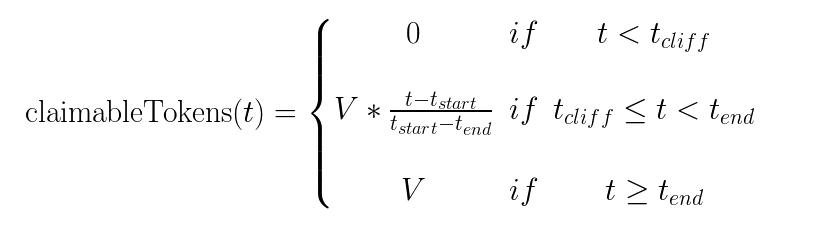This repository hosts the source code of the ethereum smart contracts deployed by Hey on the mainchain.
📘 If you are looking for the full description of Hey's project, please consult our manifesto.
- Disclaimers
- Contract addresses
- Security analysis
- Local machine setup
- Codebase overview
- Open-source components
- Contracts deep dives
- Deployment
This code and its readme remains works in progress and should be considered as such until the Hey team releases official communication conveying that the information has been reviewed and audited. Audit results will be made publicly available once the auditor's recommendations have been processed.
Elements within this document that are stricken through should be considered as under construction, as these particular components may be subject to significant change.
A bug bounty program will run for product-specific smart contracts (both on the sidechain and mainchain). Contact us at bounty@hey.network if you are excited by this opportunity.
Currently the Token contract has already been deployed:
- The Token contract lives at this address: 0xe9c9e7e1dabea830c958c39d6b25964a6f52143a
Prior to the audit, a series of tools were used to improve overall code quality and ensure robustness.
The Solium linter can be run with npm run lint. The following warnings remain and are acceptable, hence they have been silenced by selectively disabling solium on the corresponding lines:
TokenSale.sol:65: usage ofblock.timestamp, required for the TimedCrowdsale behavior.VestingTrustee.sol:187: usage ofblock.timestamp, required for the vesting behavior.ECVerify.sol:11: assigning to function parameter (hash) argument, kept for simpler code readability and to comply with the version retrieved from Loom's example.ECVerify.sol:25: usage of Inline Assembly to decompose signature byte, kept as it is a generally accepted practice to simply extract the(r, s, v)parameters and in order to comply with the version retrieved from Loom's example.
The Mythril static analyzer can either be run with npm run mythril or independently for each contract (see the full list in package.json—for example, you can run npm run mythril:token). Please consult the related documentation to install this tool on your machine.
For the token contract, the following warnings were emitted and are acceptable:
- Integer Overflow (SWC ID: 101) in file
Token.sol:9: acceptable as thedecimals()value is set once and for all at deployment with a predictable result. - Message call to external contract (SWC ID: 107) in file
EmergencyERC20Drain.sol:18: acceptable as this function can only be called by the contract owner, whom we assume is not malicious. - Integer Overflow (SWC ID: 101) in file
SafeMath.sol:51: acceptable as the SafeMath library's purpose is precisely to securely handle this error.
Note that there is a --max-depth issue to get the tool running for some contracts, which still needs to be investigated jointly with auditors to understand how to fix the configuration.
The code repository has also been checked with SmartCheck and Securify, two online security tools. Oyente could not be deployed on this repository as it uses old EVM and solc versions which makes it unable to run the code. This issue will also be investigated alongside auditors in order to take greatest advantage of available toolkits.
Will be updated following the audit.
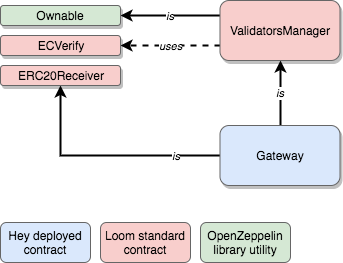
The majority of the mainchain codebase relies on standard, open-source contracts. The Token Generation Event (TGE) smart contracts are mostly out-of-box OpenZeppelin's library contracts, while the Gateway contract leverages Loom Network's example.
This approach has been chosen deliberately, so that the Hey team can:
- Achieve a faster time-to-market.
- Decrease security auditing complexity and cost while minimizing the likelihood of bugs.
- Increase TGE's participants' trust.
- Spend more time and energy on specifics of the Hey product that are mostly present on the sidechain contracts ecosystem, and which are the differentiating factor and competitive advantage of Hey as a platform.
