AMIDST Toolbox (http://www.amidsttoolbox.com)
v.0.7.2
The AMIDST Toolbox allows you to model your problem using a flexible probabilistic language based on graphical models. Then you fit your model with data using a Bayesian approach to handle modeling uncertainty.
AMIDST provides tailored parallel (powered by Java 8 Streams) and distributed (powered by Flink or Spark) implementations of Bayesian parameter learning for batch and streaming data. This processing is based on flexible and scalable message passing algorithms.
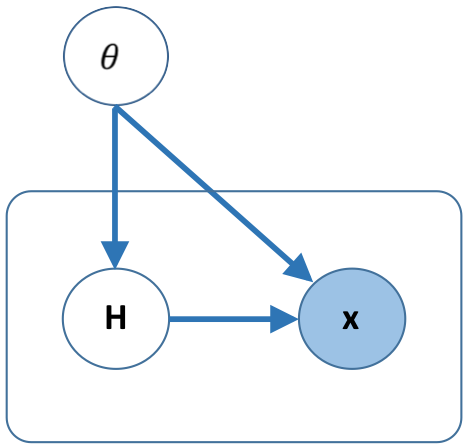
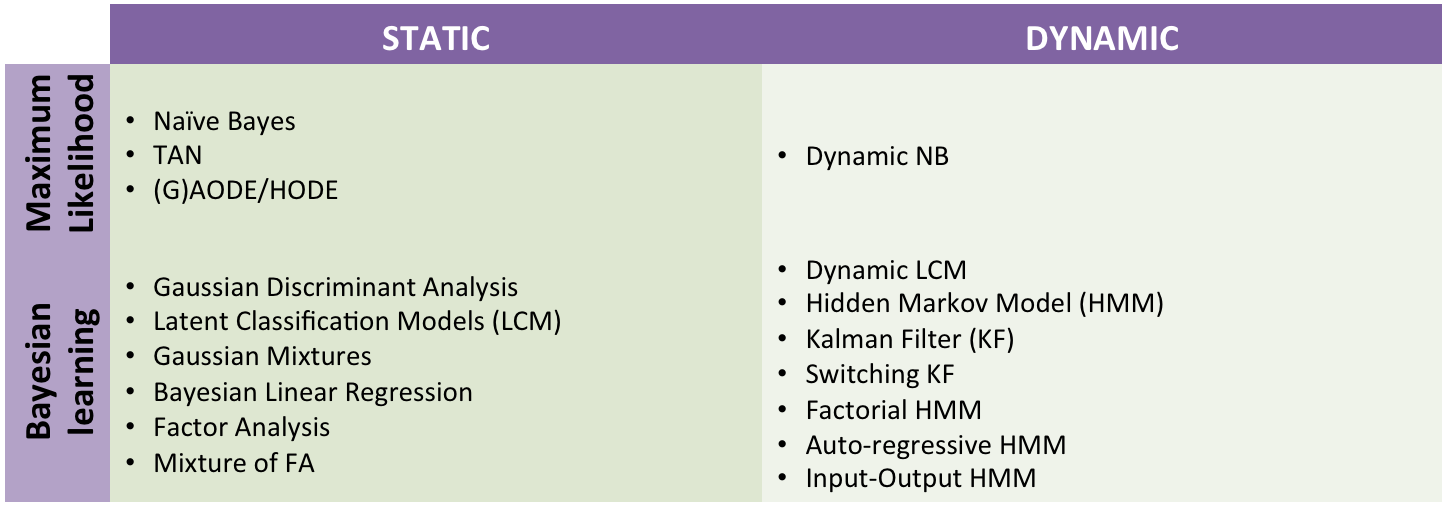
- Probabilistic Graphical Models: Specify your model using probabilistic graphical models with latent variables and temporal dependencies. AMIDST contains a large list of predefined latent variable models:
-
Scalable inference: Perform inference on your probabilistic models with powerful approximate and scalable algorithms.
-
Data Streams: Update your models when new data is available. This makes our toolbox appropriate for learning from (massive) data streams.
-
Large-scale Data: Use your defined models to process massive data sets in a distributed computer cluster using Apache Flink or (soon) Apache Spark.
-
Extensible: Code your models or algorithms within AMiDST and expand the toolbox functionalities. Flexible toolbox for researchers performing their experimentation in machine learning.
-
Interoperability: Leverage existing functionalities and algorithms by interfacing to other software tools such as Hugin, MOA, Weka, R, etc.
//Load the data
String filename = "./data.arff";
DataStream<DataInstance> data = DataStreamLoader.open(filename);
//Learn the model
Model model = new CustomGaussianMixture(data.getAttributes());
model.updateModel(data);
System.out.println(model.getModel());
// Save with .bn format
BayesianNetworkWriter.save(model.getModel(), "./example.bn"); //Load the data
String filename = "hdfs://dataDistributed.arff";
final ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataFlink<DataInstance> data = DataFlinkLoader.loadDataFromFolder(env, filename, false);
//Learn the model
Model model = new CustomGaussianMixture(data.getAttributes());
model.updateModel(data);
System.out.println(model.getModel());
// Save with .bn format
BayesianNetworkWriter.save(model.getModel(), "./example.bn");AMIDST Toolbox has been used to track concept drift and do risk prediction in credit operations, and as data is collected continuously and reported on a daily basis, this gives rise to a streaming data classification problem. This work has been performed in collaboration with one of our partners, the Spanish bank BCC. It is expected to be into production at the beginning of 2017.
