- Gradle Dependency
- Basics
- Customizing the Message
- Action Buttons
- Adding an Icon
- Callbacks
- Dismissing
- Lists
- Checkbox Prompts
- Custom Views
- Miscellaneous
- Theming
The core module contains everything you need to get started with the library. It contains all
core and normal-use functionality.
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:core:3.1.1'
}Here's a very basic example of creating and showing a dialog:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
title(R.string.your_title)
message(R.string.your_message)
}this should be a Context which is attached to a window, like an Activity.
If you wanted to pass in literal strings instead of string resources:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
title(text = "Your Title")
message(text = "Your Message")
}Note that you can setup a dialog without immediately showing it, as well:
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
dialog.show()The message function lets you trail it with a lambda, which exposes certain built-in modifiers
along with allowing you to act on the TextView directly.
MaterialDialog(this).show {
...
message(R.string.your_message) {
html() // format, color, etc. with tags in string
html { link -> // same as above, but...
// Invokes a callback when a URL is clicked instead of auto opening it in a browser
}
lineSpacing(1.4f) // modifies line spacing, default is 1.0f
// You can directly act on the message TextView as well
val textView = messageTextView
}
}There are simple methods for adding action buttons:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
positiveButton(R.string.agree)
negativeButton(R.string.disagree)
}You can use literal strings here as well:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
positiveButton(text = "Agree")
negativeButton(text = "Disagree")
}Listening for clicks on the buttons is as simple as adding a lambda to the end:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
positiveButton(R.string.agree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
negativeButton(R.string.disagree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
}If action buttons together are too long to fit in the dialog's width, they will be automatically stacked:
You can display an icon to the left of the title:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
icon(R.drawable.your_icon)
}You can pass a Drawable instance as well:
val myDrawable: Drawable = // ...
MaterialDialog(this).show {
icon(drawable = myDrawable)
}There are a few lifecycle callbacks you can hook into:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
onPreShow { dialog -> }
onShow { dialog -> }
onDismiss { dialog -> }
onCancel { dialog -> }
}Dismissing a dialog closes it, it's just a simple method inherited from the parent Dialog class:
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
