A cross-platform header only C++14 library for interactive command line interfaces (Cisco style)
- Header only
- Cross-platform (linux and windows)
- Menus and submenus
- Remote sessions (telnet)
- Persistent history (navigation with arrow keys)
- Autocompletion (with TAB key)
- Async interface
- Colors
The library has no dependencies if you don't need remote sessions.
The library depends on asio (either the standalone version or the boost version >= 1.66) only to provide telnet server (i.e., remote sessions).
The library is header-only: it consists entirely of header files containing templates and inline functions, and requires no separately-compiled library binaries or special treatment when linking.
Extract the archive wherever you want.
Now you must only remember to specify the cli (and optionally asio or boost) paths when compiling your source code.
If you fancy it, a Cmake script is provided. To install you can use:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
sudo make install
or, if you want to specify the installation path:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX:PATH=<cli_install_location>
make install
Alternatively, you can use CMake's FetchContent module to include CLI library in your project directly.
Add something like this in your CMakeLists.txt file:
include(FetchContent)
FetchContent_Declare(
cli
GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/daniele77/cli.git
GIT_TAG v2.1.0
)
FetchContent_MakeAvailable(cli)
add_executable(main-project)
target_link_libraries(main-project PRIVATE cli::cli)
You can find some examples in the directory "examples". Each .cpp file corresponds to an executable. Each example can be compiled by including cli (and optionally asio/boost header files) and linking pthread on linux (and optionally boost system).
To compile the examples using cmake, use:
mkdir build && cd build
# compile only the examples that do not require boost/asio libraries
cmake .. -DCLI_BuildExamples=ON
# compile the examples by using boost asio libraries
cmake .. -DCLI_BuildExamples=ON -DCLI_UseBoostAsio=ON
# or: cmake .. -DCLI_BuildExamples=ON -DCLI_UseBoostAsio=ON -DBOOST_ROOT=<boost_path>
# compile the examples by using standalone asio library
cmake .. -DCLI_BuildExamples=ON -DCLI_UseStandaloneAsio=ON
# or: cmake .. -DCLI_BuildExamples=ON -DCLI_UseStandaloneAsio=ON -DASIO_INCLUDEDIR=<asio_path>
cmake --build .
In the same directory you can also find:
- GNU make files (Makefile.noasio, Makefile.boostasio, Makefile.standaloneasio)
- Windows nmake files (makefile.noasio.win, makefile.boostasio.win, makefile.standaloneasio.win)
- a Visual Studio solution
If needed, you can specify asio library path in the following ways:
for boost:
make CXXFLAGS="-isystem <boost_include>" LDFLAGS="-L<boost_lib>"
example:
make CXXFLAGS="-isystem /opt/boost_1_66_0/install/x86/include" LDFLAGS="-L/opt/boost_1_66_0/install/x86/lib"
for standalone asio:
make CXXFLAGS="-isystem <asio_include>"
example:
make CXXFLAGS="-isystem /opt/asio-1.18.0/include"
(if you want to use clang instead of gcc, you can set the variable CXX=clang++)
Optionally set the environment variable ASIO or BOOST to provide the library path.
Then, from a visual studio console, start nmake passing one of the makefile.*.win files.
E.g., from a visual studio console, use one of the following commands:
# only compile examples that do not require asio
nmake /f makefile.noasio.win
# compile examples using boost asio
set BOOST=<path of boost libraries>
nmake /f makefile.boostasio.win
# compile examples using standalone asio
set ASIO=<path of asio library>
nmake /f makefile.standaloneasio.win
Set the environment variables BOOST and/or ASIO. Then, open the file
cli/examples/examples.sln
If you have doxygen installed on your system, you can get the html documentation of the library in this way:
cd doc/doxy
doxygen Doxyfile
At the start of your application, the CLI presents a prompt with the
name you provided in the Cli constructor.
This indicates you're in the root menu.
- Enter a submenu: Type the submenu name to enter it. The prompt will change to reflect the current submenu.
- Go back to parent menu: Type the name of the parent menu or
..to return. - Navigate history: Use up and down arrow keys to navigate through previously entered commands.
