A Laravel package that simplifies running code and commands when installing or updating your web app.
The package has been developed and tested to work with the following minimum requirements:
- PHP 7.2
- Laravel 6
You can install the package via Composer:
composer require ashallendesign/laravel-executorTo create a new Executor, you can use the following command:
php artisan make:executor YourExecutorNameHereThe above command would create an Executor named YourExecutorNameHere that can be found in the app/Executor
folder.
Generally, Executors are expected to be run within a console. So, when creating a new Executor, if you intend for it to be run in the console, you can use the following command:
php artisan make:executor YourExecutorNameHere -cThe command above will create the exact same boilerplate for your new Executor as the command in Creating a New Executor.
However, it will create a new command in your app/Commands folder named RunYourExecutorNameHereExecutor.
This means that you won't need a new command manually to run your executor.
Learn more in Running via the Console to find out how to run the Executor inside the commands.
To run an Artisan command via your Executor class, you can add the runArtisan() method to your Executor's run()
method. For example, the code below shows how you could set the Executor to run the built-in Laravel php artisan cache:clear
command:
<?php
namespace App\Executor;
use AshAllenDesign\LaravelExecutor\Classes\Executor;
class AppUpdate extends Executor
{
public function run(): Executor
{
return $this->runArtisan('cache:clear');
}
}In some cases, you may want to run a command that requires your input. For example, you might have a command that
creates a new user in the database and need you to input some details. In this case, you can pass true as the second
parameter to the ->runArtisan() method to specify that it is an interactive command.
To determine the process timeout for the command, you can also pass a time in seconds as the third parameter to the
->runArtisan() method.
To run a command (that can't be run with Artisan) via your Executor class, you can add the runExternal() method to your Executor's run()
method. For example, the code below shows how you could set the Executor to run the built-in Composer composer install
command:
<?php
namespace App\Executor;
use AshAllenDesign\LaravelExecutor\Classes\Executor;
class AppUpdate extends Executor
{
public function run(): Executor
{
return $this->runExternal('composer install');
}
}In some cases, you may want to run a command that requires your input. For example, you might have a command that
creates a new user in the database and need you to input some details. In this case, you can pass true as the second
parameter to the ->runExternal() method to specify that it is an interactive command.
To determine the process timeout for the command, you can also pass a time in seconds as the third parameter to the
->runExternal() method.
Sometimes you might want to run some code that doesn't necessarily fit into an existing command. In this case, you can add a closure to your Executor instead. The example below shows how to pass a simple closure to your Executor class:
<?php
namespace App\Executor;
use AshAllenDesign\LaravelExecutor\Classes\Executor;
class AppUpdate extends Executor
{
public function run(): Executor
{
return $this->runClosure(function () {
return 'I am running inside a closure.';
});
}
}If you are running your Executor via the console, you may want to display desktop notifications between some steps. To display
a desktop notification you can use either ->simpleDesktopNotification() or ->desktopNotification().
By using ->simpleDesktopNotification() you can pass just a title and body that should be displayed. The example below
shows how to create a simple desktop notification:
<?php
namespace App\Executor;
use AshAllenDesign\LaravelExecutor\Classes\Executor;
class AppUpdate extends Executor
{
public function run(): Executor
{
return $this->simpleDesktopNotification('Notification title', 'Notification body');
}
}If you want to customise your notification, you can use ->desktopNotification() and pass a Joli\JoliNotif\Notification
object as the parameter. For more information on building these types of notifications, check out the Joli\JoliNotif
documentation here.
You can also add the ->completeNotification() to your Executor so that a desktop notification can be displayed
once all the code inside the class has been run.
If you're using your Executor for updating your application on a live server, you might want to ping a URL when it's finished.
This could be useful for sending a webhook to alert you that the scripts have run successfully. To ping a URL, you can simply
use the ->ping() method.
The example below shows how to ping a website:
<?php
namespace App\Executor;
use AshAllenDesign\LaravelExecutor\Classes\Executor;
class AppUpdate extends Executor
{
public function run(): Executor
{
return $this->ping('https://ashallendesign.co.uk/executor-webhook-route');
}
}If you want to send headers in your ping(), you can pass them as a second parameter. This can be useful for if you
want to add a signature to your webhook requests to assert that they've been sent from an authorised sender.
The example below shows how to ping a website with headers:
<?php
namespace App\Executor;
use AshAllenDesign\LaravelExecutor\Classes\Executor;
class AppUpdate extends Executor
{
public function run(): Executor
{
return $this->ping('https://ashallendesign.co.uk/executor-webhook-route', [
'X-Webhook-Signature' => 'secret-signature-to-go-here'
]);
}
}As mentioned above, Executors are mainly intended for being run from within the console. This makes them ideal for adding to deploy scripts; such as the ones that can be found one Laravel Forge and Runcloud.
If you created a command at the same time as the Executor class by using the command above found in Creating an Executor with a Command,
your command will already have been given a signature. The signature is created by converting the Executor's classname into kebab case.
For example, an Executor with the name AppInstall will be given the command signature of executor:app-install.