dialog.dismiss()You can prevent a dialog from being canceled, meaning it has to be explictly dismissed with an action button or a call to the method above.
MaterialDialog(this).show {
cancelable(false) // calls setCancelable on the underlying dialog
cancelOnTouchOutside(false) // calls setCanceledOnTouchOutside on the underlying dialog
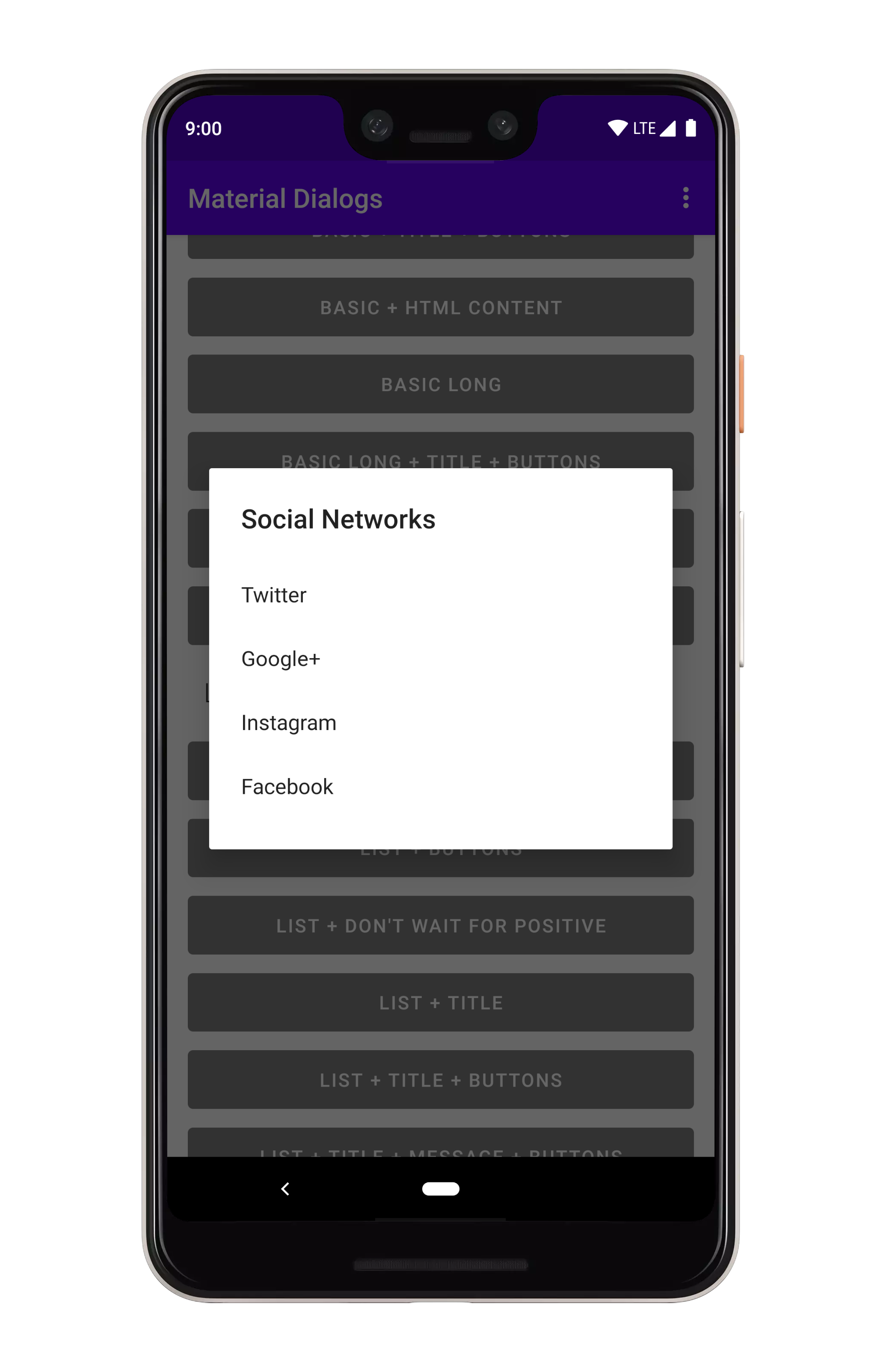
}You can show lists using the listItems extension on MaterialDialog:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItems(R.array.socialNetworks)
}You can pass a literal string array too:
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItems(items = myItems)
}To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItems(R.array.socialNetworks) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user taps an item
}
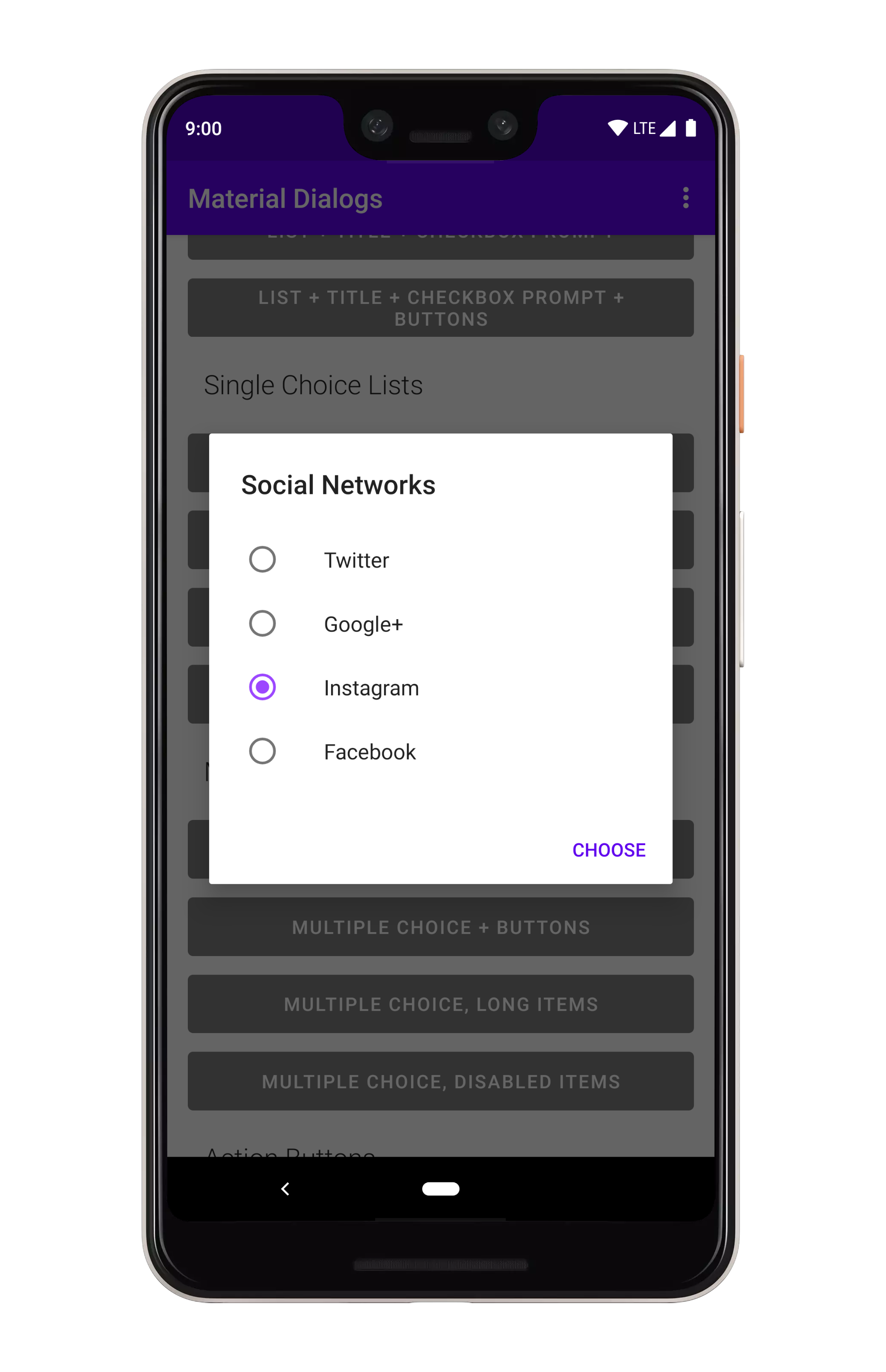
}You can show single choice (radio button) lists using the listItemsSingleChoice extension
on MaterialDialog:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items)
}You can pass a literal string array too:
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsSingleChoice(items = myItems)
}If you want an option to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an initialSelection index):
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = 1)
}To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
}Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If you add a positive action button...