- Exit: Type
exitto terminate the CLI application.
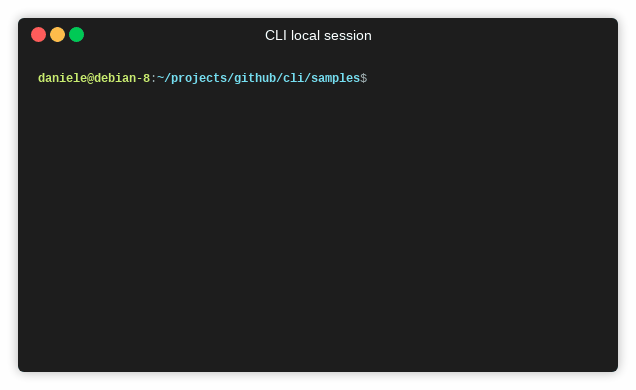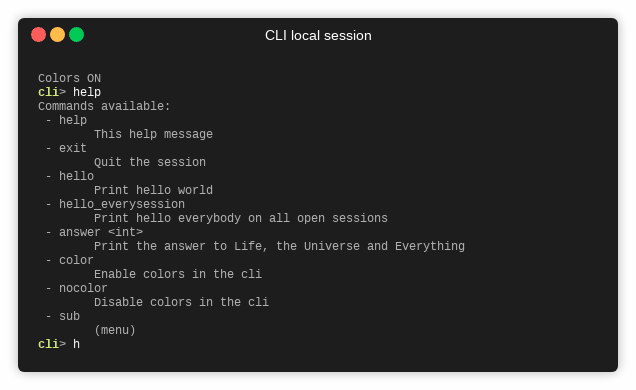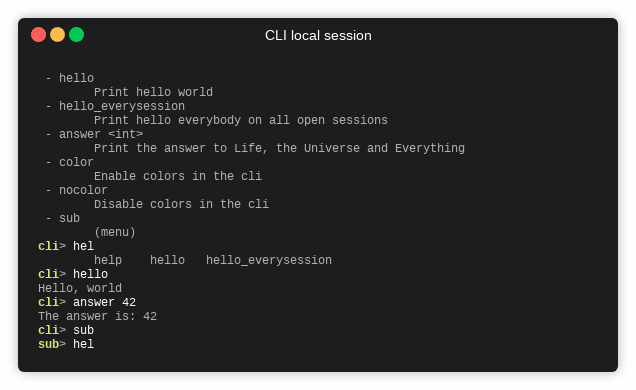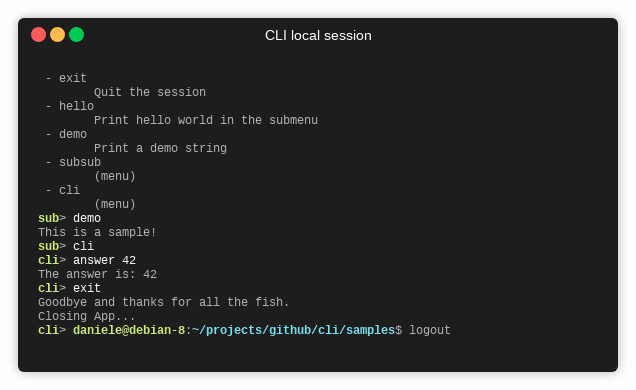
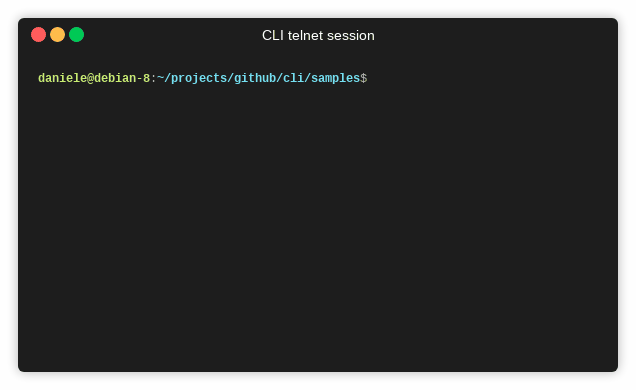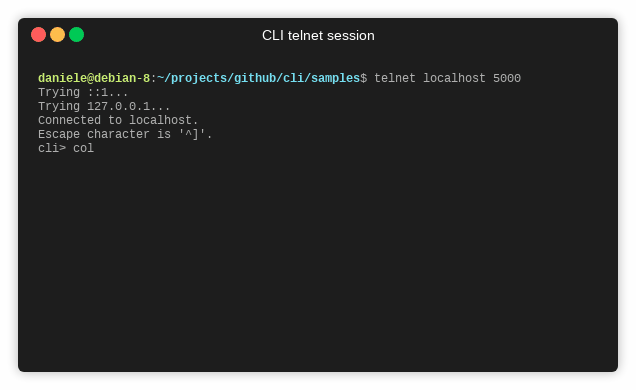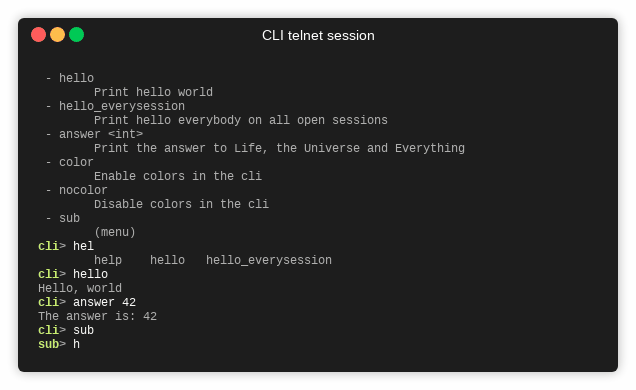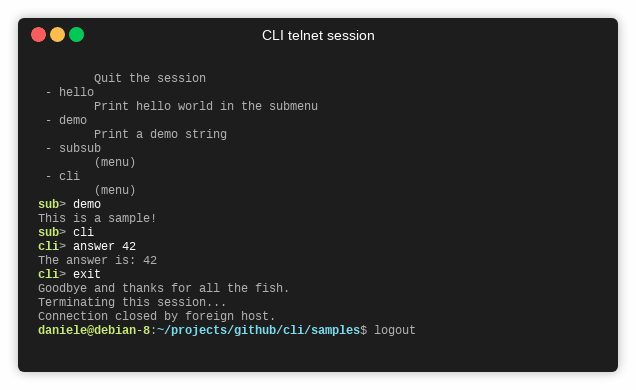
help: Prints a list of available commands with descriptions.history: Displays the list of previously entered commands.exit: Terminates the CLI application.- Command execution:
- Current menu: Enter the name of a command available in the current menu to execute it.
- Submenu (full path): Specify the complete path (separated by spaces) to a command within a submenu to execute it.
- History execution: Use
!followed by the identifier of a history item to execute that command again.
Use the Tab key to get suggestions for completing command or menu names as you type.
Press Ctrl-L to clear the screen at any time.
The CLI interpreter can handle sentences using single quotes (') and double quotes (").
Any character (including spaces) enclosed within quotes is considered a single parameter for a command.
You can use quotes within parameters by escaping them with a backslash (\).
Examples:
cli> echo "this is a single parameter"
this is a single parameter
cli> echo 'this too is a single parameter'
this too is a single parameter
cli> echo "you can use 'single quotes' inside double quoted parameters"
you can use 'single quotes' inside double quoted parameters
cli> echo 'you can use "double quotes" inside single quoted parameters'
you can use "double quotes" inside single quoted parameters
cli> echo "you can escape \"quotes\" inside a parameter"
you can escape "quotes" inside a parameter
cli> echo 'you can escape \'single quotes\' inside a parameter'
you can escape 'single quotes' inside a parameter
cli> echo "you can also show backslash \\ ... "
you can also show backslash \ ...
cli is an asynchronous library, and the handlers of commands are executed
by a scheduler, in a thread provided by the user (possibly the main thread),
this allows you to develop a single thread application
without need to worry about synchronization.
