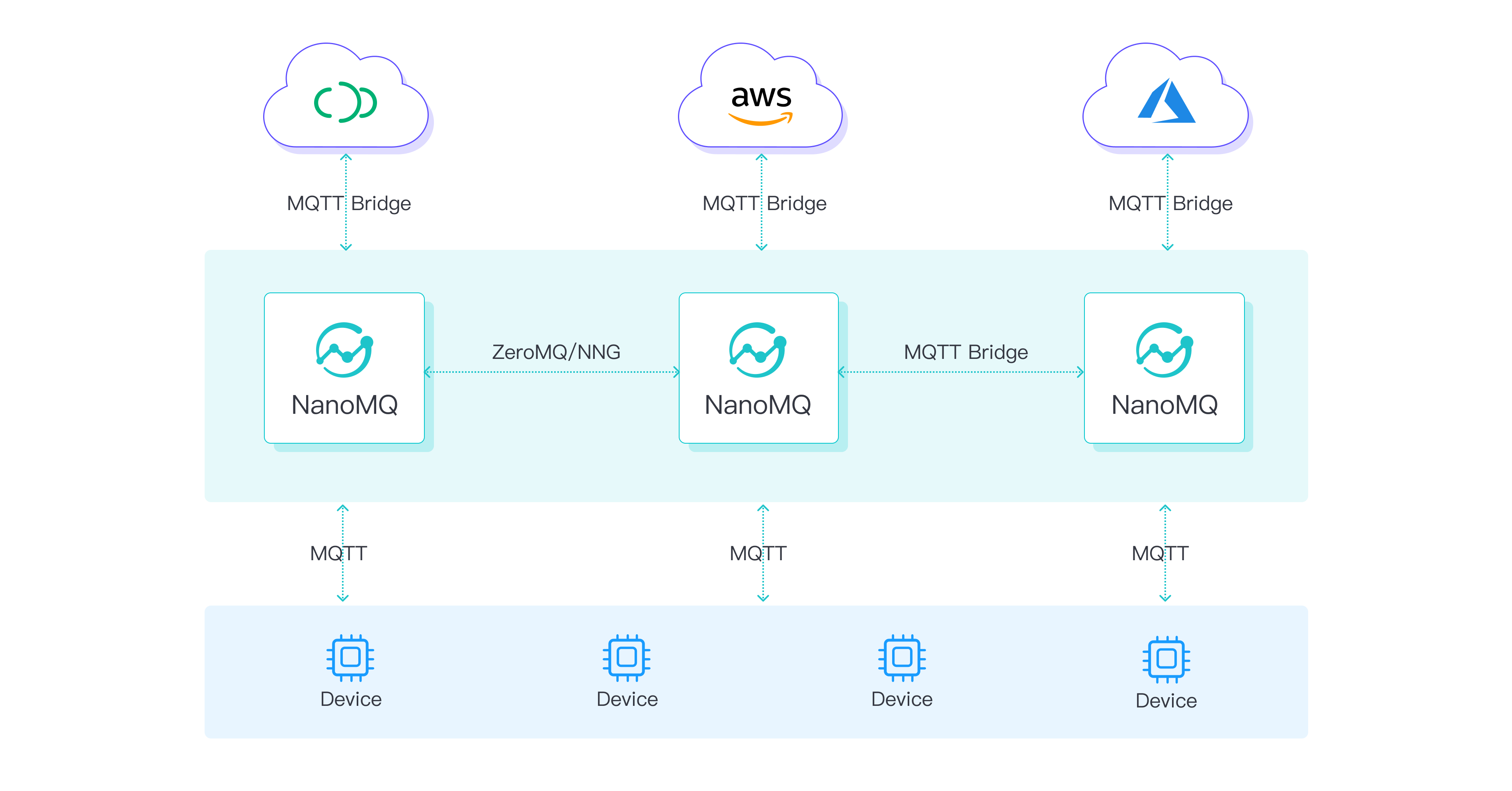
NanoMQ is the latest open-source MQTT broker project released in 2020. NanoMQ is implemented in pure C, based on NNG's asynchronous I/O with a multi-threading Actor Model. It fully supports MQTT version 3.1.1 and 5.0, SSL/TLS, and MQTT over QUIC.
One of NanoMQ's standout features is its lightweight and fast nature with a minimal memory footprint. This makes it an exceptional MQTT broker for IIoT applications, where efficiency and resource optimization are paramount. Additionally, NanoMQ can work as a messaging gateway that converts protocols such as DDS, NNG, and ZeroMQ to MQTT and then bridges the MQTT messages to the cloud.
