This is the code repository for the JATS4R client-side validator, deployed to http://jats4r.org/validator/.
This was the subject of a paper presented at Balisage, 2015: A client-side JATS4R validator using Saxon-CE.
Prerequisites:
- Python - at least version 3.5
- The instructions here assume you're working on a Unix environment with the bash shell; but should be easily adaptible to other environments.
- Files and directories
- Quick start
- Validation setup
- Validating from the command line
- Schema sources
- Generating XSLTs from Schematron sources
- Testing
- How it works
- Limitations
- Dependencies
The following are the directories and files in this repository, and what they are for.
- assets/ - static resources
- bin/ - shell scripts and XSLT files
- jats/ - scripts to download and prepare NLM and JATS schema definition files.
- samples/ - sample XML documents
- schema/ - Schematron source files; see schema sources, below.
- test/test-files/ - XML files used for testing.
- LICENSE
- README.md - This file
- index.html, validate.js, validate.css - the main validator files
The following directories are generated in the course of building the validator.
FIXME double-check these
- venv - Python virtual environment
- lib - Third party libraries and tools. See Dependencies, below.
- jats-schema - Flattened versions of all of the NLM and JATS DTDs
- generated-xsl - This contains XSLT versions of the Schematron files. The contents here should not be edited directly. See Generating XSLTs from Schematron sources, below
Here are the steps to get a working validator on your system.
The validator is deployed as a static web site, so you'll need to have access to a system with a web server such as Apache. Find a convenient location served by that server, and execute the following:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/JATS4R/validator.git
cd validator
# Initializes python's virtualenv; sets bash environment
. bin/setenv.sh
# extracts libraries, etc., and processes schematron
bin/setup.sh
Then, open the index.html page in your browser, through the web
server on your system, and you should have a working validator.
Here is some more detailed information.
Whenever you open a new shell to work on this tool, configure its environment with:
. bin/setenv.sh
After initially cloning the repository, in order to configure the necessary tools, you'll need to run
bin/setup.sh
This does the following:
- Extracts several third party libraries into the
libdirectory, - Builds flattened versions of the JATS DTDs and RNGs, writing them into the
jats-schemadirectory, and - Processes the schematron files, writing the results into
generated-xsl.
If any changes are made to the Schematron files, you can rebuild them, without rerunning the entire setup, by running
bin/process-schematron.sh
To clean up the working directory, and start from scratch, just run
bin/clean.sh
To validate a JATS file named sample.xml, use the script validate.sh. For example,
validate.sh samples/minimal.xml
This will give a report for compliance of the input file minimal.xml with respect to all topics (math and permissions). By default, it only reports errors. If you want a full report (info, warnings, and errors) then enter:
validate.sh samples/minimal.xml info
Use the -h switch to get a list of all the possible arguments.
If your setup requires an OASIS catalog file to resolve the DTDs for JATS documents, you can use the environment variable JATS_CATALOG to point to that.
For example, you can download the JATS Bundle to get all of the DTDs for several versions and flavors of JATS (up to NISO JATS draft version 0.4), and unzip it, and then set the JATS_CATALOG environment variable to point to the master catalog from that:
cd ~
wget http://jatspan.org/downloads/jats-core-bundle-0.8.zip
unzip jats-core-bundle-0.8.zip
export JATS_CATALOG=~/jatspacks/catalog.xml
Now, when you run validate.sh, it will automatically use that catalog file to resolve any DTDs. For example:
validate.sh samples/sample.xml
The master schema files are in Schematron format, in the schema subdirectory.
The "master" Schematron file, which determines conformance or non-conformance, is jats4r.sch. This includes all topics, but only the "error level" tests.
There are two other "master" Schematron files, which break down the tests in two different ways: one by message severity (info, warnings, and errors) and one by topic (math and permissions).
The test files themselves are broken down into separate modules, by topic and by severity level. So, for example, permissions-errors.sch, permissions-warnings.sch, and permissions-info.sch define the tests for the permissions topic. All three run tests on permissions, but the permissions-errors reports only those things that are errors.
In summary, the master Schematron files are:
- jats4r.sch - all topics, error level only
- jats4r-level.sch - groups tests by message severity level. Using this with
phase=info(orphase=#ALL) will run all of the tests. - jats4r-topic.sch - groups tests by topic. So, for example, when you run this
with the
phase=math, you will run just the math tests.
The generated-xsl subdirectory contains XSLT2 files that have been generated from the Schematrons, using the process-schematron.sh script. These XSLT files must not be edited directly. If a change is made to a Schematron, a new XSLT should be auto-generated, using the process-schematron.sh script.
When run against an instance, they will generate a report in Schematron Validation Report Language XML (SVRL).
To generate new XSLT files in the generated-xsl directory, first, as described above, you must source the bin/setup.sh script into your shell.
Then, use the script process-schematron.sh to convert the Schematron files into XSLT:
bin/process-schematron.sh
You can optionally pass this script an input-type (level or topic) and a
phase (which depends on the input-type). Enter bin/process-schematron.sh -h
for usage information.
