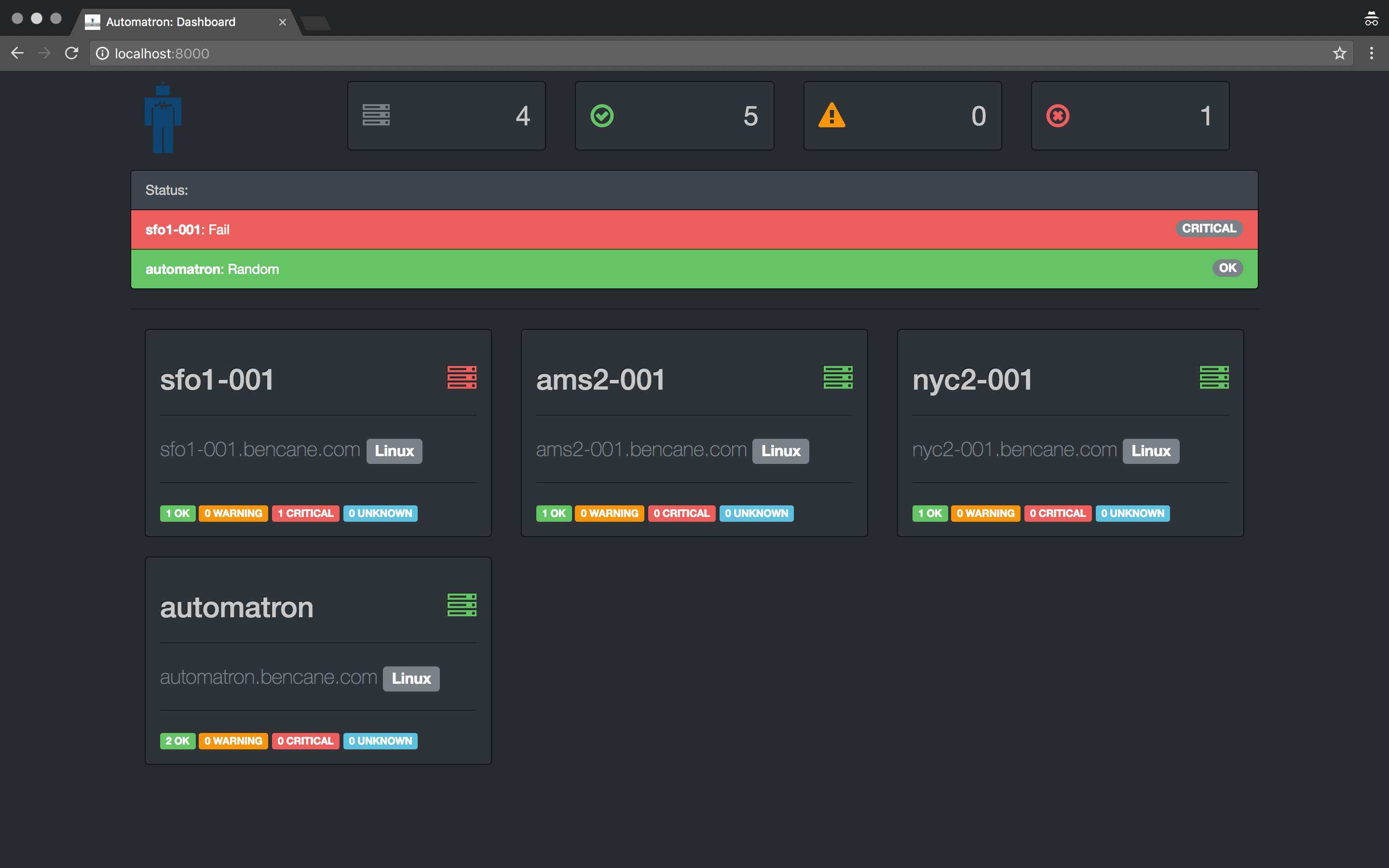
Automatron is a framework for creating self-healing infrastructure. Simply put, it detects system events & takes action to correct them.
The goal of Automatron is to allow users to automate the execution of common tasks performed during system events. These tasks can be as simple as sending an email to as complicated as restarting services across multiple hosts.
- Automatically detect and add new systems to monitor
- Monitoring is executed over SSH and completely agent-less
- Policy based Runbooks allow for monitoring policies rather than server specific configurations
- Supports Nagios compliant health check scripts
- Allows dead simple arbitrary shell commands for both checks and actions
- Runbook flexibility with Jinja2 templating support
- Pluggable Architecture that simplifies customization
The core of Automatron is based around Runbooks. Runbooks are policies that define health checks and actions. You can think of them in the same way you would think of a printed runbook. Except with Automatron, the actions are automated.
The below runbook is a very basic example, it will check if NGINX is running (every 2 minutes) and restart it after 2 unsuccessful checks.
name: Check NGINX
schedule: "*/2 * * * *"
checks:
nginx_is_running:
execute_from: target
type: cmd
cmd: service nginx status
actions:
restart_nginx:
execute_from: target
trigger: 2
frequency: 300
call_on:
- WARNING
- CRITICAL
- UNKNOWN
type: cmd
cmd: service nginx restart
The above actions will be performed every 300 seconds (5 minutes) until the health check returns an OK status. This delay allows time for NGINX to restart after each execution.
This next runbook example is a more complex version of the above. In this example we will use Jinja2 and Automatron's Facts to enhance our runbook further.
name: Check NGINX
{% if "prod" in facts['hostname'] %}
schedule:
second: */20
{% else %}
schedule: "*/2 * * * *"
{% endif %}
checks:
nginx_is_running:
execute_from: target
type: cmd
cmd: service nginx status
actions:
restart_nginx:
execute_from: target
trigger: 2
frequency: 300
call_on:
- WARNING
- CRITICAL
- UNKNOWN
type: cmd
cmd: service nginx restart
remove_from_dns:
execute_from: remote
trigger: 0
frequency: 0
call_on:
- WARNING
- CRITICAL
- UNKNOWN
type: plugin
plugin: cloudflare/dns.py
args: remove test@example.com apikey123 example.com --content {{ facts['network']['eth0']['v4'][0] }}
The above example uses Jinja2 and Facts to create a conditional schedule. If our target server has a hostname that contains the word "prod" within it. The schedule for the health check will be every 20 seconds. If not, it will be every 2 minutes.
Another addition is the remove_from_dns action, which will remove the target server's DNS entry using the CloudFlare DNS plugin.
By using Facts and Jinja2 together you can customize a single runbook to cover unique actions for multiple hosts and environments.
Copyright 2016 Benjamin Cane
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.