It's possible to localize strings also in frontend using LocalizationProvider package for .NET Core.
You have to setup middleware on particular path (by default /jsl10n). You will have possibility to customize Url when url mapping is done.
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.UseDbLocalizationProvider();
app.UseDbLocalizationClientsideProvider(); //assuming that you like also Javascript
...
}
}Depending on your routing system (either old school Mvc router or Endpoint routing) different methods should be called.
For old MVC Routing:
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services
.AddControllersWithViews(opt => opt.EnableEndpointRouting = false)
.AddMvcLocalization();
services.AddRouting();
services.AddDbLocalizationProvider(_ =>
{
_.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"));
...
});
...
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.UseDbLocalizationProvider();
app.UseDbLocalizationClientsideProvider(); //assuming that you like also Javascript
...
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapDbLocalizationClientsideProvider(path: "/jsl10n"); // assuming that you are mapping on /jsl10n/...
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}For Endpoint routing:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services
.AddControllersWithViews()
.AddMvcLocalization();
services.AddRouting();
...
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.UseRouting();
...
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
...
endpoints.MapDbLocalizationClientsideProvider(path: "/jsl01n"); // assuming that you are mapping on /jsl10n/...
});
}Then in your markup files you can use following helper method to pull down resources.
Assume that we have following resource class:
namespace MyProject
{
[LocalizedResource]
public class SampleResources
{
public static string PageHeader => "This is page header";
}
}Then by adding this code to your Razor page:
<body>
...
@Html.GetTranslations(typeof(SampleResources))
</body>You will get SampleResources class pulled down to client-side formatted as JSON object and assigned to window.jsl10n object by default. You can work with it in following way:
@Html.GetTranslations(typeof(SampleResources))
<script>
document.getElementById('...').innerHTML =
window.jsl10n.MyProject.SampleResources.PageHeader;
</script>Developer experience working with resources on client-side wanted to keep close enough with the same experience when using package on server-side.
You can also fetch only required resource keys (without pulling down whole class):
@(Html.GetTranslations(() => SampleResources.PageHeader))You can also ask to pull down various resources multiple times. All of the requested resources will be "merged" under this "jsl10n" key on window object.
Sometimes you need to assigned different resources to different scopes or somehow group them differently. This is possible by using aliases. What it means is that following code:
@Html.GetTranslations(typeof(SampleResources), "no", "norwegianScope")will return resource translations for Norwegian language for SampleResources resource under norwegianScope key on window object level. Sometimes might become handy if needed.
var headerInNorwegian = window.norwegianScope.MyProject.SampleResources.PageHeader;Pulled down translated object needs to be assigned to something in order to work with it. I chose window object, but it could be anything actually.
But you might ask - what about case when I need to dynamically pull down resources on my own and don't need to pollute global scope with some weird objects?
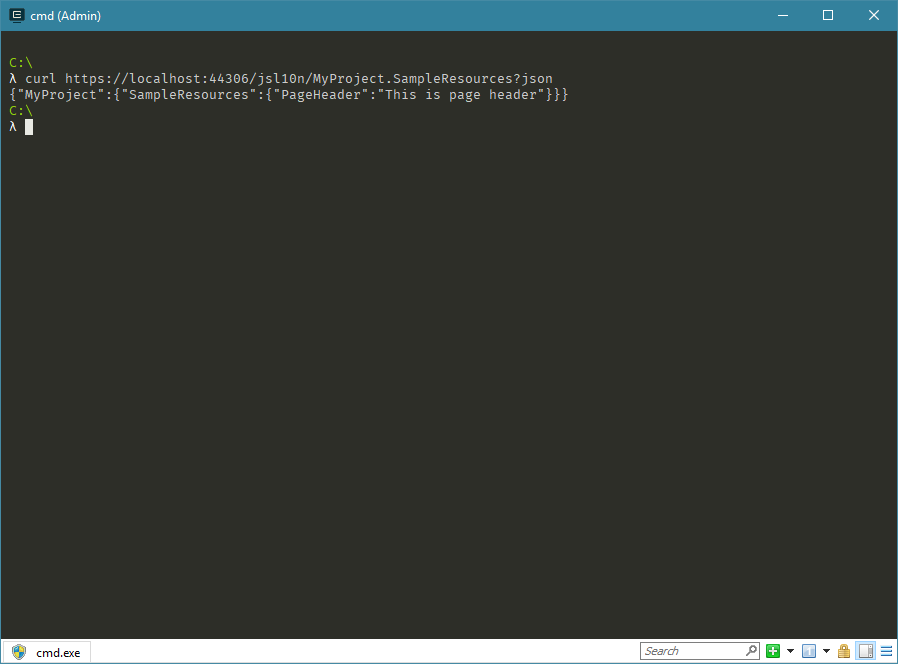
In these cases you can issue request directly to localization provider endpoint and get only JSON representation of the resource class translations.
For example, issuing request straight to resource endpoint and providing json query parameter, you will get back only JSON object.
Or you can just fire any standard XHR request and localization provider will try its best to detect that request is of ajax type. If so - translations will be served in JSON format by default.