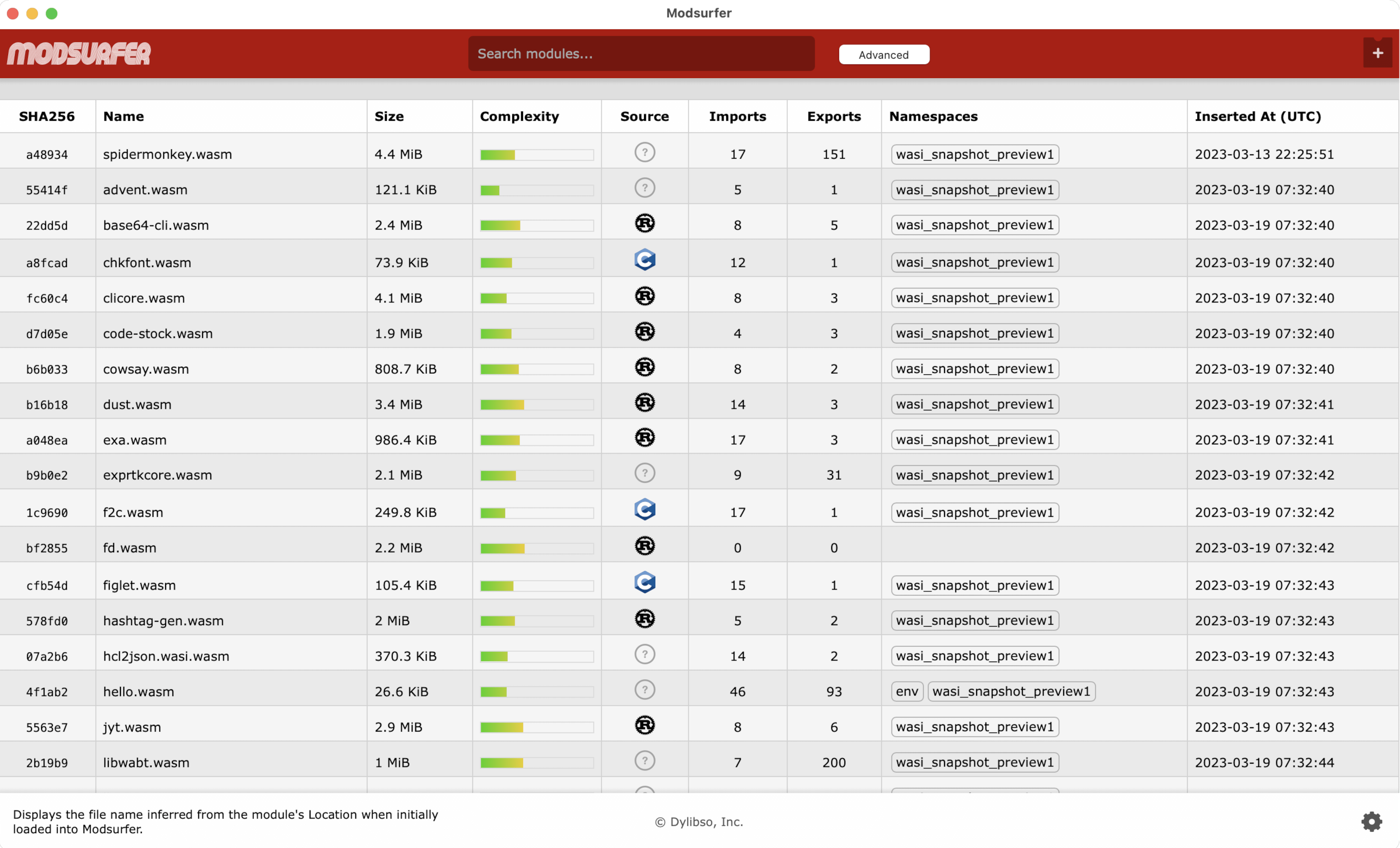
For developers, SRE, DevOps, and engineering leaders: understand what the WebAssembly in your system is all about. Modsurfer provides critical information about WebAssembly code through a handy GUI, or directly at your fingertips via our CLI.
Use Modsurfer for:
- at-a-glance insights into WebAssembly module data (code size & complexity, imports/exports & more)
- search for details about modules (hash, ID, function names, strings, namespaces, errors & more)
- off-the-shelf System of Record: easily audit and track all the WebAssembly code in your stack
- debug & triage issues otherwise difficult to pinpoint in opaque WebAssembly format
The desktop application is free and available to download from Dylibso, and is a useful debugging, visibility, and diagnostics tool for anyone working with WebAssembly.
If you're running WebAssmebly code in production, you may be interested in using the Enterprise version of Modsurfer. Please reach out to us at support@dylibso.com and we'll be happy to get you more information about licensing and self-managed deployment requirements.
This is a collection of Rust crates and other code that is used for a variety of Modsurfer-related purposes. You can find a list and description of these below.
