Arrays in Data Structures and Algorithms with JavaScript - There are lot of resources out there that covers Arrays in JavaScript but only few explain the topic for the purpose of Data Structures and Algorithms. In this explanation, I will scratch the surface of the topic to give you a great understanding of Arrays in Data Structures and Algorithms with JavaScript. Maybe, this will prompt a short book on Data Structures and Algorithms with Javascript. You are free to ask question and as well contribute to make it better.
Arrays is one of the most powerful and widely use data structure concept in any programming language. It can as well be called Arrays Data Structure.
Arrays are use to store or holds a fixed number of values of a single type.
For any Array created, you can perform four operations on it which are Access, Insertion, Deletion, and Search.
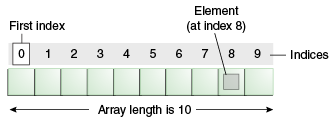
Another interesting thing about Arrays - It has length (fixed when it is created) and index. Let's look at image below and example 1.0 to understand what I meant by length and index.
Figure 1.0: An array of 10 elements. Image credit: Oracle
var myArray = [3, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6];
If you count the elements inside myArray, it has 6 elements. Which means, it has a length of 6 and index of 5 (note: counting index always start from 0).
You can access an Array or element(s) in array by specifying the index number of the array you want to access such as arrayName[index]. Let's take a look at Example 1.1 below
var myArray = [3, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6];
myArray[2]; //will return 4.
myArray[4]; //will return 7
Accessing array is that simple. 😄
I need to mention that the time complexity of accessing an array at a specified index only takes constant time O(1). Simply put, the access method uses the index to get the value directly from the address in memory. Don't worry about how we got this, I will cover Big O Notation (Time Complexity and Space) in another topic soon and put a link here.
As the name implies, it is use to insert an element inside array data structure. To do this in JavaScript we .push(element) method.
The .push(element) adds the element at the end of the array. The time complexity also takes constant time O(1).
var myArray = [3, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6];
myArray.push(9); //it will add 9 and myArray will return [3, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6, 9].
myArray.push(4); //it will add 4 and myArray will return [3, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6, 9, 4]
Deleting element(s) is an interesting operations in Arrays. It simply means to remove element. There are two methods to it, the first method .shift() is used to remove the first element and the second method .pop() is used to remove the last element.
var myArray = [3, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6];
myArray.pop(); //it will print/ remove 6 and myArray will return [3, 8, 4, 9, 7].
myArray.shift(); //it will print/ remove 3 and myArray will return [8, 4, 9, 7]
Also, the time complexity of .shift() and .pop() is constant time O(1).
Search or popularly known as Iteration. Iteration is an interest process. It is a simple way of accessing each element present in the array data structure. Since we are iterating through an nth element, all Iteration method has a time complexity of n that is O(n).