So, your application must have a scheduler and pass it to CliLocalTerminalSession.
The library provides three schedulers:
LoopSchedulerBoostAsioSchedulerStandaloneAsioScheduler
LoopScheduler is the simplest: it does not depend on other libraries
and should be your first choice if you don't need remote sessions.
BoostAsioScheduler and StandaloneAsioScheduler are wrappers around
asio io_context objects.
You should use one of them if you need a BoostAsioCliTelnetServer or a StandaloneAsioCliTelnetServer
because they internally use boost::asio and asio.
You should use one of them also if your application uses asio in some way.
After setting up your application, you must call Scheduler::Run()
to enter the scheduler loop. Each command handler of the library
will execute in the thread that called Scheduler::Run().
You can exit the scheduler loop by calling Scheduler::Stop()
(e.g., as an action associated to the "exit" command).
You can submit work to be executed by the scheduler invoking the method
Scheduler::Post(const std::function<void()>& f).
Schedulers are thread safe, so that you can post function object
from any thread, to be executed in the scheduler thread.
This is an example of use of LoopScheduler:
...
LoopScheduler scheduler;
CliLocalTerminalSession localSession(cli, scheduler);
...
// in another thread you can do:
scheduler.Post([](){ cout << "This will be executed in the scheduler thread\n"; });
...
// start the scheduler main loop
// it will exit from this method only when scheduler.Stop() is called
// each cli callback will be executed in this thread
scheduler.Run();
...This is an example of use of BoostAsioScheduler
...
BoostAsioScheduler scheduler;
CliLocalTerminalSession localSession(cli, scheduler);
BoostAsioCliTelnetServer server(cli, scheduler, 5000);
...
scheduler.Run();
...Finally, this is an example of use of BoostAsioScheduler
when your application already uses boost::asio and has
a boost::asio::io_context object (the case of standalone asio is similar).
...
// somewhere else in your application
boost::asio::io_context ioc;
...
// cli setup
BoostAsioScheduler scheduler(ioc);
CliLocalTerminalSession localSession(cli, scheduler);
BoostAsioCliTelnetServer server(cli, scheduler, 5000);
...
// somewhere else in your application
ioc.run();
...You must provide at least a root menu for your cli:
// create a menu (this is the root menu of our cli)
auto rootMenu = make_unique<Menu>("myprompt");
... // fills rootMenu with commands
// create the cli with the root menu
Cli cli(std::move(rootMenu));
You can add menus to existing menus, to get a hierarchy:
auto rootMenu = make_unique<Menu>("myprompt");
auto menuA = make_unique<Menu>("a_prompt");
auto menuAA = make_unique<Menu>("aa_prompt");
auto menuAB = make_unique<Menu>("ab_prompt");
auto menuAC = make_unique<Menu>("ac_prompt");
auto menuACA = make_unique<Menu>("aca_prompt");
auto menuB = make_unique<Menu>("b_prompt");
auto menuBA = make_unique<Menu>("ba_prompt");
auto menuBB = make_unique<Menu>("bb_prompt");
menuAC->Insert( std::move(menuACA) );
menuB->Insert( std::move(menuBA) );
menuB->Insert( std::move(menuBB) );
menuA->Insert( std::move(menuAA) );
menuA->Insert( std::move(menuAB) );
menuA->Insert( std::move(menuAC) );
rootMenu->Insert( std::move(menuA) );
rootMenu->Insert( std::move(menuB) );This results in this tree:
myprompt
|
+--- a_prompt
| |
| +--- aa_prompt
| |
| +--- ab_prompt
| |
| +--- ac_prompt
| |
| +--- aca_prompt
|
+--- b_prompt
|
+--- ba_prompt
|
+--- bb_prompt
Finally, you can add commands to menus, using the Menu::Insert method.
