class: frontpage
- Recap
- Introduction
- What is not
- What is it?
- Why we should use it?
- Explanation
- Core concepts
- How it works
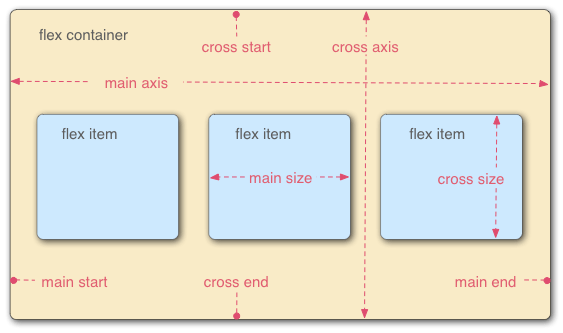
- Main & cross axes
- Flex container and flex items
- Flex container
- Flex items
- Next steps
- CSS property
- Box sizing
- Another kind of grid
Officialy it's name is
"...In the flex layout model, the children of a flex container can be laid out in any direction, and can “flex” their sizes, either growing to fill unused space or shrinking to avoid overflowing the parent."
From W3C Candidate Recommendation, 19 October 2017
distribution between items in an interface and powerful alignment capabilities.
When we describe flexbox as being one dimensional we are describing the fact that flexbox deals with layout in one dimension at a time (row or column). This can be contrasted with the two-dimensional model of CSS Grid Layout, which controls columns and rows together.
- No coming changes on the distant future
- Is the default layout on native web development
Let's talk about direction & align
.row {
display: flex;
}An area of a document laid out using flexbox is called a flex container. To create a flex container, we set the value of the area's container's display property to flex.
.row {
display: flex;
}As soon as we do this the direct children of that container become flex items.
How flex items are placed in the flex container defining the main axis and the direction
.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-direction: column;
flex-direction: row-reverse;
flex-direction: column-reverse;
}Specifies whether flex items are forced into a single line or can be wrapped onto multiple lines.
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;
}Is is a shorthand property for flex-direction and flex-wrap individual properties.
.container {
display: flex;
/* flex-flow: <'flex-direction'> and <'flex-wrap'> */
flex-flow: row nowrap;
flex-flow: column wrap;
flex-flow: column-reverse wrap-reverse;
}Defines how the browser distributes space between and around content items along the main-axis of their container.
.container {
display: flex;
/* Positional alignment */
justify-content: center;
justify-content: flex-start;
justify-content: flex-end;
justify-content: left;
justify-content: right;
/* Distributed alignment */
justify-content: space-between;
justify-content: space-around;
justify-content: space-evenly;
justify-content: stretch;
}Sets the align-self (flex item property) value on all direct children as a group. It controls the alignment of items on the cross axis
.container {
display: flex;
/* Basic keywords */
align-items: normal;
align-items: stretch;
/* Positional alignment */
align-items: center;
align-items: flex-start;
align-items: flex-end;
align-items: baseline;
}Handles the remaining space between and around content items along the cross-axis with multiple lines.
.container {
display: flex;
/* Basic keywords */
align-content: center;
align-content: flex-start;
align-content: flex-end;
/* Baseline alignment */
align-content: baseline;
/* Distributed alignment */
align-content: space-between;
align-content: space-around;
align-content: space-evenly;
align-content: stretch;
}To have more control over flex items we can target them directly. We do this by way of three properties
flex-basisflex-growflex-shrinkflexalign-selforder
Specifies the initial main size of a flex item. This property determines the size of the content-box
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex-basis: 33%;
}Specifies what amount of space inside the flex container the item should take up. The flex grow factor of a flex item is relative to the size of the other children in the flex-container.
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex-grow: 1;
}Flex items will shrink to fill the container according to the flex-shrink number, when the default size of flex items is larger than the flex container.
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex-shrink: 1;
}Is a shorthand property that sets flex-grow, flex-shrink, and flex-basis.
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex: 1 1 25%;
}Aligns flex items of the current flex line overriding the align-items value. If any of the item's cross-axis margin is set to auto, then align-self is ignored.
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
align-self: center; /* Put the item around the center */
align-self: flex-start; /* Put the flex item at the start */
align-self: flex-end; /* Put the flex item at the end */
}Specifies the order used to lay out a flex or grid item in its flex container. Items within the same container are laid out in ascending order according to their order values. Elements with the same order value are laid out in the order in which they appear in the source code.
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
order: 1;
order: -1;
}Do Flex Froggy
class: frontpage