A simple Arduino button library modelled as a state machine
This library is intended for simple projects which need a quick and easy way of being controlled by push-buttons. It doesn't use any callbacks or interrupts.
Button constructor receives one mandatory and three optional arguments.
Button (pin [, activeState [, firstHoldTime [, subsqHoldTime]]]);Examples:
Button button1(5);
Button button2(6, LOW);
Button button3(7, HIGH, 500, 300);- pin - Arduino pin to which the button is connected
- activeState - HIGH for for active-high, LOW for active-low (default: HIGH)
- firstHoldTime - time required to trigger the first HOLD event (default: 800 ms)
- subsqHoldTime - time required to trigger all subsequent HOLD events after the first one (default: 200 ms)
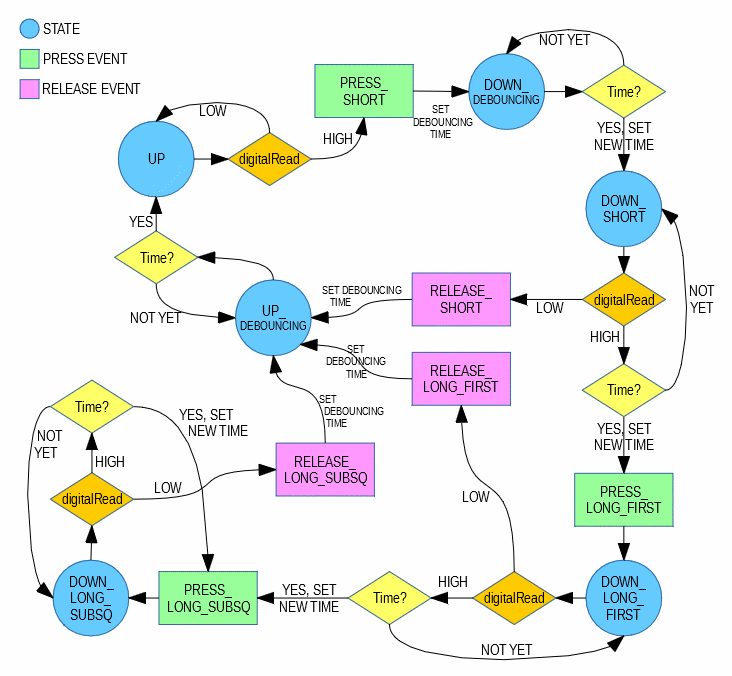
Apart from the button constructor, the library provides only one function which serves two roles: to continuously check and store the button state, and to return the current state of the button to the caller function.
In order for the library to work properly, this function needs to be called continuously, so you shouldn't use any delays or other functions which will hang the main program for a long time. No interrupts are used in this library, and if the function is not called often enough and the user manages to push and release a button in-between two function calls, those actions will not be registered.
byte Button.state();Example:
byte s = button1.state();When the state() function is called and an event has occured since the previous call, it returns one of the following values:
- PRESS_SHORT - The button has just been pushed down.
- PRESS_LONG_FIRST - The first hold event has just been triggered.
- PRESS_LONG_SUBSQ - A non-first hold event has just been triggered.
- RELEASE_SHORT - The button has just been released, and was not held long enough for any hold event to occur.
- RELEASE_LONG_FIRST - The button has just been released after one hold event has occured.
- RELEASE_LONG_SUBSQ - The button has just been released after two or more hold events have occured.
In all other cases, when there is no event to report, it returns one of the following values:
- UP - The button is currently up.
- DOWN_SHORT - The button has been pushed and is held down.
- DOWN_LONG_FIRST - The button is being held and one hold event has occured.
- DOWN_LONG_SUBSQ - The button is being held and two or more hold events have occured.
Three macros are provided with the library which evaluate a button state from a byte:
- ISDOWN(byte) - Evaluates true for any state in which the button must be down
- PRESSEVENT(byte) - Evaluates true for any PRESS event
- RELEASEEVENT(byte) - Evaluates true for any RELEASE event
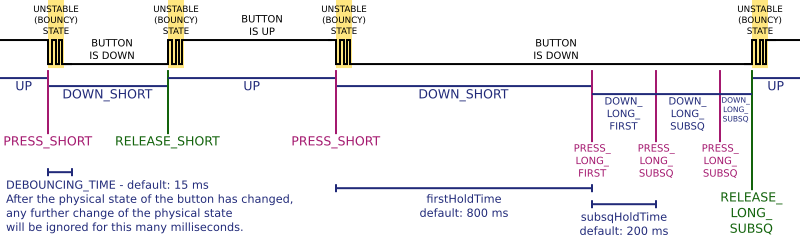
In the following example the user makes one short press and one long press (which is held enough to trigger three long-press events). Black line represents the physical state of the button. Logical states and press-release events are marked below.
The following code increments the minutes variable by one, waits for a while (firstHoldTime), and then keeps increasing by one in shorter intervals (subsqHoldTime). This is a behavior similar to real-world digital clocks when their time is being set.
Button btn(3);
int minutes = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(3, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
byte s = btn.state();
if (PRESSEVENT(s))
{
minutes++;
Serial.println(minutes);
}
}The following code allows the user to perform two different actions by either short-pressing or long-pressing the button (without triggering the short-press action if they only intended to perform the long-press action).
Button btn(3);
void shortPressAction() { Serial.println("Short-press"); }
void longPressAction() { Serial.println("Long-press"); }
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(3, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
byte s = btn.state();
switch (s) {
case RELEASE_SHORT: shortPressAction(); break;
case PRESS_LONG_FIRST: longPressAction(); break;
}
}Debouncing time can be changed by changing the DEBOUNCING_TIME macro in the library source code. By default it is 15 ms.
Note: DEBOUNCING_UP and DEBOUNCING_DOWN are internal states, abstracted inside the class. When the button is in the DEBOUNCING_UP state, UP is returned, and when it's in the DEBOUNCING_DOWN state, DOWN_SHORT is returned.