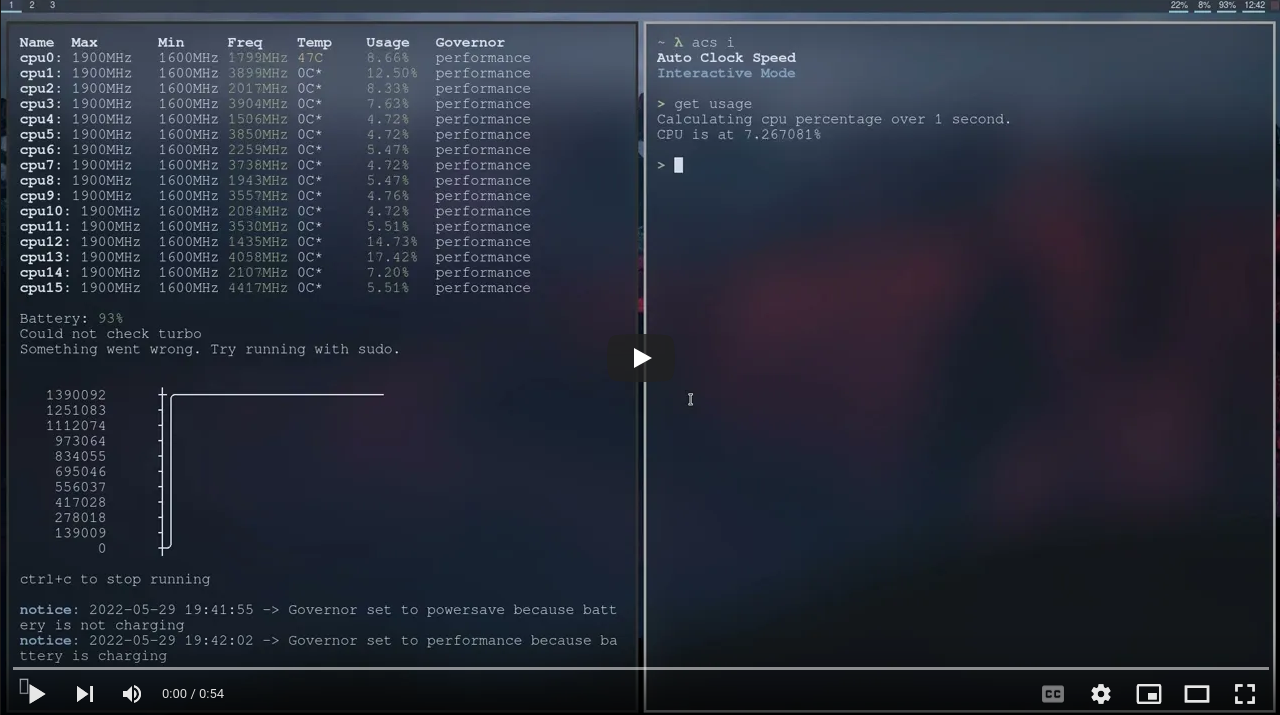
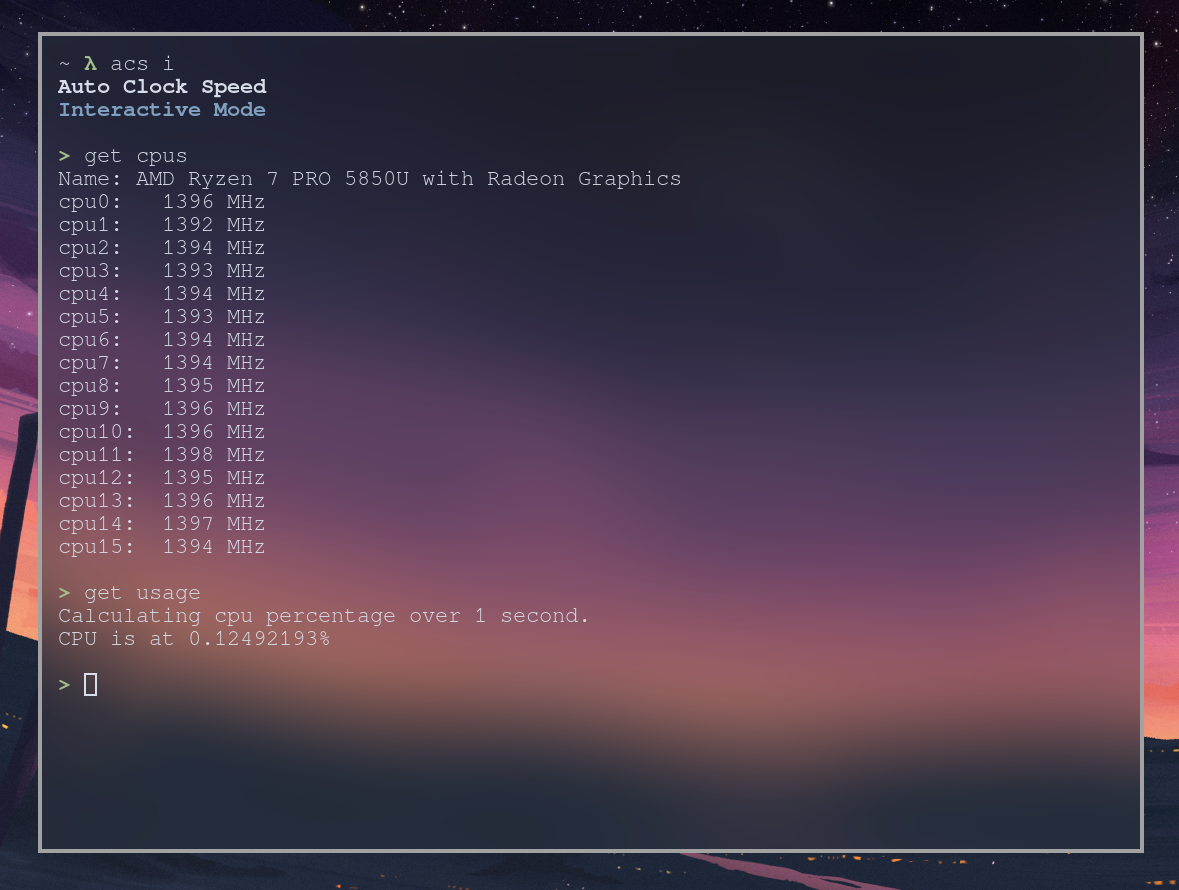
A utility to check stats about your CPU, and auto regulate clock speeds to help with either performance or battery life. This proram is designed for Linux and Intel laptops, although it should theoretically work on AMD systems and sometimes desktops as well. If you encounter any issues or bugs, please refer to the wiki to see if there is a solution.
- First and foremost, this is a project to learn about Rust and Linux
- Secondly, try to improve upon AdnanHodzic's already amazing auto-cpufreq
- Add options to display raw output of governors, clockspeed, turbo, battery, etc. for use in scripts or display panels like polybar.
- Read our CONTRIBUTING.md for some helpful tips
- Find an issue - "good first issue" recommended
- Feel free to ask questions!
If you have cargo on your machine, skip to step 3
-
Go to
rustup.rsto install rust. -
Setup rust
rustup override set stable rustup update stable -
Clone the project and install
git clone https://github.com/JakeRoggenbuck/auto-clock-speed cargo install --path auto-clock-speed # This is needed to have the root version of acs match the local installed version sudo cp ~/.cargo/bin/acs /usr/bin/acs
Note: The latest release of acs can also be installed locally with the following
cargo install autoclockspeedIn order to have auto-clock-speed start when you restart your computer you must follow these instructions
# IMPORTANT: Modify the service file (acs.service) in the
# project directory to include the path to the binary file
# (usually /home/username/.cargo/bin/acs)# In the auto clock speed directory run this command to
# move the service file into your systemd directory
sudo cp acs.service /etc/systemd/system/# Start and enable the service
sudo systemctl start acs
sudo systemctl enable acs
# Check service is up and running
systemctl status acsThe line after [Service] in acs.service is the command that will be run. You may want to add or remove arguments, mainly --quiet.
