Adversarial Image Perturbation for Privacy Protection -- A Game Theory Perspective, ICCV'17
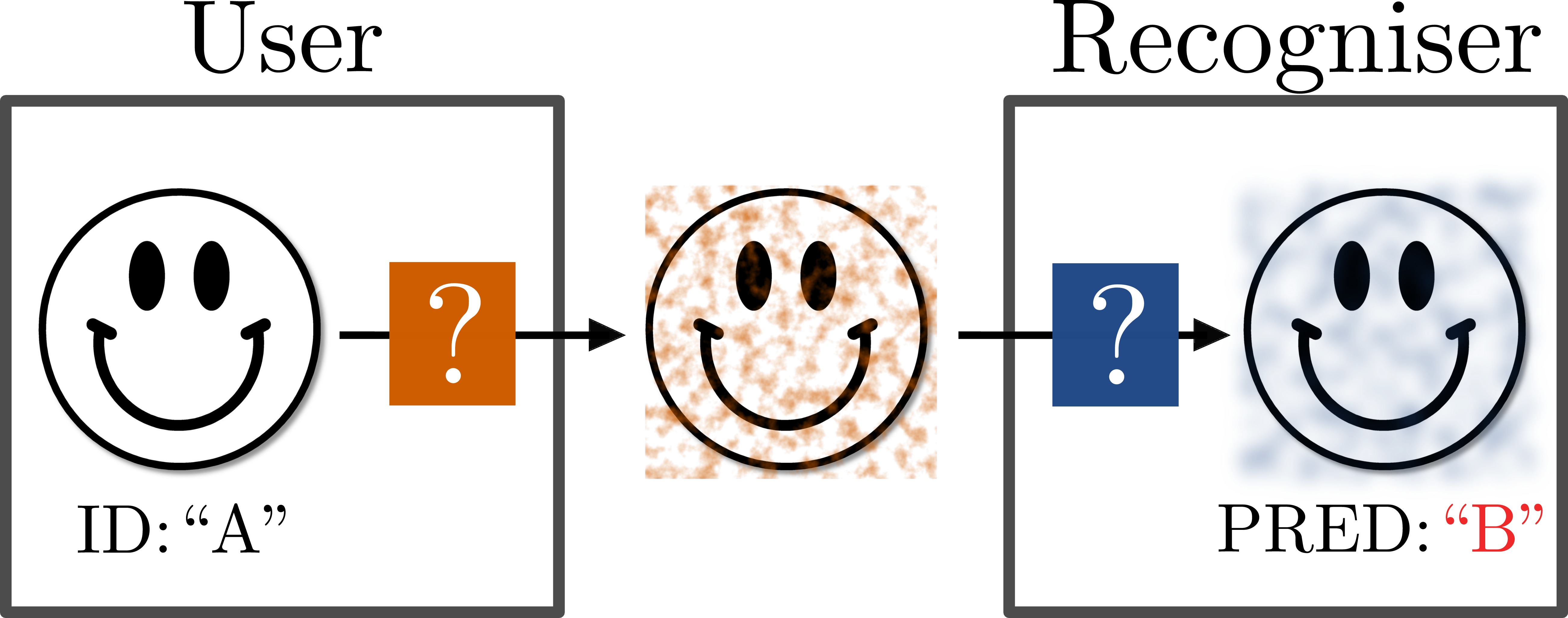
Users like sharing personal photos with others through social media. At the same time, they might want to make automatic identification in such photos difficult or even impossible. Classic obfuscation methods such as blurring are not only unpleasant but also not as effective as one would expect. Recent studies on adversarial image perturbations (AIP) suggest that it is possible to confuse recognition systems effectively without unpleasant artifacts. However, in the presence of counter measures against AIPs, it is unclear how effective AIP would be in particular when the choice of counter measure is unknown. Game theory provides tools for studying the interaction between agents with uncertainties in the strategies. We introduce a general game theoretical framework for the user-recogniser dynamics, and present a case study that involves current state of the art AIP and person recognition techniques. We derive the optimal strategy for the user that assures an upper bound on the recognition rate independent of the recogniser's counter measure.
Clone this repository recursively.
$ git clone https://github.com/coallaoh/AIP.git --recursive$ cd caffeFollow caffe installation to configure Makefile.config, and run
$ make -j50 && make pycaffeInstall Liblinear for crawling pretrained svm models.
Install Python requirements.
$ pip install numpy scipy && pip install -r ./pip-requirementsInstall OpenCV for python, following the instructions in: http://opencv.org.
Download the pretrained person recognition models (convnet + svm), head crops, and PIPA annotations.
$ ./downloads.shThe script for computing different variants of adversarial perturbations in the paper and evaluating them against recogniser's defense measures on the PIPA vallidation set is
$ ./src/aip/test.pyBefore running it, please change the following variables according to your local machine.
liblinearpythonloc: Liblinear Python library.
The script can then run on the command line. After computing the game table for every strategy pair (e.g. table 4 in the paper), the equilibrium (optimal) strategies and the value of the game is computed via Nashpy (https://github.com/drvinceknight/Nashpy). Run the script
$ ./src/game/eq.pyto obtain the game theoretical results in the paper.
For any problem with implementation or bug, please contact Seong Joon Oh (coallaoh at gmail).
@inproceedings{joon17iccv,
title = {Adversarial Image Perturbation for Privacy Protection -- A Game Theory Perspective},
author = {Oh, Seong Joon and Fritz, Mario and Schiele, Bernt},
year = {2017},
booktitle = {International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
note = {to appear},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}