This writes the output files into the generated-xsl directory.
To test the online validator, use the files in the test/test-files directory.
Automated tests coming soon. See issue 8.
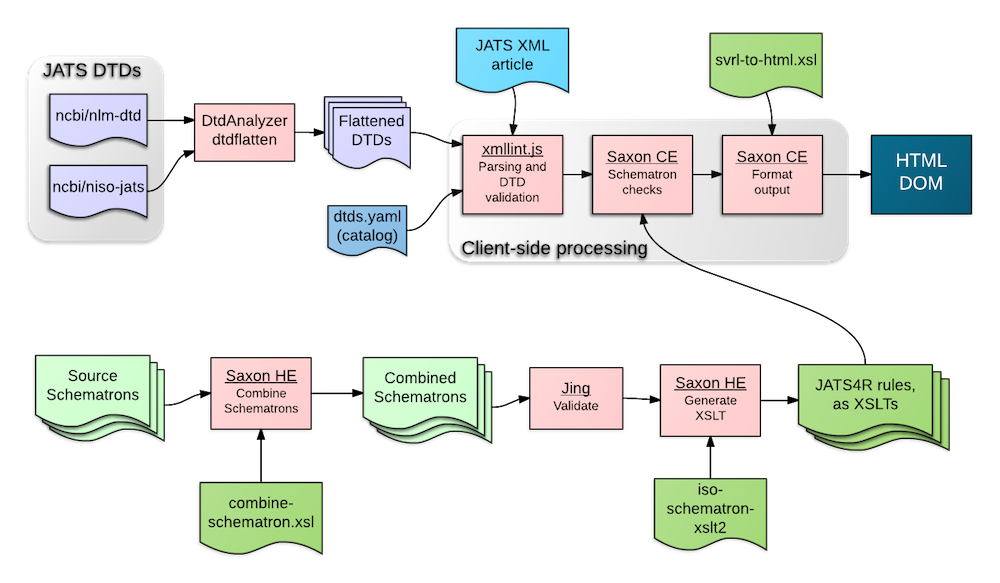
For information on this implementation of this tool, see the paper we submitted to Balisage 2015, "A client-side JATS4R validator using Saxon-CE". The following is the data-flow diagram from that paper, illustrating in a compact form what is happening under the hood.
Since it runs on the client, and we don't have access to all the features of
libxml, the first phase, in which the tool looks for <?xml-model?> processing
instructions and the doctype declaration, is done with a custom parser, that is
not very robust. Therefore, some things will be missed: for example, if a
processing instruction (PI) is "commented out", this validator will not notice the
comment delimiters, and will treat the PI as though it weren't.
This tool has a number of dependencies. Some are system tools, that
are present on many Unix systems, or that can be installed easily,
and others are fetched and installed by the
bin/setup.sh script.
You'll need to make sure that your system has the following.
- wget
- Java version 7 or later
- Python 3
- The Python pyyaml module
Polyfill for the Promise feature.
This was downloaded from the GitHub
jakearchibald/es6-promise repo,
specifically, this
version, and put into assets/es6-promise.min.js.
In setup.sh, this is copied into lib/es6-promise.min.js.
Polyfill for the EcmaScript 6 fetch feature.
From the GitHub github/fetch repo, this
version
was downloaded and put into the assets directory.
In setup.sh, this is copied to lib/fetch.js.
Open-source client-side XSLT 2.0 processor.
Can be downloaded from this page.
In setup.sh, this is downloaded and extracted to lib/Saxonce.
For now, this is saved in this repository in the assets directory.
This is generated from the code in the jats4r/xml.js
repository, which was forked from Alf Eaton's
hubgit/xml.js repo, which was in turn forked
from kripken/xml.js.
The setup.sh script copies this into lib.
The setup.sh script downloads these from the
NCBI/nlm-dtd and
NCBI/niso-jats repositories, and
extracts under the lib directory.
This tool is used by the flatten.py script, to flatten each of the various JATS DTDs.
In setup.sh, this is downloaded into the lib/DtdAnalyzer-0.5 directory.
The saxon9he.jar file is included with the DtdAnalyzer.
This is the schema that defines what is a valid Schematron file. This version is from 2005, and is included here as assets/isoSchematron.rng.
The setup.sh script copies this into lib.
This was originally downloaded from
here,
and was added to the assets directory of this repository.
The setup.sh script extracts this into lib/jing-20081028.
Downloaded from
here on 2015-04-02,
and included as assets/iso-schematron-xslt2.zip.
The setup.sh script extracts this into lib/iso-schematron-xslt2.
Downloaded from here on 2015-04-02, and included as assets/xml-commons-resolver-1.2.zip.
The setup.sh script extracts this into lib/xml-commons-resolver-1.2.
For syntax highlighting. This was downloaded from the Prism site with:
- Languages: only "markup"
For the select "sample articles" dropdown menu. See their home page.
Portions of this software were borrowed from the following sources: