This repository contains some research I did on these three chips to be able to use them on my own PCB.
The chips contain a 8051 core that executes code from a mask ROM. On boot this code copies extra firmware from an external EEPROM that will be called from some configurable (fixed-address) hooks in the ROM. The MS2130 has the full firmware in external FLASH and it does not make use of the ROM after booting. Of course I cannot post the original firmware as I don't know its license. Surprisingly, all chips work quite well with only the ROM code. Of course you can read the EEPROM from a commercial module.
I wrote my own firmware from scratch for the MS2106 and may upload this on a later date.
The Golang library in the folder 'mshal' interfaces to the factory HID interface of the chip. By default the ROM allows access to the 8051 XDATA and EEPROM. The MS2106 has an extra memory region that contains the video decoder register map. The MS2109 has some other commands that I didn't investigate.
The library can patch the currently running firmware to add extra functionality:
- GPIO Control
- I2C Bus
- EEPROM Read/Write (much faster than via the ROM)
- FLASH Read/Write
- CODE Read (8051 MOVC)
- Call any ROM/FW function and load custom ones.
Depending on which firmware is running, it is possible that the patch code may fail. To resolve this you can either fix the issue or tell the HAL to use the ROM code only.
In the folder 'cli' there is a simple Golang application that uses mshal to talk to the device. It supports the following functions:
- list-dev: List HID devices.
- list-regions: List available memory regions.
- read region addr [amount]: Read and dump memory.
- write region addr value: Write value to memory.
- write-file region addr filename: Write file to memory.
- dump-rom filename: Dump ROM (code) to file by uploading custom code. It is recommended to use this with --no-patch to get an unpatched dump.
- i2c-scan: Scan I2C bus and show discovered devices.
- i2c-txfr addr: Perform I2C transfer.
- gpio-set command: Set GPIO pin value and direction.
- gpio-get: Get GPIO values.
Most commands have extra options. To get help simply run the program as follows:
Main program: ./cli --help
Command: ./cli read --help
Example commands for EEPROM programming:
- Write: ./cli --no-firmware --log-level 2 write-file --verify EEPROM 0 /tmp/eeprom.bin
- Read: ./cli --no-firmware --log-level 2 read EEPROM 0 --filename=/tmp/eeprom.bin
Example commands for FLASH programming (on MS2130):
- Write: ./cli --log-level=7 write-file --verify FLASH 0 YuzukiLOHCCPro.bin
- Read: ./cli --log-level=7 read FLASH 0 --filename=/tmp/flash.bin
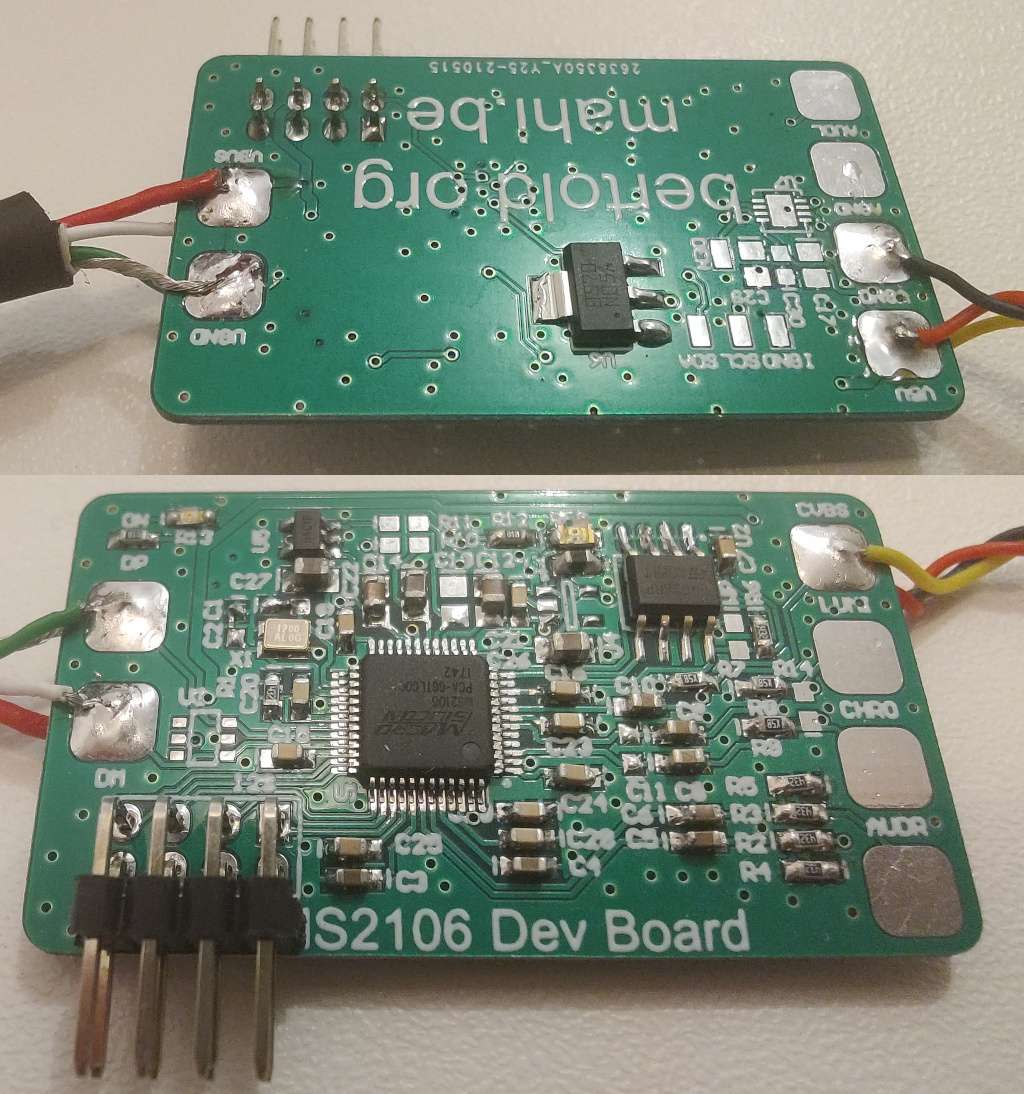
This repository contains the schematics and Gerbers of a simple PCB with the MS2106 chip. You can find it in the folder 'board/ms2106'. Here you can see a picture of the completed board:
These are randomly selected links after a quick Aliexpress search, I have no relation to the seller.
MS2106:
- https://aliexpress.com/item/33013186767.html
- https://aliexpress.com/item/4001066406950.html
- https://aliexpress.com/item/1005002943812391.html
You can buy packaged solutions as well, but there are many chips that convert CVBS->USB and you never know which one you get. Almost all single-chip embedded modules seem to be MS2106 based. The MS2106(s) is obsolete and you may get a MS2107, which is also supported.
MS2109:
- https://aliexpress.com/item/1005001880861192.html
- https://aliexpress.com/item/4001063622632.html
- https://aliexpress.com/item/1005001599431974.html
It seems any cheap HDMI->USB converter contains the MS2109 chip.
MS2130:
- https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005004883158574.html
- https://github.com/YuzukiHD/YuzukiLOHCC-PRO (DIY board)
This is a true HDMI->USB3.0 single chip solution. Experimental support has been added to this library.