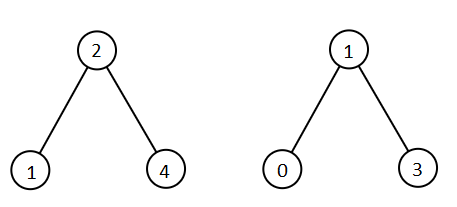
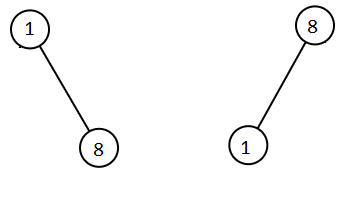
Given two binary search trees root1 and root2, return a list containing all the integers from both trees sorted in ascending order.
Example 1:
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3] Output: [0,1,1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input: root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1] Output: [1,1,8,8]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Companies:
Facebook
Related Topics:
Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Sorting, Binary Tree
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/all-elements-in-two-binary-search-trees/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(A + B)
// Space: O(HA + HB)
class BstIterator {
stack<TreeNode*> s;
void pushNodes(TreeNode *node) {
for (; node; node = node->left) s.push(node);
}
public:
BstIterator(TreeNode *root) {
pushNodes(root);
}
int peek() {
return hasNext() ? s.top()->val : INT_MIN;
}
bool hasNext() {
return s.size();
}
void next() {
if (!hasNext()) return;
auto n = s.top();
s.pop();
pushNodes(n->right);
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAllElements(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b) {
BstIterator i(a), j(b);
vector<int> ans;
while (i.hasNext() || j.hasNext()) {
if (!j.hasNext() || (i.hasNext() && i.peek() <= j.peek())) {
ans.push_back(i.peek());
i.next();
} else {
ans.push_back(j.peek());
j.next();
}
}
return ans;
}
};Or
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/all-elements-in-two-binary-search-trees/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(A + B)
// Space: O(HA + HB)
class Solution {
void pushNodes(stack<TreeNode*> &s, TreeNode *node) {
for (; node; node = node->left) s.push(node);
}
public:
vector<int> getAllElements(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b) {
vector<int> ans;
stack<TreeNode*> sa, sb;
pushNodes(sa, a);
pushNodes(sb, b);
while (sa.size() || sb.size()) {
auto &s = sb.empty() || (sa.size() && sa.top()->val <= sb.top()->val) ? sa : sb;
ans.push_back(s.top()->val);
auto n = s.top();
s.pop();
pushNodes(s, n->right);
}
return ans;
}
};