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
positiveButton(R.string.select)
}...then the callback isn't invoked until the user selects an item and taps the positive action
button. You can override that behavior using the waitForPositiveButton argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
}There are methods you can use in a built dialog to modify checked states:
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
dialog.checkItem(index)
dialog.uncheckItem(index)
dialog.toggleItemChecked(index)
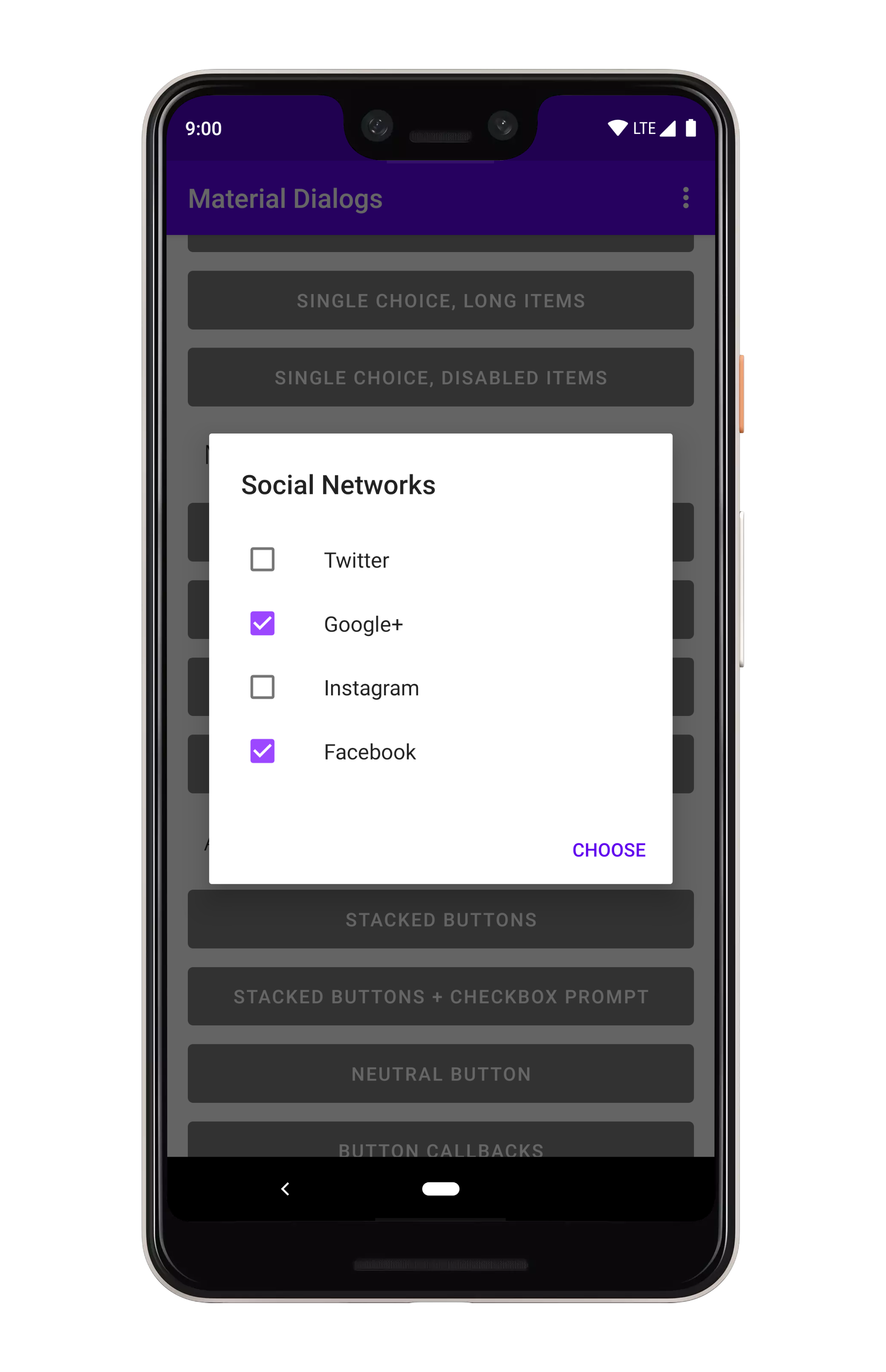
val checked: Boolean = dialog.isItemChecked(index)You can show multiple choice (checkbox) lists using the listItemsMultiChoice extension on MaterialDialog:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects item(s)
}
}You can pass a literal string array too:
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsMultiChoice(items = myItems)
}If you want option(s) to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an initialSelection index):
val indices = intArrayOf(1, 3)
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = indices)
}To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
}Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If you add a positive action button...
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
positiveButton(R.string.select)
}...then the callback isn't invoked until the user select one or more items and taps the positive
action button. You can override that behavior using the waitForPositiveButton argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this).show {
listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
}There are methods you can use in a built dialog to modify checked states:
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val indices: IntArray = // ...
dialog.checkItems(indices)
dialog.uncheckItems(indices)
dialog.toggleItemsChecked(indices)
dialog.checkAllItems()
dialog.uncheckAllItems()
dialog.toggleAllItemsChecked()
val checked: Boolean = dialog.isItemChecked(index)If you want to customize lists to use your own views, you need to use a custom adapter.
