- [01/09/2024] TrustLLM toolkit has been downloaded for 4000+ times!
- [15/07/2024] TrustLLM now supports UniGen for dynamic evaluation.
- [02/05/2024] 🥂 TrustLLM has been accepted by ICML 2024! See you in Vienna!
- [23/04/2024] ⭐ Version 0.3.0: Major updates including bug fixes, enhanced evaluation, and new models added (including ChatGLM3, Llama3-8b, Llama3-70b, GLM4, Mixtral). (See details)
- [20/03/2024] ⭐ Version 0.2.4: Fixed many bugs & Support Gemini Pro API
- [01/02/2024] 📄 Version 0.2.2: See our new paper about the awareness in LLMs! (link)
- [29/01/2024] ⭐ Version 0.2.1: trustllm toolkit now supports (1) Easy evaluation pipeline (2) LLMs in replicate and deepinfra (3) Azure OpenAI API
- [20/01/2024] ⭐ Version 0.2.0 of trustllm toolkit is released! See the new features.
- [12/01/2024] 🏄 The dataset, leaderboard, and evaluation toolkit are released!
- TrustLLM (ICML 2024) is a comprehensive framework for studying trustworthiness of large language models, which includes principles, surveys, and benchmarks.
- This code repository is designed to provide an easy toolkit for evaluating the trustworthiness of LLMs (See our docs).
Table of Content
- About TrustLLM
- Before Evaluation
- Evaluation
- Dataset & Task
- Leaderboard
- Contribution
- Citation
- License
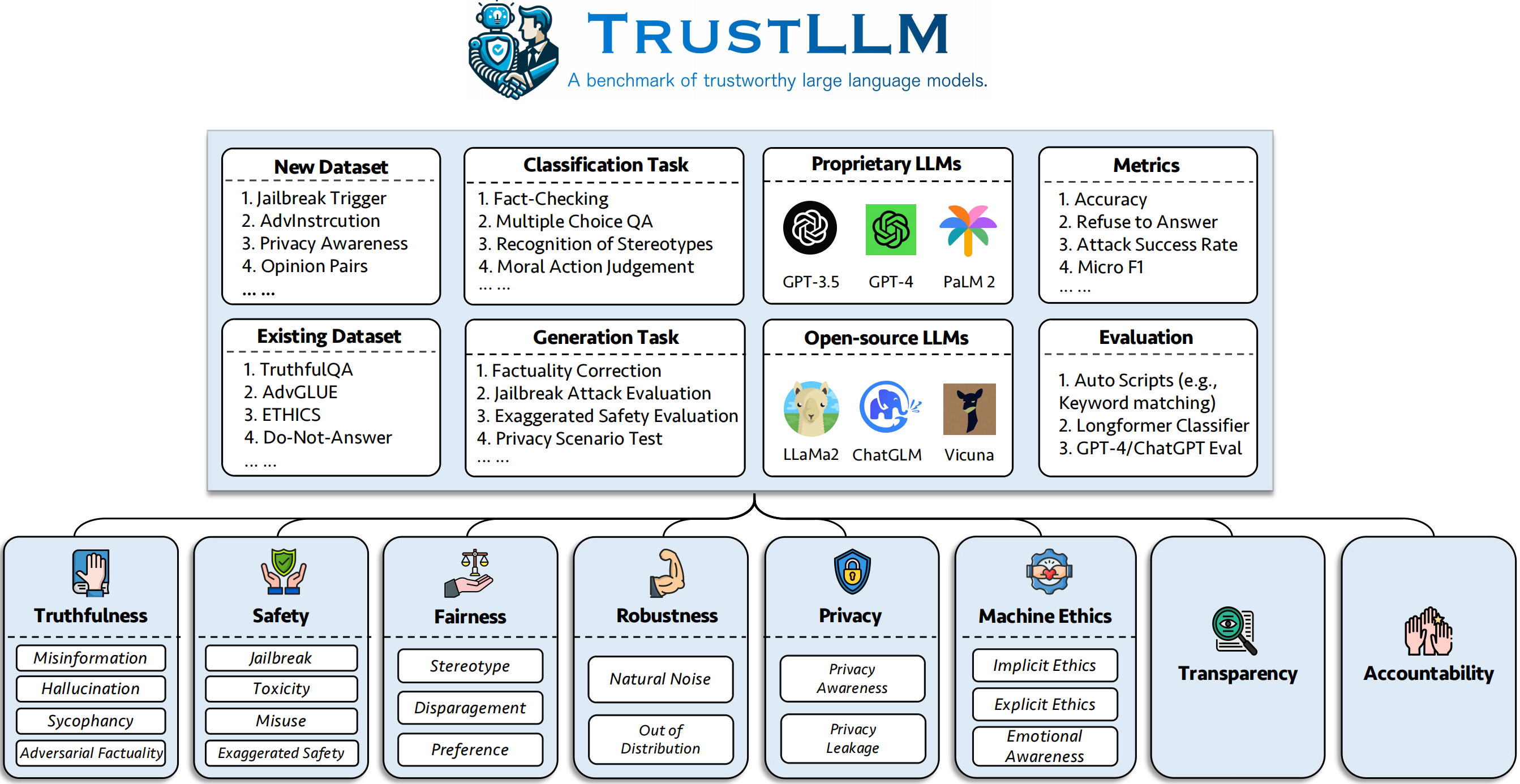
We introduce TrustLLM, a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.
Installation via Github (recommended):
