| OS: | Windows | ||||||||||||||||
| Type: | A Windows PowerShell script | ||||||||||||||||
| Language: | Windows PowerShell | ||||||||||||||||
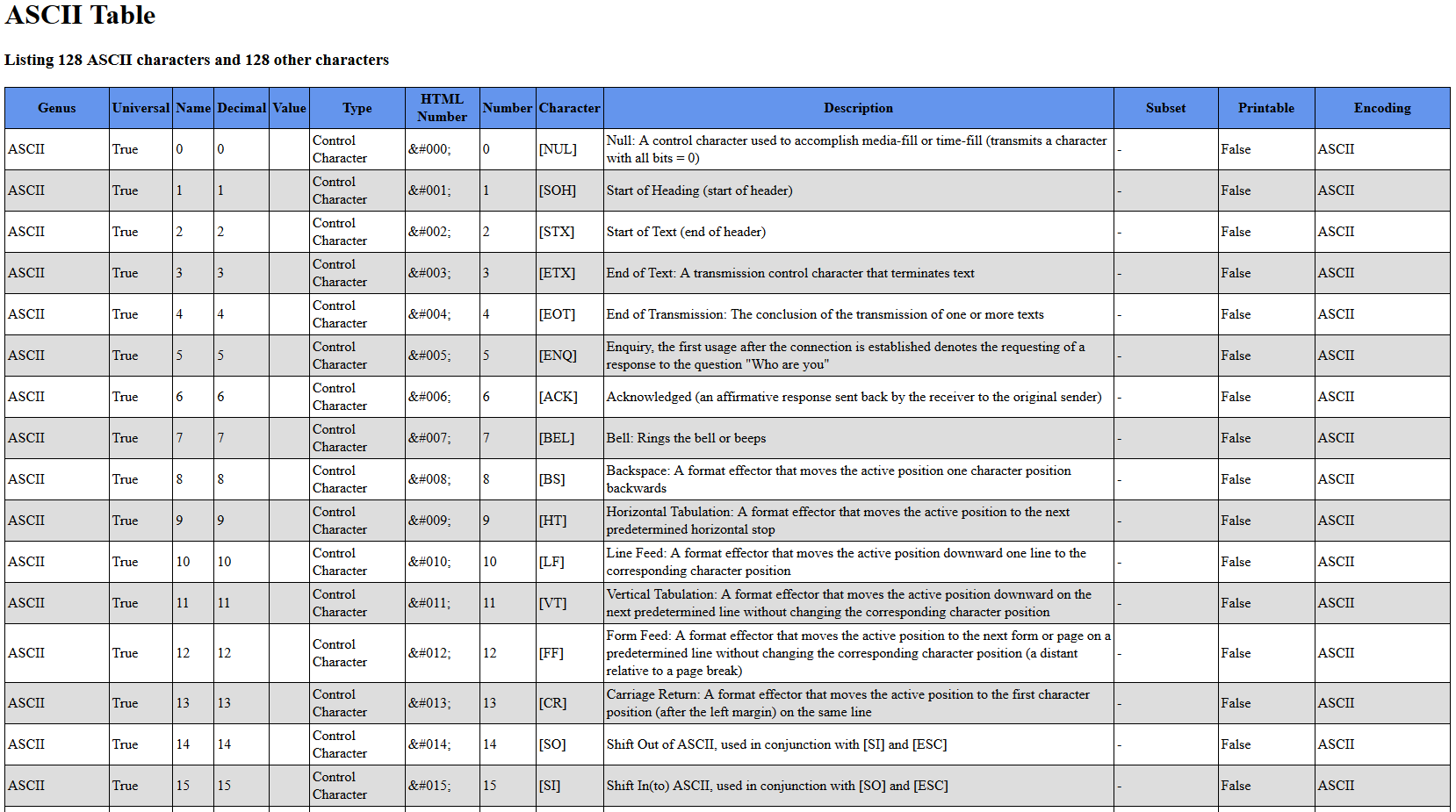
| Description: | ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII).
ASCII was originally developed during the sixties for use with teleprinters and other teletypewriters (TTY) to code the messages, which were sent over various communications channels. The earliest teleprinters emulated the behavior of actual typewriters with rotating disks and other mechanical parts. The character set in the ASCII code is fairly limited; the ASCII code consists of 128 characters, which include 33 non-printing control characters (that affect how the text is being processed, but are nowadays rarely used for their original purposes) and 95 printable characters. Unfortunately there isn't any unified version of "extended ASCII" characters, only different encoding systems, such as ISO 8859-1 (also called as ISO Latin-1), which may or may not build upon the ASCII characters. Get-AsciiTable generates a series of numbers ranging from 0 to 255, and uses those numbers as a basis for the character retrieval system built in the PowerShell by using the " | ||||||||||||||||
| Homepage: | https://github.com/auberginehill/get-ascii-table
Short URL: http://tinyurl.com/hdjlqdu |
||||||||||||||||
| Version: | 1.1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Sources: |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Downloads: | For instance Get-AsciiTable.ps1. Or everything as a .zip-file. |
| 📐 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ➡️ |
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| 📖 | To open this code in Windows PowerShell, for instance: | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Find a bug? Have a feature request? Here is how you can contribute to this project:
| Bugs: | Submit bugs and help us verify fixes. | |
| Feature Requests: | Feature request can be submitted by creating an Issue. | |
| Edit Source Files: | Submit pull requests for bug fixes and features and discuss existing proposals. |