Some templates and templatetags to be used with django-CMS and Bootstrap3/Bootstrap4.
Django-CMS is frontend agnostic, which is a good thing. However, in combination with Bootstrap3/4 the menu structure does not quite fit. This is because Bootstrap3/4 only allows one nested menu level.
djangocms-bootstrap adds a few modified templatetags, which render the existing page tree into a menu structure, suitable for the navbar in Bootstrap3/4.
With the concept of mobile first, there is no mouse-over event we could use to open a drop-down element showing the sub-menu-items. Instead the user has to click onto the main menu item in order to open a drop-down element. Now however, there wouldn't be any more distinction between clicking onto a menu-item to either open the drop-down or to click onto the page referenced by that menu item.
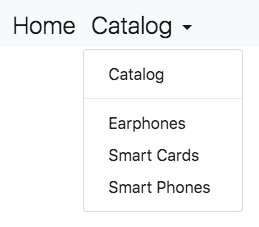
In this example djangocms-bootstrap uses a special templatetag to render the navbar. Here the CMS page Catalog has three children. Clicking onto Catalog in the navbar, opens a drop-down menu, which contains another entry for Catalog. This is the link which sends us onto the desired page. Using this approach we can navigate through a django-CMS page-tree, without having to use the mouse-over effect to open drop-down menus.
Rendering the navbar to show a menu to navigate though the page-tree in django-CMS:
{% load bootstrap_tags %}
<div class="container">
<nav class="navbar" role="navigation">
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto">
{% main_menu "bootstrap4/menu/navbar.html" %}
</ul>
</nav>
</div>The templatetag {% main_menu ... %} takes an extra parameter, template, which can be used to
fine-tune the rendering of the navigation items. Also note that only CMS pages, where the checkbox
for "Menu" is active, show up in the navbar.
In Bootstrap-3 and 4, the navigation bar normally is much more than the short snippet shown above.
Therefore djangocms-bootstrap is shipped with two HTML snippets, which do the heavy lifting and
which shall be included in the base template of your project. By using
{% include "bootstrap4/includes/nav-navbar.html" %} in addition to the navbar, a branding icon
and a navbar toggle button is rendered, all according to the Bootstrap's style guides.
By appending with navbar_classes="navbar-light bg-light fixed-top" to the include statement,
one can style the navbar using the provided CSS classes.
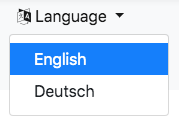
If django-CMS is configured to run in a multilingual environment, often it is desirable to add
an option, allowing the user the select his native language. For this purpose djangocms-bootstrap
offers a templatetag language_chooser rendering a drop-down menu with all languages available
through the CMS. To render this select options, add this HTML snippet inside or above of the main
navbar:
{% language_chooser "bootstrap4/includes/language-chooser.html" %}Write the docs.
The Django list view class django.views.generic.ListView, by default adds a Paginator object to
the rendering context, if there is the member attribute paginate_by = .... To render this
paginator following Bootstrap's best practices, add this HTML snippet above or below the list of
items you are going to render:
{% load bootstrap_tags %}
<nav aria-label="Paginator example">{% paginator %}</nav>By prepending {% with paginator_classes="pagination justify-content-center" %} to the paginator
statement, one can style the paginator using the provided CSS classes. Don't forget to append
{% endwith %} afterwards.