[Unit]
Description=Manages Clock Speed
[Service]
ExecStart=/home/your-user-here/.cargo/bin/acs run --no-animation --quiet
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
WARN: Using default config. Create file '/etc/acs/acs.toml' for custom config or run 'acs initconfig' to setup default config automatically.This warning recommends creating a config file, use the initconfig command to automatically create one for you!
sudo acs initconfigalso the default settings if no config is provided
# acs.toml
powersave_under = 20
overheat_threshold = 80
active_rules = [ "battery_percent_rule", "lid_open_rule", "ac_charging_rule", "cpu_usage_rule" ]If you would like to turn off auto-clock-speed, here are the steps.
Note: This should be done during testing of acs run mode.
# Temporarily stop (only lasts until reboot)
sudo systemctl stop acs
# Permanently stop until turned on
sudo systemctl disable acsHere is how to uninstall the binary and the systemctl service.
# Remove local binary
cargo uninstall acs
# Remove system shared binary
rm /usr/bin/acs
# Remove systemctl entry
rm /etc/systemd/system/acs.serviceHere are some examples of how acs can be used.
# Monitor mode
acs monitor
# Run as root
sudo acs run
# Get all speeds
acs get speeds
# Select gov from dmenu
sudo acs set gov $(acs get available-govs --raw | dmenu)Detailed usage can be found on our wiki
Automatic CPU frequency scaler and power saver
USAGE:
acs <SUBCOMMAND>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
SUBCOMMANDS:
get Get a specific value or status
help Prints this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
interactive Interactive mode for auto clock speed commands
monitor Monitor each cpu, it's min, max, and current speed, along with the governor
run Run the daemon, this checks and edit your cpu's speed
set Set a specific value
showconfig Show the current config in use