Priority scheduling is a method of scheduling processes based on priority. In this method, the scheduler chooses the tasks to work as per the priority, which is different from other types of scheduling, for example, a simple round robin.
Priority scheduling involves priority assignment to every process, and processes with higher priorities are carried out first, whereas tasks with equal priorities are carried out on a first-come-first-served (FCFS) or round robin basis. An example of a general-priority-scheduling algorithm is the shortest-job-first (SJF) algorithm.
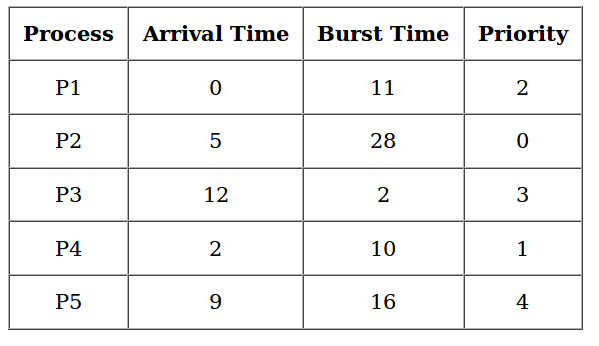
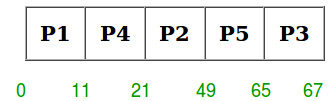
Priority scheduling is a non-preemptive algorithm and one of the most common scheduling algorithms in batch systems. Each process is assigned first arrival time (less arrival time process first) if two processes have same arrival time, then compare to priorities (highest process first). Also, if two processes have same priority then compare to process number (less process number first). This process is repeated while all process get executed.
- First input the processes with their arrival time, burst time and priority.
- Sort the processes, according to arrival time if two process arrival time is same then sort according process priority if two process priority are same then sort according to process number.
- Now simply apply FCFS algorithm.
process no-> 1 2 3 4 5
arrival time-> 0 1 3 2 4
burst time-> 3 6 1 2 4
priority-> 3 4 9 7 8
| Process_no | Start_time | Complete_time | Trun_Around_Time | Wating_Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | 3 | 9 | 8 | 2 |
| 4 | 9 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
| 3 | 11 | 12 | 9 | 8 |
| 5 | 12 | 16 | 12 | 8 |
Average Wating Time is : 5.0
Average Trun Around time is : 8.2