The efficiency of charging point management is crucial for advancing and popularizing new energy vehicles. Building an intelligent, connected platform for operating charging points using technologies like IoT allows for seamless access, real-time remote monitoring, instant fault diagnosis, and proactive alarm prevention. This can significantly improve the operational efficiency and management standards of charging points.
The charging point infrastructure network is vast with numerous sites and stations spread out across various locations. The primary challenge of building an interconnected charging point operation and management system is to ensure stable and reliable access to these stations in complex environments and enable efficient connection with cloud platforms.
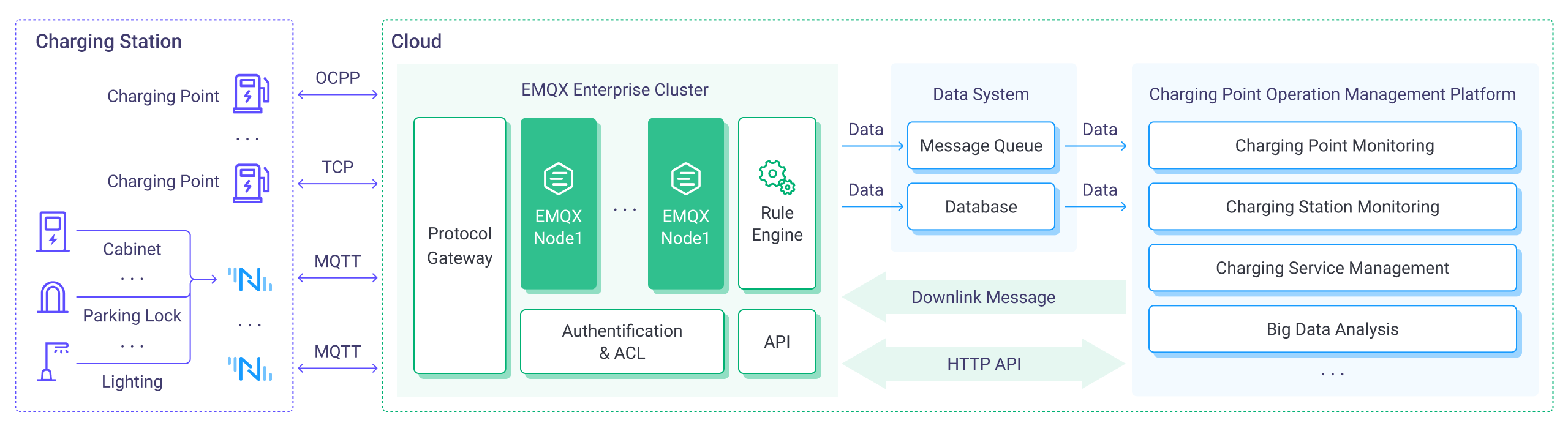
There are various equipment that need to be connected to the charging stations besides charging points. Smart control units are deployed to connect charging points, meters, payment devices, etc., to collect and process charging and payment data. Additional equipment like cabinets, transformers, barriers, sensors, and smart lighting can be connected for environmental and security monitoring. Communication gateway devices are required to aggregate and upload data to cloud platforms using IoT protocols like MQTT, LwM2M, and CoAP.
charging point management platforms need to collect and process a vast amount of charging data and user information, necessitating strict information security measures to ensure stable operation and data security of charging points. This is crucial for safeguarding user interests and data integrity and promoting the healthy development of charging point management platforms.
Cloud-based operation management platforms encompass applications such as operational status monitoring, charging process monitoring, fault diagnosis, predictive maintenance, energy efficiency optimization, and transaction management. Handling vast amounts of data collected from the device perception layer, the platform not only needs to perform real-time storage and sharing comprehensively but also generate flexible historical data based on business requirements for querying, analysis, and uncovering data value.
EMQ provides a cloud-edge collaborative solution based on the EMQX MQTT platform. It offers device connectivity, data transmission, processing, and integration capabilities, helping customers quickly build secure and efficient charging point operation management platforms.