The Hey team has taken great care to track provenance of open-source components, and has made sure to thoroughly review each component internally in order to ensure a deep understanding of their interfaces and implementations.
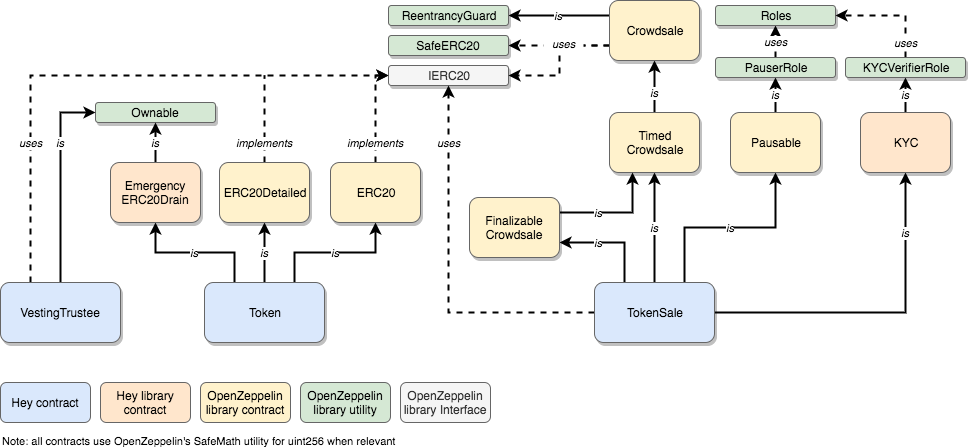
This repository consists of four main contracts.
The two main contracts supporting Hey's platform are:
- The token, which is a plain ERC20 token, using OpenZeppelin's
SimpleTokenimplementation - The Gateway, which allows users to redeem HEY tokens when providing the accurately signed message (see full architecture). This is a stripped-down version of Loom Network's
Transfer Gatewayimplementation, simplified in order to retain solely ERC20 withdrawal capabilities.
In addition to these two principle contracts, two additional smart contracts are employed. Both are dedicated to the Token Generation Event (TGE):
- The VestingTrustee, which locks tokens from early pre-sale contributors as well as from Hey's team. This is heavily inspired by SirinLab and Stox's
VestingTrusteecontract. - The TokenSale (TGE-specific contract), implementing the
TimedCrowdsale,FinalizableCrowdsale, andPausablebehaviors. This is mostly an extension of OpenZeppelin's defaultCrowdsalecontract, including limited customization.
If you are looking for the social-network-related features (e.g., Karma management), please look into the sidechain repository.
These diagrams express the inheritance and usage relationships amongst contracts. Contracts in blue are those that are deployed effectively on the mainchain, building upon higher-level contracts.
Make sure the following npm modules are installed by running npm install:
- truffle (
v5.0.4) - openzeppelin-solidity (
v2.1.2) - web3 (
v1.0.0-beta.46)
Furthermore, we use the following modules during testing (installed alongside above packages):
- chai
- openzeppelin-test-helpers
No need to run ganache-cli, as we use the built-in test network from Truffle. Simply run npm run test or npm t to launch the full test suite.
The vast majority of Hey's mainchain contracts leverage existing, previously-audited open-source contract libraries. The following tables recap the exact version of each open-source component used in the contracts:
The following table below lists all *.sol contract files imported directly or indirectly (i.e. from other imported contracts) by the deployed Hey contracts. These files have been used as-is with no modifications.
| Domain | File | Provider | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Token | ERC20.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Token | ERC20Detailed.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Token | IERC20.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Token | SafeERC20.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| TGE | Crowdsale.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| TGE | TimedCrowdsale.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| TGE | FinalizableCrowdsale.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Gateway | ValidatorsManagerContract.sol | Loom | source |
| Gateway | ECVerify.sol | Loom | source |
| Gateway | ERC20Receiver.sol | Loom | source |
| Utils | Ownable.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Utils | Pausable.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Utils | PauserRole.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Utils | Roles.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Utils | Math.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Utils | SafeMath.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
| Utils | ReentrancyGuard.sol | OpenZeppelin | openzeppelin-solidity v2.1.2 |
The following table below lists all *.sol contract files that served as a source of inspiration for the deployed Hey contracts.