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = // some sort of adapter implementation...
MaterialDialog(this).show {
customListAdapter(adapter)
}You can retrieve your adapter again later from the dialog instance:
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = dialog.getListAdapter()You can also retrieve the RecyclerView that the adapter is hosted in:
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
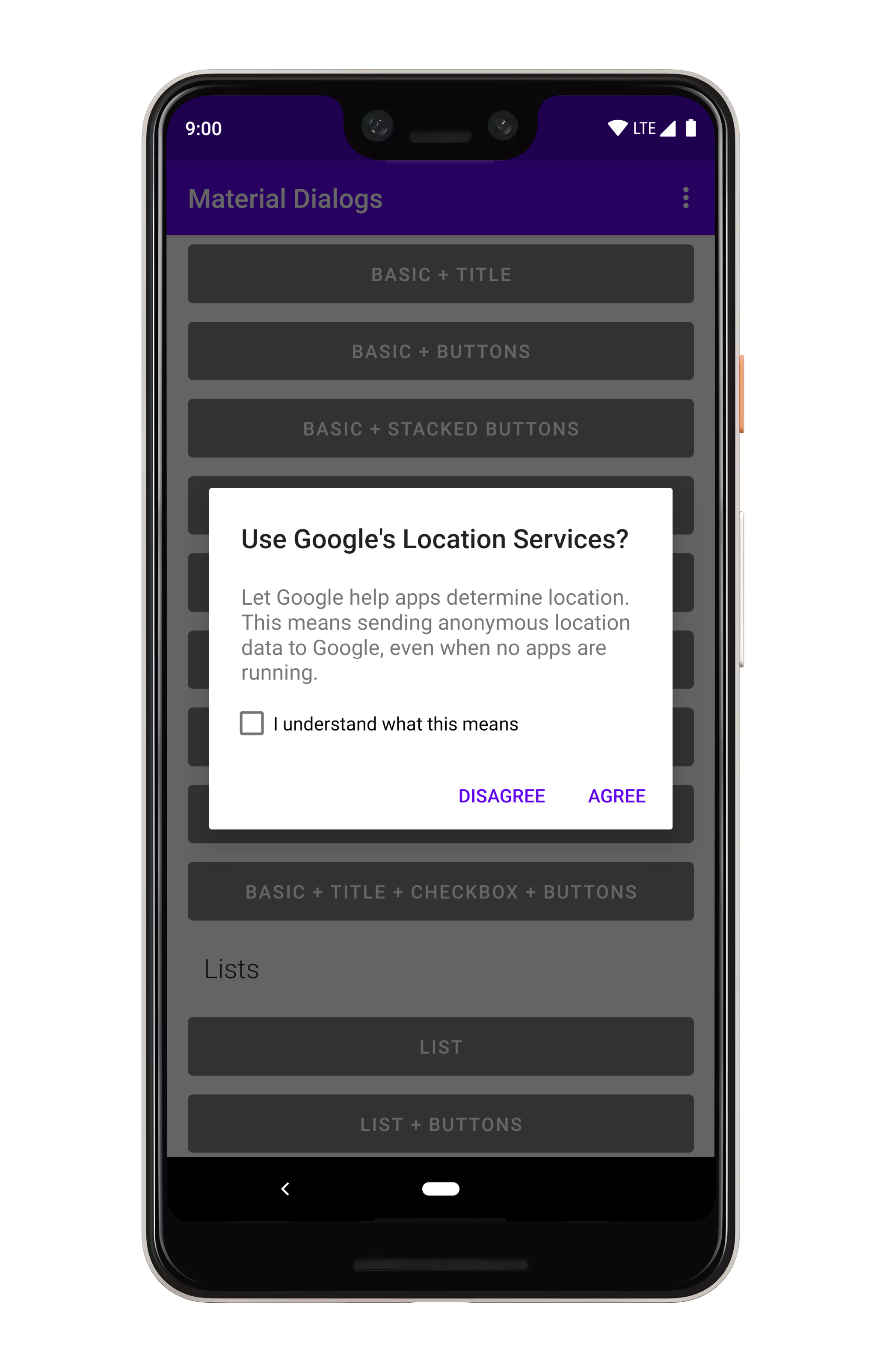
val recyclerView: RecyclerView = dialog.getRecyclerView()Checkbox prompts can be used together with any other dialog type, it gets shown in the same view which shows the action buttons.