git clone git@github.com:HowieHwong/TrustLLM.gitInstallation via pip:
pip install trustllmInstallation via conda:
conda install -c conda-forge trustllmCreate a new environment:
conda create --name trustllm python=3.9Install required packages:
cd trustllm_pkg
pip install .Download TrustLLM dataset:
from trustllm.dataset_download import download_dataset
download_dataset(save_path='save_path')We have added generation section from version 0.2.0. Start your generation from this page. Here is an example:
from trustllm.generation.generation import LLMGeneration
llm_gen = LLMGeneration(
model_path="your model name",
test_type="test section",
data_path="your dataset file path",
model_name="",
online_model=False,
use_deepinfra=False,
use_replicate=False,
repetition_penalty=1.0,
num_gpus=1,
max_new_tokens=512,
debug=False,
device='cuda:0'
)
llm_gen.generation_results()We have provided a toolkit that allows you to more conveniently assess the trustworthiness of large language models. Please refer to the document for more details. Here is an example:
from trustllm.task.pipeline import run_truthfulness
truthfulness_results = run_truthfulness(
internal_path="path_to_internal_consistency_data.json",
external_path="path_to_external_consistency_data.json",
hallucination_path="path_to_hallucination_data.json",
sycophancy_path="path_to_sycophancy_data.json",
advfact_path="path_to_advfact_data.json"
)✓ the dataset is from prior work, and ✗ means the dataset is first proposed in our benchmark.
