Node.js module to read values from the INA226 bi-directional current and power monitor.
For more information about the INA226 please consult the data sheet from Texas Instruments.
- Read shunt and bus voltages.
- Calculate current and power.
- Read the value from a register.
- Write a value to a register.
Make sure you are using Node.js v8.x or higher.
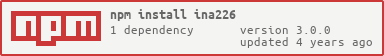
npm install ina226
This module is written in TypeScript and typings are included.
Note that you need to construct the i2c-bus object and pass it in to the INA226 class.
The example blow can be found in the examples directory of this package together with a TypeScript example.
// Require the ina226 module
var INA226 = require('ina226').INA226;
// Require the i2c-bus module and open the bus
var i2cBus = require('i2c-bus').openSync(1);
// Define the address of the INA226 and the shunt resistance value
var addr = 0x40;
var rShunt = 0.1;
// Init a new INA226
var ina = new INA226(i2cBus, addr, rShunt);
// Write to the Configuration Register
// 0x4427 means 16 averages, 1.1ms conversion time, shunt and bus continuous
ina.writeRegister(CONFIGURATION_REGISTER, 0x4427)
.then(function(){
console.log('Configuration written');
});
// Read the actual bus voltage
ina.readBusVoltage()
.then(function(busVoltage){
console.log('Bus Voltage: ' + busVoltage.toFixed(2) + 'V');
});
// Read the actual shunt voltage
ina.readShuntVoltage()
.then(function(shuntVoltage){
console.log('Shunt Voltage: ' + shuntVoltage.toFixed(5) + 'V');
});
// Read the actual shunt voltage and calculate the current
ina.readShuntVoltage()
.then(function(){
var current = ina.calcCurrent();
console.log('Current: ' + current.toFixed(2) + 'A');
})
// Then read the actual bus voltage and calculate the power
.then(ina.readBusVoltage.bind(ina))
.then(function(){
var power = ina.calcPower();
console.log('Power: ' + power.toFixed(2) + 'W');
});constructor(i2cBus:I2cBus, address:number, rShunt:number=0.1)Constructor for a new INA226 instance.
i2cBus- Instance of an opened i2c-bus.address- The address of the INA226 IC.rShunt- The shunt resistance value. Defaults to 0.1 Ohm.
Note that you need to construct the i2c-bus object and pass it in to the module.
writeRegister(register:number, value:number):Promise<{}>Writes a value to a specific register. Returns a Promise which will be resolves if the value is written, or rejected in case of an error.
register- The register address.value- The value. Should be 16bit integer.
readRegister(register:number):Promise<number>Reads a value from a specific register. Returns a Promise which will be resolved with the read value, or rejected in case of an error.
register- The register address.
readBusVoltage():Promise<number>Reads the actual bus voltage. Returns a Promise which will be resolved with the bus voltage, or rejected in case of an error.
readShuntVoltage():Promise<number>Reads the actual shunt voltage. Returns a Promise which will be resolved with the shunt voltage, or rejected in case of an error.
calcCurrent(shuntVoltage?:number):numberCalculates the current in Ampere based on the shunt voltage an the shunt resistance value.
shuntVoltage- Optional. The shunt voltage which is used for the calculation. Defaults to the last read shunt voltage.
calcPower(busVoltage?:number, shuntVoltage?:number):numberCalculates the power in Watt based on the bus voltage, the shunt voltage and the shunt resistance value.
busVoltage- Optional. The bus voltage which is used for the calculation. Defaults to the last read bus voltage.shuntVoltage- Optional. The shunt voltage which is used for the calculation. Defaults to the last read shunt voltage.
The register addresses are exported as constants.
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| CONFIGURATION_REGISTER | 0x00 |
| SHUNT_VOLTAGE_REGISTER | 0x01 |
| BUS_VOLTAGE_REGISTER | 0x02 |
| POWER_REGISTER | 0x03 |
| CURRENT_REGISTER | 0x04 |
| CALIBRATION_REGISTER | 0x05 |
| MASK_ENABLE_REGISTER | 0x06 |
| ALERT_LIMIT_REGISTER | 0x07 |
| MANUFACTOR_ID_REGISTER | 0xFE |
| DIE_ID_REGISTER | 0xFF |
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Copyright (c) 2017-2021 Peter Müller peter@crycode.de https://crycode.de/