This project is about the implementation of the LZ77 and Deflate COMPRESSION algorithm.
main.c file contains implementations of both LZ77 and Deflate algorithm. It also contains the huffman code and huffman tree code required for the deflate algorithm.
The project aims to compress and store the text document file with .txt extension, which is received as input.
To do this, LZSS (Lempel – Ziv – Storer – Szymanski) and DEFLATE algorithm are used. LZSS algorithm aims to compress by eliminating repetitive places.
LZ77 iterates sequentially through the input string and stores any new match into a search buffer. The process of compression can be divided in 3 steps:
1-Find the longest match of a string that starts at the current position with a pattern available in the search buffer.
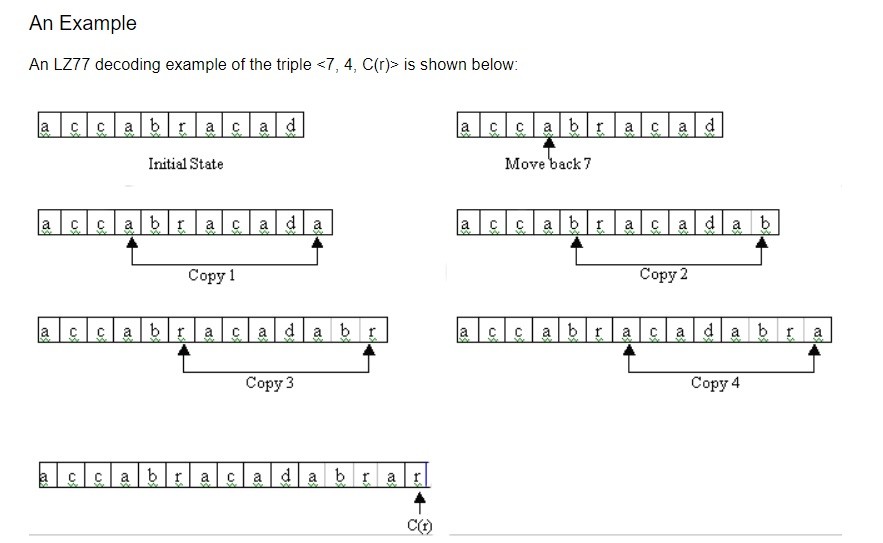
2- Output a triple (o, l, c) where,
-> o: offset, represents the number of positions that we would need to move backwards in order to find the start of the matching string.
-> l: length, represents the length of the match.
-> c: character, represents the character that is found after the match.
Move the cursor l+1 positions to the right.
for more information: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-data-compression-works-exploring-lz77-3a2c2e06c097
The DEFLATE compressed data format consists of a series of blocks, corresponding to successive blocks of input data. Each block is compressed using a combination of the LZ77 algorithm and Huffman coding . The LZ77 algorithm finds repeated substrings and replaces them with backward references (relative distance offsets). The LZ77 algorithm can use a reference to a duplicated string occurring in the same or previous blocks, up to 32K input bytes back.
It is written in C language and Dev-C ++ IDE is used.
!!! IMPORTANT WARNING: The program causes a problem in compressing text documents over 200-300Kb. (Also explained in the report) !!!
!!!!! Just put the text documents to be tested in the input folder, and there is no need for another folder for either algorithm. !!!!!
1- Since two different compression algorithms will be used, there are two different input folders. (INPUT), (INPUTDEFLATE)
2- Among them, INPUT contains the txt files required for "LZSS algorithm" and "DEFLATE". You don't need to add anything to other folders.
3- Txt files must be in the same number and content for comparison.
4- The names of the txt files placed in the folders are 461-465. It should be corrected harmoniously between the lines.
5- In the same way, the same steps are valid for the output files.
6- There are 3 test txt in the folder of the program by default.
7- After the necessary steps are done, all you have to do is compile and run the program.
8- After the program runs, the (LZSS-DEFLATE) algorithms work in order to perform the necessary compression operations.
9- Compression rates and file sizes are displayed to the user through the program.
10- There may be changes in compression rates depending on the test text used. If adequate matching is not achieved, one of the disadvantages of the algorithm,
"PADDING" ie inflating process is done and the file size increases. (In the compression ratio can be "-" ratio).
11- After the program runs, in the positions specified in lines 467 and 477; LZFG (Our own extension) extension in the "output" folder for LZ77,
For DEFLATE, files with .def (short for Deflate) extension are created in the "outputDEFLATE" folder.
12- These created files are the compressed version of the .txt files received in the input folder.
• https://cs.stanford.edu/people/eroberts/courses/soco/projects/data-compression/lossless/lz77/index.htm
• https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/e8d7/c01594cf4359c3d50aef7db88b0153c7fcbd.pdf
• http://corpus.canterbury.ac.nz/descriptions/#cantrbry
• http://altanmesut.trakya.edu.tr/pubs/DR_Tez.pdf
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0vMyw4Lv3Hw
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=goOa3DGezUA
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JsTptu56GM8
• https://ysar.net/algoritma/lz77.html
• https://zlib.net/feldspar.html
• https://sites.google.com/site/datacompressionguide/lz77
• http://michael.dipperstein.com/lzss/
• http://www.mathcs.emory.edu/~cheung/Courses/255/Syllabus/1-C-intro/bitarray.html
• https://github.com/dbrgn/algorithms/blob/master/lz/lz77.c
• https://github.com/ggz/huffman_coding
• https://people.ok.ubc.ca/ylucet/DS/Huffman.html
• https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Simplified-DEFLATEalgorithm_fig3_228411140