MaterialDialog(this).show {
checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label) { checked ->
// Check box was checked or unchecked
}
}You can pass a literal string for the label too:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World")
}You can also append a lambda which gets invoked when the checkbox is checked or unchecked:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World") { checked -> }
}If you only care about the checkbox state when the positive action button is pressed:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label)
positiveButton(R.string.button_text) { dialog ->
val isChecked = dialog.isCheckPromptChecked()
// do something
}
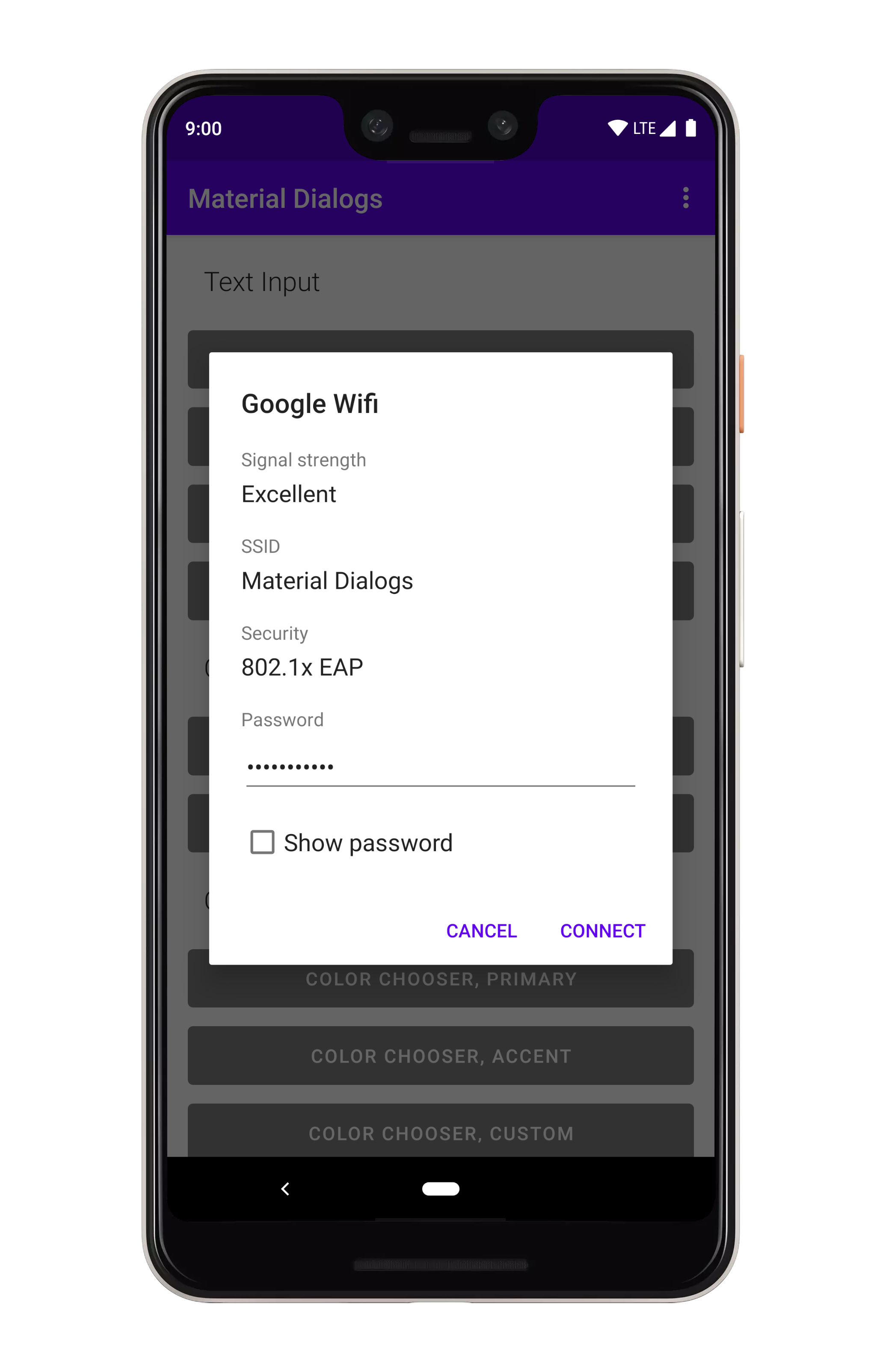
}A lot of the included extensions use custom views, such as the color chooser dialog. There's also a simple example in the sample project.
MaterialDialog(this).show {
customView(R.layout.my_custom_view)
}You can also pass a literal view:
val myView: View = // ...
MaterialDialog(this).show {
customView(view = myView)
}If your custom view may be taller than the dialog, you'll want to make it scrollable:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
}For later access, you can use dialog.getCustomView():
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
val customView = dialog.getCustomView()
// Use the view instance, e.g. to set values or setup listeners
dialog.show()There are little details which are easy to miss. For an example, auto dismiss controls whether pressing the action buttons or tapping a list item will automatically dismiss the dialog or not. By default, it's turned on. You can disable it:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
noAutoDismiss()
}Google's newer mindset with Material Theming (vs the 2014 mindset) is flexible. If you take their "Crane example", you see that they change fonts, corner rounding, etc.
Light and dark theming is automatic based on your app's theme (basically whether android:textColorPrimary
is more light or more dark):