Typically, a charging point management and operation system can be divided into three layers:
- Device Layer: NeuronEX industrial gateway provided by EMQ aggregates real-time data from various devices using different protocols and uploads it to the cloud platform side via the MQTT protocol.
- Network Layer: Utilizing MQTT’s features like keep alive, session persistence, and QoS, even if there are connection disruptions in complex station network environments, message delivery can resume after reconnection.
- Cloud Layer: The EMQX MQTT platform supports multi-protocol, high-concurrency access and has robust data processing capabilities. Through its built-in rule engine, EMQX can flexibly bridge data from charging points and various other devices to the corresponding databases based on different business needs.
NeuronEX provides services for device data collection and intelligent analysis at the edge. It is deployable on various gateway devices, industrial control computers, and servers. With support for standard industrial protocols like Modbus and OPC UA, power industry protocols like IEC104, station automation protocols like KNXnet, and other mainstream PLC protocols, NeuronEX enables unified access to various devices like smart control units, transformers, smart lighting, and sensors. It supports high-frequency, low-latency data collection and aggregates data for transmission to the cloud via the MQTT protocol. Additionally, NeuronEX features efficient streaming data analysis and processing capabilities, allowing operations such as data aggregation, filtering, format conversion, and monitoring metric calculations at the edge. This enhances data value extraction at the edge, reducing network bandwidth and cloud data storage pressures.
EMQX can access various industry protocols and private protocols. EMQX supports OCPP protocol, capable of receiving OCPP Websocket or Websocket over TLS (ws/wss) connections from charging point OCPP clients, converting the uplink and downlink messages of the charging point clients into standard MQTT messages. Additionally, charging points using proprietary TCP protocols can also integrate with EMQX's Extension Protocol (ExProto) gateway.
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is a global open communication standard developed by the Open Charge Alliance (OCA) based in the Netherlands, aimed at addressing various communication issues between private charging networks. Today, OCPP is used in over 49 countries with more than 40,000 charging facilities worldwide.
With a high availability distributed cluster architecture, EMQX supports up to billions of concurrent connections, millisecond-level real-time message routing, and millions of TPS data throughput. This robust infrastructure provides strong support for concurrent data and control instructions from a large number of charging points.
EMQX supports TLS/DTLS security protocols, providing TLS one-way and two-way authentication to protect connections between charging points, gateway devices, and vehicles. It also supports interaction with PKI/CA systems, enabling a one-device-one-key authentication scheme. Additionally, EMQX offers features like authentication and access control to ensure data access security.
EMQX has a built-in rule engine that can be used to process structured perception data from different devices. Rules can be created using SQL statements or low-code methods to perform tasks such as real-time encoding, decoding, filtering, and aggregation. The processed data can then be integrated into various message queues and time-series databases.
- Comprehensive Data Perception from Multiple Sources: Achieves unified data access for charging points, gateways, and various electrical devices, helping customers rapidly establish device perception and data transmission layers across different stations and accelerating overall platform construction.
- Edge Data Value Extraction: NeuronEX's edge data processing and analysis capabilities help customers deeply explore high-value data at the edge, enhancing cloud storage resource utilization.
- Adaptation to Future Business Development: EMQX's highly available cluster architecture supports hot upgrades and configurations, ensuring high SLA for the system. Its horizontal scalability helps the system flexibly expand as management scales increase.
- Business Innovation with Low-Code: By writing simple SQL statements, operations such as data filtering, transformation, aggregation, and persistence can be quickly and flexibly performed based on business needs. Processed data can be easily integrated into various message queues, SQL/NoSQL, and time-series databases, accelerating business application development.
- Operations and Maintenance Visualization: Provides an intuitive visual monitoring and management interface while also supporting the pushing of monitoring data to mainstream third-party monitoring systems like Prometheus, facilitating real-time monitoring of vehicle-machine connection statuses and message traffic metrics for users. Additionally, features like slow subscription statistics and log tracking help diagnose specific issues such as vehicle-machine connection anomalies and excessive message reception latency.