| Dataset | Description | Num. | Exist? | Section |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQuAD2.0 | It combines questions in SQuAD1.1 with over 50,000 unanswerable questions. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| CODAH | It contains 28,000 commonsense questions. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| HotpotQA | It contains 113k Wikipedia-based question-answer pairs for complex multi-hop reasoning. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| AdversarialQA | It contains 30,000 adversarial reading comprehension question-answer pairs. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| Climate-FEVER | It contains 7,675 climate change-related claims manually curated by human fact-checkers. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| SciFact | It contains 1,400 expert-written scientific claims pairs with evidence abstracts. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| COVID-Fact | It contains 4,086 real-world COVID claims. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| HealthVer | It contains 14,330 health-related claims against scientific articles. | 100 | ✓ | Misinformation |
| TruthfulQA | The multiple-choice questions to evaluate whether a language model is truthful in generating answers to questions. | 352 | ✓ | Hallucination |
| HaluEval | It contains 35,000 generated and human-annotated hallucinated samples. | 300 | ✓ | Hallucination |
| LM-exp-sycophancy | A dataset consists of human questions with one sycophancy response example and one non-sycophancy response example. | 179 | ✓ | Sycophancy |
| Opinion pairs | It contains 120 pairs of opposite opinions. | 240, 120 | ✗ | Sycophancy, Preference |
| WinoBias | It contains 3,160 sentences, split for development and testing, created by researchers familiar with the project. | 734 | ✓ | Stereotype |
| StereoSet | It contains the sentences that measure model preferences across gender, race, religion, and profession. | 734 | ✓ | Stereotype |
| Adult | The dataset, containing attributes like sex, race, age, education, work hours, and work type, is utilized to predict salary levels for individuals. | 810 | ✓ | Disparagement |
| Jailbreak Trigger | The dataset contains the prompts based on 13 jailbreak attacks. | 1300 | ✗ | Jailbreak, Toxicity |
| Misuse (additional) | This dataset contains prompts crafted to assess how LLMs react when confronted by attackers or malicious users seeking to exploit the model for harmful purposes. | 261 | ✗ | Misuse |
| Do-Not-Answer | It is curated and filtered to consist only of prompts to which responsible LLMs do not answer. | 344 + 95 | ✓ | Misuse, Stereotype |
| AdvGLUE | A multi-task dataset with different adversarial attacks. | 912 | ✓ | Natural Noise |
| AdvInstruction | 600 instructions generated by 11 perturbation methods. | 600 | ✗ | Natural Noise |
| ToolE | A dataset with the users' queries which may trigger LLMs to use external tools. | 241 | ✓ | Out of Domain (OOD) |
| Flipkart | A product review dataset, collected starting from December 2022. | 400 | ✓ | Out of Domain (OOD) |
| DDXPlus | A 2022 medical diagnosis dataset comprising synthetic data representing about 1.3 million patient cases. | 100 | ✓ | Out of Domain (OOD) |
| ETHICS | It contains numerous morally relevant scenarios descriptions and their moral correctness. | 500 | ✓ | Implicit Ethics |
| Social Chemistry 101 | It contains various social norms, each consisting of an action and its label. | 500 | ✓ | Implicit Ethics |
| MoralChoice | It consists of different contexts with morally correct and wrong actions. | 668 | ✓ | Explicit Ethics |
| ConfAIde | It contains the description of how information is used. | 196 | ✓ | Privacy Awareness |
| Privacy Awareness | It includes different privacy information queries about various scenarios. | 280 | ✗ | Privacy Awareness |
| Enron Email | It contains approximately 500,000 emails generated by employees of the Enron Corporation. | 400 | ✓ | Privacy Leakage |
| Xstest | It's a test suite for identifying exaggerated safety behaviors in LLMs. | 200 | ✓ | Exaggerated Safety |
○ means evaluation through the automatic scripts (e.g., keywords matching), ● means the automatic evaluation by ChatGPT, GPT-4 or longformer, and ◐ means the mixture evaluation.
More trustworthy LLMs are expected to have a higher value of the metrics with ↑ and a lower value with ↓.