The Modsurfer CLI provides two primary functions:
- HTTP Client to interace with Modsurfer (either the desktop app, or your Enterprise deployment)
- Validation to ensure that WebAssembly binaries:
- are compatible with various host ABIs
- have no known security issues / comply with your policy
- meet the runtime requirements in terms of size and code complexity (RAM/CPU limits, etc)
Modsurfer CLI can be downloaded via:
- the latest GitHub Release
- the GitHub container registry (for Docker environments)
docker pull ghcr.io/dylibso/modsurfer:latest
Modsurfer CLI provides a novel feature to process and validate a WebAssembly
module based on policy/properties of the module that you define. In a
"checkfile" (see the mod.yaml below), declare certain properties of a
WebAssembly module and Modsurfer will verify that they are true, or report which
properties of your binary are invalid.
validate:
# simply require that a module can have WASI functionality or not
allow_wasi: false
# ensure that various imports and exports are included/exlcuded such that a module
# will run properly in any host environment
imports:
include:
# ensure these named functions are in the imports of this module
- log_message
- proc_exit
# further specify the function beyond its name
- namespace: env
name: http_get
params: [I32, I32]
results: [I32]
exclude:
- fd_write
namespace:
include:
- env
exclude:
# phasing out old APIs? exclude these from acceptable namespaces/module names
- some_future_deprecated_module_name
- wasi_snapshot_preview1
exports:
# only want exactly 2 functions exported: `_start` and `bar` for the host to call:
max: 2
# secure your modules by ensuring that there is no superfluous functionality hidden inside a binary
include:
- _start
- name: bar
params: []
results: [I32, I32, I32, I32]
# and/or ensuring no unwanted functions to be exported.
exclude:
- name: init
results: []
- foo
# use a human-readable module size to prevent overly large binaries from running in your environment
size:
max: 4MB
# our Cyclomatic Complexity analysis can help prevent risk of CPU exhaustion from deteriorating
# your user experience and slowing down your system
# (override these low, medium, high optional values with environment variables $MODSURFER_RISK_{LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH})
complexity:
max_risk: lowYou can also point to a remote check file to track up-to-date requirements:
validate:
url: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fermyon/spin/main/tools/modsurfer/http/mod.yamlModsurfer runs validation tests on compiled .wasm binaries. It uses a
"checkfile" to compare with the contents of a .wasm binary. The modsurfer CLI
provides
a number of commands to
create and use a checkfile, as well as to interact as a client to a remote
service that stores and organizes your WebAssembly modules available over HTTP
(via this protobuf API).
modsurfer generate -p path/to/my.wasm -o mod.yaml
NOTE: this checkfile will be very restrictive, and you likely want to edit it to fit less (or more) restricted environments.
To run validation, you can use our GitHub Action, or call the validate command directly:
modsurfer validate -p path/to/my.wasm -c path/to/mod.yaml
If any of the restrictions or expectations declared in your checkfile are not satisfied, Modsurfer will report them:
┌────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────┬──────────┬──────────┬───────────────────┬────────────┐
│ Status │ Property │ Expected │ Actual │ Classification │ Severity │
╞════════╪══════════════════════════════════════════════════╪══════════╪══════════╪═══════════════════╪════════════╡
│ FAIL │ allow_wasi │ false │ true │ ABI Compatibility │ |||||||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ complexity.max_risk │ <= low │ medium │ Resource Limit │ | │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ exports.exclude.main │ excluded │ included │ Security │ ||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ exports.include.bar │ included │ excluded │ ABI Compatibility │ |||||||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ exports.max │ <= 100 │ 151 │ Security │ |||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ imports.include.http_get │ included │ excluded │ ABI Compatibility │ |||||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ imports.include.log_message │ included │ excluded │ ABI Compatibility │ |||||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ imports.namespace.exclude.wasi_snapshot_preview1 │ excluded │ included │ ABI Compatibility │ |||||||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ imports.namespace.include.env │ included │ excluded │ ABI Compatibility │ |||||||| │
├────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ FAIL │ size.max │ <= 4MB │ 4.4 MiB │ Resource Limit │ | │
└────────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────┴──────────┴──────────┴───────────────────┴────────────┘
NOTE: convert this table into JSON with the
--output-format jsonoption, supported by thevalidatecommand and many others.
Find more information about the CLI in its dedicated README,
or download the tool and run modsurfer -h.
Before running or integrating a WebAssembly module on your platform (Emscripten, Extism, Fastly, Shopify, Spin, Suborbital, wasmCloud, Workers)
From the root of the repo, run the following to see a basic validation report:
make test-climake empty-climake unknown-cli
test/ contains a mod.yaml, which declares expected properties of a
WebAssembly module, as well as a spidermonkey.wasm file to use as example
input to use for the validation. wasm/ contains a set of WebAssembly binaries
downloaded from the wapm package manager used for analysis
and testing.
This directory contains the Protobuf definitions for the types used in the API.
Messages have various levels of documentation as well as endpoints if they are
request types. Use the api.proto to generate a language client if you'd like
to interact with Modsurfer API programmatically from your application.