AMIDST Toolbox has been used to prototype models for early recognition of traffic maneuver intentions. Similarly to the previous case, data is continuously collected by car on-board sensors giving rise to a large and quickly evolving data stream. This work has been performed in collaboration with one of our partners, DAIMLER.
-
Getting Started! explains how to install the AMIDST toolbox, how this toolbox makes use of Java 8 new functional style programming features, and why it is based on a module based architecture.
-
Toolbox Functionalities describes the main functionalities (i.e., data streams, BNs, DBNs, static and dynamic learning and inference engines, etc.) of the AMIDST toolbox.
- Bayesian networks: Code Examples includes a list of source code examples explaining how to use some functionalities of the AMIDST toolbox.
- Dynamic Bayesian networks: Code Examples includes some source code examples of functionalities related to Dynamic Bayesian networks.
- FlinkLink: Code Examples includes some source code examples of functionalities related to the module that integrates Apache Flink with AMIDST.
-
SparkLink: some source code examples of functionalities related to the module that integrates Apache Spark with AMIDST.
-
API JavaDoc of the AMIDST toolbox.
Scalability is a main concern for the AMIDST toolbox. Java 8 streams are used to provide parallel implementations of our learning algorithms. If more computation capacity is needed to process data, AMIDST users can also use more CPU cores. As an example, the following figure shows how the data processing capacity of our toolbox increases given the number of CPU cores when learning an a probabilistic model (including a class variable C, two latent variables (dashed nodes), multinomial (blue nodes) and Gaussian (green nodes) observable variables) using the AMIDST's learning engine. As can be seen, using our variational learning engine, AMIDST toolbox is able to process data in the order of gigabytes (GB) per hour depending on the number of available CPU cores with large and complex PGMs with latent variables. Note that, these experiments were carried out on a Ubuntu Linux server with a x86_64 architecture and 32 cores. The size of the processed data set was measured according to the Weka's ARFF format.
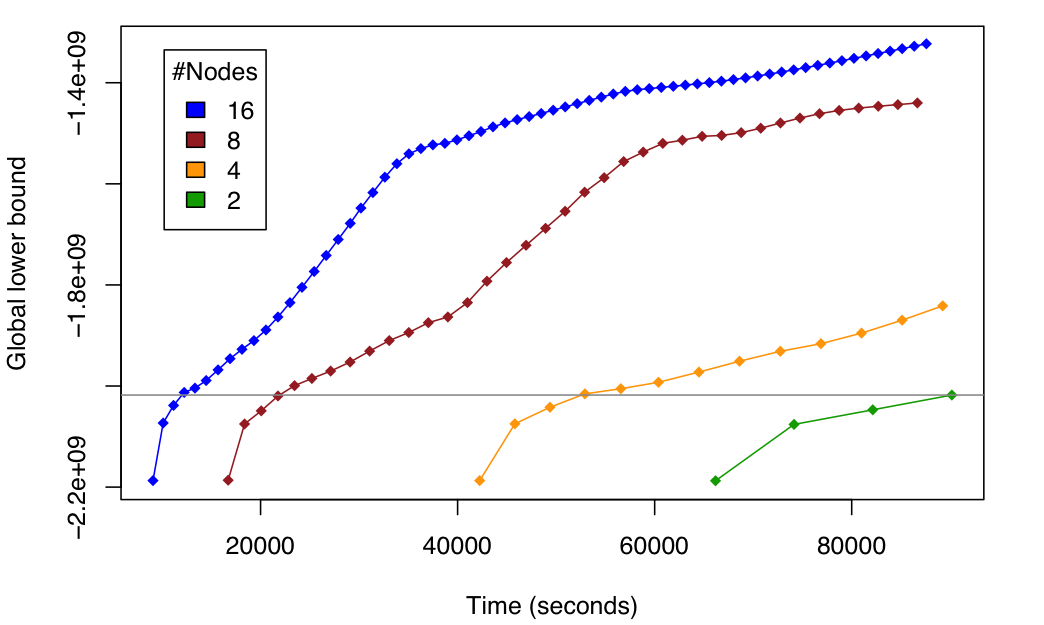
If your data is really big and can not be stored in a single laptop, you can also learn your probabilistic model on it by using the AMIDST distributed learning engine based on a novel and state-of-the-art distributed message passing scheme implemented on top of Apache Flink. As detailed in this paper, we were able to perform inference in a billion node (i.e. 10^9) probabilistic model in an Amazon's cluster with 2, 4, 8 and 16 nodes, each node containing 8 processing units. The following figure shows the scalability of our approach under these settings.
This module integrates the functionality of the AMIDST toolbox with the Apache Spark platform.
The following functionality is already implemented on the sparklink module:
- Data Sources integration: Reading and writing data from SparkSQL on AMIDST
- Distributed Sampling of Bayesian Networks
- Parametric learning from distributed data (Maximum Likelihood)
More information here
The following repository https://github.com/amidst/toolbox-usecases contains the source code and details about the publications and use-cases using the AMIDST toolbox.
The AMIDST toolbox is an expanding project and upcoming developments include for instance the ongoing integration of the toolbox in Spark to enlarge its scalability capacities. In addition, a new link to R is still in progress which will expand the AMIDST user-base.
AMIDST is an open source toolbox and the end-users are encouraged to upload their contributions (which may include basic contributions, major extensions, and/or use-cases) following the indications given in this link.
# Acknowledgements and License This software was performed as part of the AMIDST project. AMIDST has received funding from the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration under grant agreement no 619209.
This software is distributed under Apache License Version 2.0