A lightweight python module for building event driven distributed systems.
pip install eventifyDevelopers need a easy and fast way to implement business logic in a modern asynchronous way. Developers should not have to worry about service communication.
TBD
Below is everything you need to get started using the eventify project.
Create an Event handler function to receive events. To publish events, use session.emit_event() within the Event handler function. To start your service (and begin listening for events), pass the Event handler function as a callback to run a Service.
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""
Minimal viable microservice
"""
import asyncio
import logging
import sys
from eventify.base_handler import BaseHandler
from eventify.event import Event
from eventify.service import Service
class GoogleCollector:
"""
Google Specific Collector
"""
async def collect_vm_data(self):
print('...collecting data from gce api...')
await asyncio.sleep(1)
class Collector(BaseHandler, GoogleCollector):
"""
Generic collector
"""
async def init(self):
"""
Service initialization
"""
print('...service initialized...')
def run():
"""
Run an eventify service
"""
Service(
config_file='config.json',
handlers=[Collector]
).start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
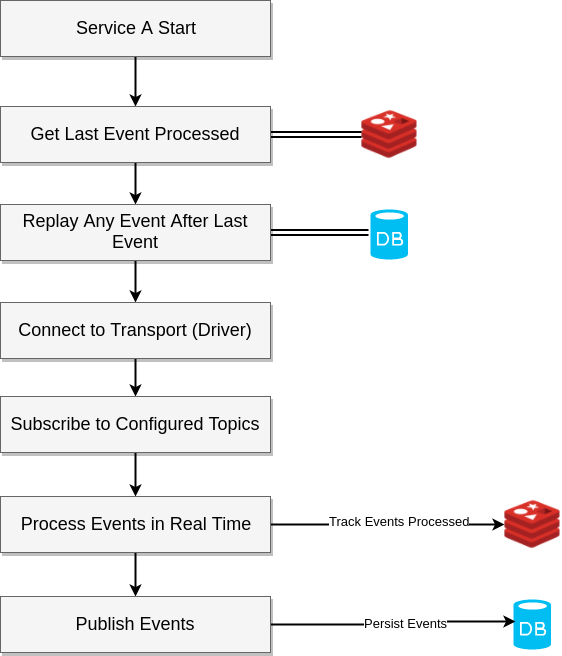
run()Each application (service, microservice, etc.) can publish to 0 or 1 topic and subscribe to 0 or more topics. Thus each application requires its own configuration file which defines its publications & subscriptions. Each configuration file also specifies the location of the transport host.
{
"_comment": "service configuration",
"name": "example",
"image": "example/service",
"driver": "crossbar",
"transport_host": "ws://events-server:8080/ws",
"pub_options": {
"acknowledge": true,
"retain": true
},
"publish_topic": {
"topic": "example",
"timeout": 20,
"reply_in": 0
},
"subscribed_topics": [
"ui-events"
],
"replay_events": true,
"replay_type": "event_store"
}To add event history support add the @event_tracker decorator to any event handler your define.
- EVENT_DB_HOST
Hostname of database server
- EVENT_DB_USER
Username for database server
- EVENT_DB_PASS
Password for username
- EVENT_DB_TYPE
Database driver type - defaults to postgres
- EVENT_DB_POOL_SIZE
Database connection pool size - defaults to 5
- EVENT_TRACKING_HOST
For use with replay functionality - host of in memory cache
- Crossbar
- Kafka
Quickest way to get started with crossbar is to use docker; both redis and postgresql are required for a minimal working service.
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -it crossbario/crossbar:latest- TBD
docker run -d -p 6379:6379 -t redis:latestdocker run --name postgres-container -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword -d postgresNote: This does not have a volume or persistant storage so in a production environment you would want to configure a volume