The example below shows how a command (that has been unaltered) can be run the AppInstall Executor:
php artisan executor:app-installNote: To register the command with your Laravel application, you will want to add the command class name to the $commands array in your
app/Console/Kernel.php file.
There may be times when you want to run an Executor class outside of the command line. To do this, you simply need to call
the ->run() method on your class. The example below shows how to manually run an Executor named AppInstall:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Executor\AppInstall;
class Controller
{
public function index()
{
(new AppInstall())->run();
}
}The example below shows how to create an Executor class that can be run after pulling a new branch of project down from a remote repository:
<?php
namespace App\Executor;
use AshAllenDesign\LaravelExecutor\Classes\Executor;
class AppUpdate extends Executor
{
public function run(): Executor
{
return $this->simpleDesktopNotification('Starting Executor', 'Starting the AppUpdate Executor.')
->runExternal('composer install')
->runArtisan('migrate')
->runArtisan('cache:clear')
->completeNotification();
}
}Assuming that the above Executor class is still using the default command signature, each time the branch is pulled down,
the following command could be run: php artisan executor:app-update.
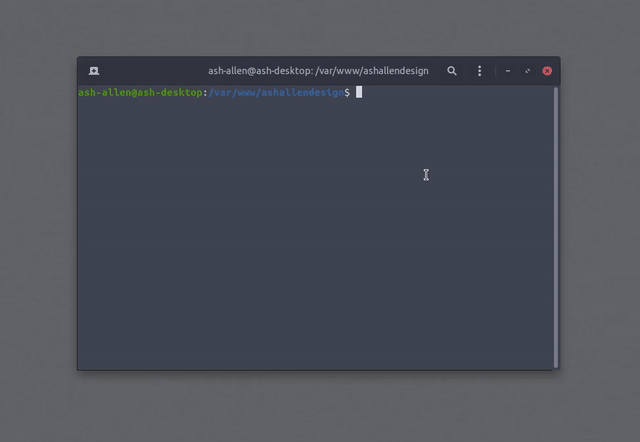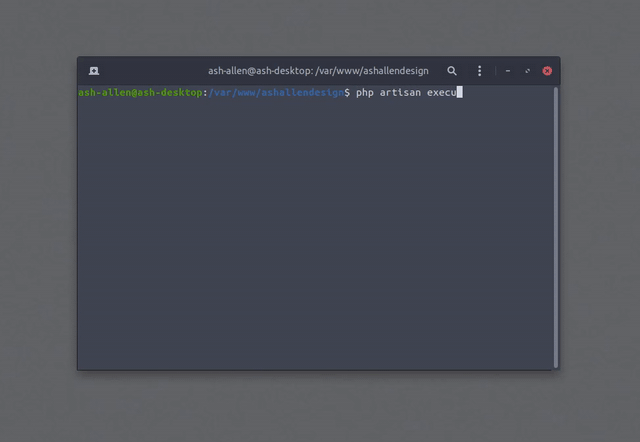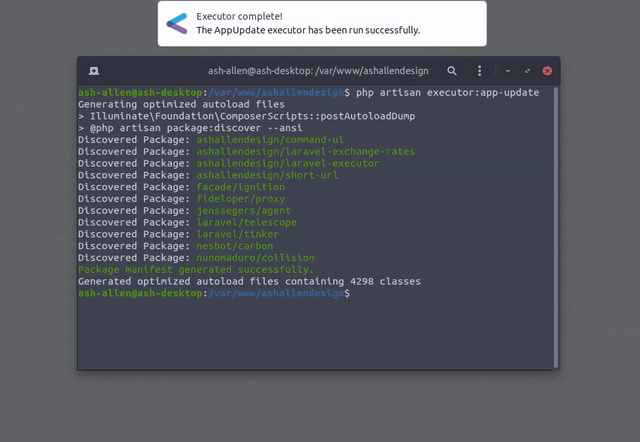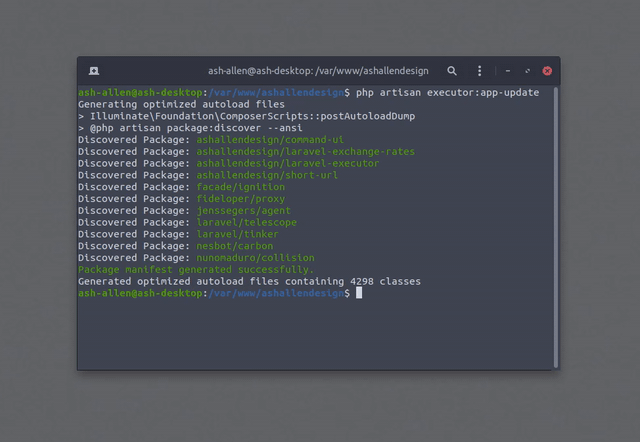
The image below shows how a simple Executor command could be run. It's only executing composer du -o but demonstrates
how Laravel Executor can provide feedback with real-time output and desktop notifications.
If you find any security related issues, please contact me directly at mail@ashallendesign.co.uk to report it.
If you wish to make any changes or improvements to the package, feel free to make a pull request.
Note: A contribution guide will be added soon.
Check the CHANGELOG to get more information about the latest changes.
The MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.