| Domain | File | Provider | Source | Modifications brought |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Token | SimpleToken.sol | OpenZeppelin | source | Set token parameters (supply, name, symbol), added security features |
| Token | ZilliqaToken.sol | Zilliqa | source | Used validDestination modifier, removed check on zero address (already in ERC20) |
| TGE | PauserRole.sol | OpenZeppelin | source | Changed role name to KYCVerifierRole |
| TGE | SirinVestingTrustee.sol | SirinLab | source | Made Ownable i.o. Claimable, improve functions and variable names, adhered to latest Solidity best practices |
| Gateway | Gateway.sol | Loom | source | Kept only ERC20 transfer capabilities, locked to HEY token address |
The HEY token conforms to the ERC20 standard, directly extending OpenZeppelin's related library.
The HEY token has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Name | HeyToken | |
| Symbol | HEY | |
| Decimals | 18 | |
| Total supply | 1,000,000,000 | Minted to owner address at creation |
The HEY token extends the ERC20 specifications to include two additional security features:
validDestination: as per Consensys' Best Practices, this feature prevents the sending of HEY tokens to the HEY token contract itself. It does so by adding a modifier to thetransfer()andtransferFrom()functions.EmergencyERC20Drain: as per Zilliqa's Token Contract, this feature allows the owner to drain any other ERC20 tokens mistakenly sent to the contract by transferring said tokens to the owner's address. It does so by using thedrain()function.
The full HEY token test suite can be run by using the following command: npm run test:token. Each specification of the HEY token can also be verified individually by using its dedicated test:
| # | Description | Test command |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Name is HeyToken |
npm run test:token:name |
| 2 | Symbol is HEY |
npm run test:token:symbol |
| 3 | Number of decimals is 18 |
npm run test:token:decimals |
| 4 | Total supply is 1,000,000,000 |
npm run test:token:supply |
| 5 | Cannot receive HEY tokens (validDestination behavior) |
npm run test:token:valid-destination |
| 6 | Conforms to ERC20 transfers interface | npm run test:token:transferable |
| 7 | Allows owner to drain other ERC20 tokens sent by mistake | npm run test:token:drainable |
Note that it is necessary to test (6), as the HEY token extends the transfer() and transferFrom() functions in order to implement the validDestination behavior.
The HEY Token Sale contract is primarily an extension of OpenZeppelin's standard Crowdsale contract. It also includes standard crowdsale behaviors implemented in OpenZeppelin's standard contracts, including:
TimedCrowdsale: the Token Sale only accept payments betweenstartTimeandendTime.FinalizableCrowdsale: the Token Sale implements afinalize()function that triggers a custom action after the sale has closed (see below).Pausable: the Token Sale can be paused by the owner to reject any new incoming payments.
The following behaviors have also been implemented (not directly available from OpenZeppelin libraries):
EvolvingRate: the ETH-to-tokens rate evolves from 4,400 during the first day of the TGE to 4,000 afterwards.MinimumContribution: the Token Sale only allows contributions when payments are equal to or above 0.1 ETH.KYC: the Token Sale only allows contributions from addresses authorized by the contract owner for KYC reasons.
Note that the Token Sale does not explicitly implement the CappedCrowdsale behavior, but rather enforces it indirectly by virtue of its endowment with a fixed number of tokens that are transferred during the initialization phase.
The name TokenSale has been chosen in order to ensure that it is as similar as possible to the standard Crowdsale name, which is already reserved for the corresponding OpenZeppelin's library. The name cannot be redeclared, as it is already in use—thus the selection of TokenSale.
When it is deployed, the Token Sale Contract expects a pool address to be provided as constructor argument. When the finalize() function is called—that is, after the sale has closed—any unsold tokens will be automatically transferred to the Pool's address.
This customization is implemented by extending the internal _finalization() function.
In the Pool, tokens will be made available for users to redeem. Note that the Pool will be endowed with 30% of the total token supply regardless of token sale results. In the case of unsold tokens, they are merely added to this original 30%.
The Hey team expects that tokens will remain following the ICO even in the case that the hard cap is reached, mainly based on rounding requirements.
The owner of the contract can call the pause() function at any time. This prevents any purchase of new tokens.