Material Dialogs uses the value of the colorBackgroundFloating attribute in your Activity theme
for the background color of dialogs. You can also use the md_background_color attribute in your
theme, which will take precedence.
Material Dialogs uses the value of the ?android:colorControlHighlight attribute in your Activity
theme for the ripple color of list items, buttons, etc. by default. You can override this with the
md_ripple_color theme attribute as well.
Corner radius is the rounding of dialog corners:
it can be changed with an attribute in your app theme. It defaults to 2dp:
<style name="AppTheme.Custom" parent="Theme.AppCompat">
<item name="md_corner_radius">16dp</item>
</style>There is also a programmatic setter for this value:
MaterialDialog(this).show {
// literal, internally converts to dp so 16dp
cornerRadius(16f)
// Using a dimen instead is encouraged as it's easier to have all instances changeable from one place
cornerRadius(res = R.dimen.my_corner_radius)
}By default, android:textColorPrimary and android:textColorSecondary attributes from your Activity
theme are used for the title and content colors of dialogs. colorPrimary is used for the default
text color of action buttons. If you wish to override these, there are attributes provided:
<style name="AppTheme.Custom" parent="Theme.AppCompat">
<item name="md_color_title">@color/your_color</item>
<item name="md_color_content">@color/your_color</item>
<item name="md_color_button_text">@color/your/color</item>
</style>This library supports using custom fonts, powered by the Support libraries ResourcesCompat class.
With raw font files or XML font files in your /res/font folder, you can use them in Material Dialogs
using attributes in your app's theme.
<style name="AppTheme.Custom" parent="Theme.AppCompat">
<item name="md_font_title">@font/your_font</item>
<item name="md_font_body">@font/your_font</item>
<item name="md_font_button">@font/your_font</item>
</style>See the "Custom Theme" example in the sample project (open the overflow menu for the theme switcher).