The library supports adding commands handler via:
- free functions
std::function- lambdas
static void foo(std::ostream& out, int x) { out << x << std::endl; }
std::function<void(std::ostream& out, int x)> fun(foo);
...
myMenu->Insert("free_function", foo);
myMenu->Insert("std_function", fun);
myMenu->Insert("lambda", [](std::ostream& out, int x){ out << x << std::endl; } );
There is no limit to the number of parameters that a command handler can take.
They can be basic types and std::strings
myMenu->Insert(
"mycmd",
[](std::ostream& out, int a, double b, const std::string& c, bool d, long e)
{
...
} );
myMenu->Insert(
"complex",
[](std::ostream& out, std::complex c)
{
...
} );Or they can be custom types by overloading the std::istream::operator>>:
struct Foo
{
friend istream & operator >> (istream &in, Foo& p);
int value;
};
istream & operator >> (istream& in, Foo& p)
{
in >> p.value;
return in;
}
myMenu->Insert(
"foo",
[](std::ostream& out, Foo f)
{
...
} );
If you need it, you can have a command handlers taking an arbitrary
number of std::string parameters:
myMenu->Insert(
"mycmd",
[](std::ostream& out, const std::vector<std::string>& pars)
{
...
} );
Please note that in this case your command handler must take only one
parameter of type std::vector<std::string>.
You can add an enter action and/or an exit action (for example to print a welcome/goodbye message every time a user opens/closes a session, even a remote one):
Cli cli(std::move(rootMenu));
cli.EnterAction(
[&enterActionDone](std::ostream& out) { out << "Welcome\n"; });
cli.ExitAction(
[&enterActionDone](std::ostream& out) { out << "Goodbye\n"; });You can modify the default behavior of the library for cases where the user enters an unknown command or its parameters do not match:
Cli cli(std::move(rootMenu));
cli.WrongCommandHandler(
[](std::ostream& out, const std::string& cmd)
{
out << "Unknown command or incorrect parameters: "
<< cmd
<< ".\n";
}
);You can handle cases where an exception is thrown inside a command handler by registering a specific handler:
Cli cli(std::move(rootMenu));
cli.StdExceptionHandler(
[](std::ostream& out, const std::string& cmd, const std::exception& e)
{
out << "Exception caught in CLI handler: "
<< e.what()
<< " while handling command: "
<< cmd
<< ".\n";
}
);cli uses the input and output stream objects provided by the standard library (such as std::cin and std::cout) by default, so currently cli does not have effective support for unicode input and output.
If you want to handle unicode input and output, you need to provide custom i/o unicode aware stream objects derived from std::istream or std::ostream.
For example, you can use boost::nowide as an alternative to implement UTF-8 aware programming in a out-of-box and cross-platform way:
#include <boost/nowide/iostream.hpp> // for boost::nowide::cin and boost::nowide::cout
// other headers...
cli::Cli app{/*init code*/};
// FileSession session{app}; // default
// now, all parameters is in a UTF-8 encoded std::string
// pass boost::nowide::cin and boost::nowide::cout as parameters(FileSession requires std::istream and std::ostream)
FileSession session{app, boost::nowide::cin, boost::nowide::cout};
/*....*/
// you can call this command funtion and get UTF-8 encoded input data (p), just use it.
// boost::noide helps us avoid the trouble
// caused by inconsistent default code page and encoding of the console under different platforms.
void a_command_function(std::ostream& os, std::string const& p) {
/* implements */
}
Of course, you can also pass stream objects with other capabilities to achieve more customized input and output functions.
Distributed under the Boost Software License, Version 1.0. (See accompanying file LICENSE.txt or copy at http://www.boost.org/LICENSE_1_0.txt)
Please report issues here: http://github.com/daniele77/cli/issues
and questions, feature requests, ideas, anything else here: http://github.com/daniele77/cli/discussions
You can always contact me via twitter at @DPallastrelli
Any feedback from users and stakeholders, even simple questions about how things work or why they were done a certain way, carries value and can be used to improve the library.
Even if you just have questions, asking them in GitHub Discussions provides valuable information that can be used to improve the library - do not hesitate, no question is insignificant or unimportant!
If you or your company uses cli library, please consider becoming a sponsor to keep the project strong and dependable.