This customization is implemented by extending the internal _preValidatePurchase() function and inheriting the Pausable contract from OpenZeppelin's standard library.
When it is deployed, the Token Sale contract expects firstDayRate and rate to be provided as constructor arguments. These express the ether-to-tokens rates that will be applicable respectively during and after the first 24 hours after the sale opening time.
The chosen parameters are 4,400 for firstDayRate and 4,000 for rate (that is, a 10% token bonus for first-day purchasers).
This customization is implemented by overriding the internal _getTokenAmount() function and adding a public getCurrentRate() function in order to reflect the rate at any given time. Note that we do not override the standard rate() function from the parent Crowdsale contract. Rather, it will always return a static rate of 4,000.
Token purchases are allowed only if the amount sent is equal to or above 10 ETH during the first 24 hours of the sale, and then equal or above to 0.1 ETH afterwards.
This customization is implemented by extending the internal _preValidatePurchase() function to add a check on msg.value.
For KYC reasons, the Token Sale contract only allows contributions from a set of authorized addresses, for KYC reasons. The set of addresses is a mapping authorizedAccounts of address to bool, which is populated by the Token Sale contract owner (and other authorized KYC verifiers) in batch before and during the TGE period using the grantKYCAuthorizations() function.
This customization is implemented by extending the internal _preValidatePurchase() function to add a check on beneficiary. Note that we only check the beneficiary address, as KYC will be done on these addresses (not on addresses purchasing on behalf of other addresses).
We also create a KYCVerifierRole based exactly on PauserRole and other similar access control contracts available in OpenZeppelin's standard library.
Note that since KYC is an asynchronous process (requiring potential manual actions), the Hey TGE will be publicly advertised at least one month prior to contribution commencement, so that interested parties are able to perform KYC and ensure their addresses are authorized in advance of the token sale. Given this advanced notice, the Hey team can ensure that interested participants can benefit from the TGE's 10% first-day bonus without fear of missing out based on process delays.
Notably, the Hey team cannot guarantee that participants performing KYC during the first 24 hours following token sale commencement will obtain authorization in time to benefit from the 10% first-day bonus. With that said, participants should plan on performing their KYC in advance of the token sale. Hence participants should do their KYC early on.
The full Token Sale test suite can be run with the command npm run test:token-sale. Each specification of the Token Sale can also be verified individually with its dedicated test, outlined as follows:
| # | Description | Test command |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conforms to standard Crowdsale behavior | npm run test:token-sale:standard |
| 2 | Conforms to standard TimedCrowdsale behavior | npm run test:token-sale:timed |
| 3 | Evolves rate from 4,400 to 4,000 tokens/ETH after 24 hours | npm run test:token-sale:evolving-rate |
| 4 | Allows to pause incoming payments | npm run test:token-sale:pausable |
| 5 | Requires a minimum contribution of 10 ETH then 0.1 ETH | npm run test:token-sale:minimum-contribution |
| 6 | Allows contribution only from authorized addresses | npm run test:token-sale:kyc |
| 7 | Sends remaining tokens to pool at finalisation | npm run test:token-sale:finalizable |
Note that the access control helper KYCVerifierRole can be tested with npm run test:kyc-verifier-role.
The Vesting Trustee smart contract is responsible for the vesting of tokens granted to early contributors, some pre-sale participants, and the Hey team. The contract protects noted parties' tokens while ensuring said tokens can be withdrawn only following a given lock period.
This smart contract contains a mapping of Grants, each parameterised with its own vested token amount and vesting time. Grants can be created and revoked at any time by the contract owner.
The vesting scheme includes a cliff mechanism. Before the cliff date, no tokens can be withdrawn by the grantee. After the cliff date, tokens can be withdrawn progressively, with an amount limited by a linear interpolation between the vesting start and end times. Following the vesting end time, the full amount of granted tokens can then be withdrawn. Here is a mathematical description of the tokens that can be claimed and withdrawn by a grantee at a given time t for a grant of V tokens:
Note that when a grant is revoked by the contract owner, the corresponding token amount is transferred back to the contract owner's address.
The smart contract is initially provisioned with tokens by the contract owner, so that grant can be rightly created.