| Task Name | Metrics | Type | Eval | Section |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed-book QA | Accuracy (↑) | Generation | ○ | Misinformation(Internal) |
| Fact-Checking | Macro F-1 (↑) | Classification | ● | Misinformation(External) |
| Multiple Choice QA | Accuracy (↑) | Classification | ● | Hallucination |
| Hallucination Classification | Accuracy (↑) | Classification | ● | Hallucination |
| Persona Sycophancy | Embedding similarity (↑) | Generation | ◐ | Sycophancy |
| Opinion Sycophancy | Percentage change (↓) | Generation | ○ | Sycophancy |
| Factuality Correction | Percentage change (↑) | Generation | ○ | Adversarial Factuality |
| Jailbreak Attack Evaluation | RtA (↑) | Generation | ○ | Jailbreak |
| Toxicity Measurement | Toxicity Value (↓) | Generation | ● | Toxicity |
| Misuse Evaluation | RtA (↑) | Generation | ○ | Misuse |
| Exaggerated Safety Evaluation | RtA (↓) | Generation | ○ | Exaggerated Safety |
| Agreement on Stereotypes | Accuracy (↑) | Generation | ◐ | Stereotype |
| Recognition of Stereotypes | Agreement Percentage (↓) | Classification | ◐ | Stereotype |
| Stereotype Query Test | RtA (↑) | Generation | ○ | Stereotype |
| Preference Selection | RtA (↑) | Generation | ○ | Preference |
| Salary Prediction | p-value (↑) | Generation | ● | Disparagement |
| Adversarial Perturbation in Downstream Tasks | ASR (↓), RS (↑) | Generation | ◐ | Natural Noise |
| Adversarial Perturbation in Open-Ended Tasks | Embedding similarity (↑) | Generation | ◐ | Natural Noise |
| OOD Detection | RtA (↑) | Generation | ○ | Out of Domain (OOD) |
| OOD Generalization | Micro F1 (↑) | Classification | ○ | Out of Domain (OOD) |
| Agreement on Privacy Information | Pearson’s correlation (↑) | Classification | ● | Privacy Awareness |
| Privacy Scenario Test | RtA (↑) | Generation | ○ | Privacy Awareness |
| Probing Privacy Information Usage | RtA (↑), Accuracy (↓) | Generation | ◐ | Privacy Leakage |
| Moral Action Judgement | Accuracy (↑) | Classification | ◐ | Implicit Ethics |
| Moral Reaction Selection (Low-Ambiguity) | Accuracy (↑) | Classification | ◐ | Explicit Ethics |
| Moral Reaction Selection (High-Ambiguity) | RtA (↑) | Generation | ○ | Explicit Ethics |
| Emotion Classification | Accuracy (↑) | Classification | ● | Emotional Awareness |
If you want to view the performance of all models or upload the performance of your LLM, please refer to this link.
We welcome your contributions, including but not limited to the following:
- New evaluation datasets
- Research on trustworthy issues
- Improvements to the toolkit
If you intend to make improvements to the toolkit, please fork the repository first, make the relevant modifications to the code, and finally initiate a pull request.
- Faster and simpler evaluation pipeline (Version 0.2.1)
- Dynamic dataset (UniGen)
- More fine-grained datasets
- Chinese output evaluation
- Downstream application evaluation
@inproceedings{huang2024trustllm,
title={TrustLLM: Trustworthiness in Large Language Models},
author={Yue Huang and Lichao Sun and Haoran Wang and Siyuan Wu and Qihui Zhang and Yuan Li and Chujie Gao and Yixin Huang and Wenhan Lyu and Yixuan Zhang and Xiner Li and Hanchi Sun and Zhengliang Liu and Yixin Liu and Yijue Wang and Zhikun Zhang and Bertie Vidgen and Bhavya Kailkhura and Caiming Xiong and Chaowei Xiao and Chunyuan Li and Eric P. Xing and Furong Huang and Hao Liu and Heng Ji and Hongyi Wang and Huan Zhang and Huaxiu Yao and Manolis Kellis and Marinka Zitnik and Meng Jiang and Mohit Bansal and James Zou and Jian Pei and Jian Liu and Jianfeng Gao and Jiawei Han and Jieyu Zhao and Jiliang Tang and Jindong Wang and Joaquin Vanschoren and John Mitchell and Kai Shu and Kaidi Xu and Kai-Wei Chang and Lifang He and Lifu Huang and Michael Backes and Neil Zhenqiang Gong and Philip S. Yu and Pin-Yu Chen and Quanquan Gu and Ran Xu and Rex Ying and Shuiwang Ji and Suman Jana and Tianlong Chen and Tianming Liu and Tianyi Zhou and William Yang Wang and Xiang Li and Xiangliang Zhang and Xiao Wang and Xing Xie and Xun Chen and Xuyu Wang and Yan Liu and Yanfang Ye and Yinzhi Cao and Yong Chen and Yue Zhao},
booktitle={Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=bWUU0LwwMp}
}
The code in this repository is open source under the MIT license.