NanoMQ is highly compatible and portable, relying only on the native POSIX API. This makes deploying on any POSIX-compatible platform easy and runs smoothly on various CPU architectures, including x86_64, ARM, MIPS, and RISC-V.
- Multi-threading and Async IO
- Small booting footprint
- Bridging with brokerless protocols
- Project in early stage
- No clustering support
- Automotive Manufacturing
- Robotics: Edge service convergence
- IIoT Edge Gateway
The following chart shows a side-by-side comparison of the top 3 open-source MQTT brokers:
| EMQX | Mosquitto | NanoMQ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protocols | MQTT 5.0/3.1.1 MQTT over QUIC |
MQTT 5.0/3.1.1 | MQTT 5.0/3.1.1 MQTT over QUIC ZeroMQ & NanoMSG |
| Scalability | Excellent | Moderate | Good |
| Availability | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate |
| Performance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Latency | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Reliability | High | High | High |
| Security | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Integrations | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate |
| Compatibility | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Ease of Use | Good | Excellent | Good |
| Community Support | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
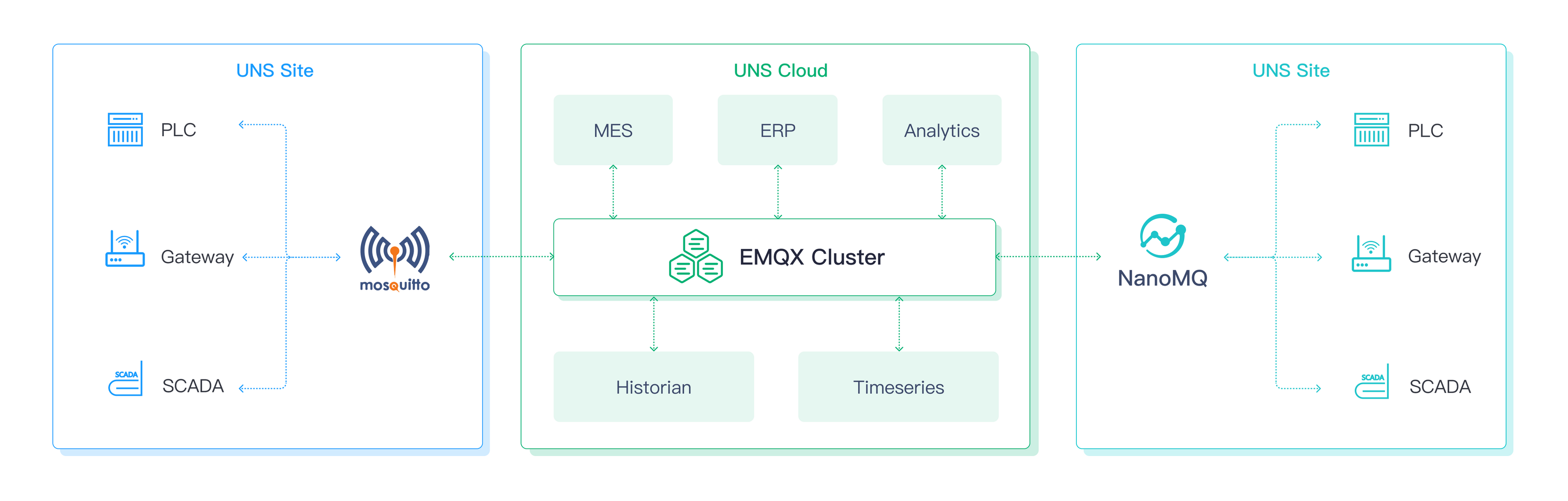
Unified Namespace (UNS) is a solution architecture built on the MQTT broker for Industrial IoT and Industry 4.0. It provides a unified namespace for MQTT topics and a centralized repository for messages and structured data.
The 3 MQTT brokers can work together to build the UNS architecture. A cohesive system is created by deploying Mosquitto and NanoMQ on industrial gateways while deploying EMQX as a centralized hub in the cloud. This configuration allows for the seamless aggregation and ingestion of IIoT data from the edge to the cloud via MQTT bridges.
Based on the earlier introduction and comparison, each MQTT broker offers distinct strengths for different deployment scenarios. EMQX is highly scalable with enterprise features, suitable for cloud deployment. Mosquitto and NanoMQ are fast and lightweight, ideal for industrial gateways.
These three MQTT brokers play a significant role in industrial IoT applications, leading the way in implementing the UNS architecture and facilitating the convergence of IT and OT domains. When considering your specific IIoT projects, you can choose one or two of these MQTT brokers based on your requirements. By leveraging their strengths, you can create a cohesive system where the MQTT brokers work together, synergizing their capabilities.