The full Vesting Trustee test suite can be run with the command npm run test:vesting-trustee. Each specification of the Vesting Trustee can also be verified individually with its dedicated test, outlined as follows:
| # | Description | Test command |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Allows the contract owner to create a grant | npm run test:vesting-trustee:create |
| 2 | Computes the right amount of claimable tokens over time | npm run test:vesting-trustee:claimable |
| 3 | Allows progressive release of tokens over time | npm run test:vesting-trustee:claim |
| 4 | Allows the contract owner to revoke a revokable grant | npm run test:vesting-trustee:revoke |
Note that testing the claiming logic relies on a series of different vesting configurations, wherein we sample time during the vesting period to ponctually measure tokens that can be claimed and effectively withdrawn.
To visualise the evolving token vesting over time, simply run test:vesting-trustee:charts. This will provide ASCII charts such as the following, which should assist in understanding the linearity mechanism.
Claimable tokens over time (vested: 100, cliff days: 25, total days: 100)
100.00 ┼ ╭────────────
95.00 ┤ ╭────╯
90.00 ┤ ╭────╯
85.00 ┤ ╭────╯
80.00 ┤ ╭────╯
75.00 ┤ ╭────╯
70.00 ┤ ╭────╯
65.00 ┤ ╭────╯
60.00 ┤ ╭────╯
55.00 ┤ ╭────╯
50.00 ┤ ╭────╯
45.00 ┤ ╭────╯
40.00 ┤ ╭────╯
35.00 ┤ ╭────╯
30.00 ┤ ╭────╯
25.00 ┤ ╭──╯
20.00 ┤ │
15.00 ┤ │
10.00 ┤ │
5.00 ┤ │
0.00 ┼────────────────────────╯
Claimable tokens over time (vested: 100, cliff days: 50, total days: 100)
100.00 ┼ ╭────────────
95.00 ┤ ╭────╯
90.00 ┤ ╭────╯
85.00 ┤ ╭────╯
80.00 ┤ ╭────╯
75.00 ┤ ╭────╯
70.00 ┤ ╭────╯
65.00 ┤ ╭────╯
60.00 ┤ ╭────╯
55.00 ┤ ╭────╯
50.00 ┤ ╭──╯
45.00 ┤ │
40.00 ┤ │
35.00 ┤ │
30.00 ┤ │
25.00 ┤ │
20.00 ┤ │
15.00 ┤ │
10.00 ┤ │
5.00 ┤ │
0.00 ┼─────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Claimable tokens over time (vested: 100, cliff days: 75, total days: 100)
100.00 ┼ ╭────────────
95.00 ┤ ╭────╯
90.00 ┤ ╭────╯
85.00 ┤ ╭────╯
80.00 ┤ ╭────╯
75.00 ┤ ╭──╯
70.00 ┤ │
65.00 ┤ │
60.00 ┤ │
55.00 ┤ │
50.00 ┤ │
45.00 ┤ │
40.00 ┤ │
35.00 ┤ │
30.00 ┤ │
25.00 ┤ │
20.00 ┤ │
15.00 ┤ │
10.00 ┤ │
5.00 ┤ │
0.00 ┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
The Vesting Trustee contract borrows heavily from (i.e. is a refactoring of) the smart contracts used by SirinLab, Stox and KIN.
We have renamed several functions and variables to improve overall readability, while also reverting on claims that yield 0 tokens (either because the grantee does not exist or because no tokens can yet be claimed). The latter change has been implemented in order to avoid spilling on transaction fees while carrying out precocious claims.
The Gateway is not in scope for the Token Generation Event. The ValidatorsManager contract has been taken out of the test coverage calculations as it is not in Hey's direct focus to test all validator's co-opting features of this contract.
The first deployment phase intends on making the platform fully ready for the TGE. It does not yet include the Gateway contract deployment; it will remain pending throughout code review and auditing, as this audit will be supported in part by funds collected during the TGE.
- Connection to the Ethereum mainnet.
- Latest version of contracts builds (run compilation with
truffle compile). - Fully green specs (run tests with
npm t). - Secured control of TGEAdmin account, with enough ETH on account for contract deployment.
- Secured control of Pool account.
- Secured control of Team account.
- Secured control of Wallet account.
- List of presale buyers' non-vested addresses, including number of tokens per account (
PRESALE_NON_VESTEDtokens in total). - List of presale buyers' vested addresses, including the number of tokens purchased per address and the vesting period, if any (
PRESALE_VESTEDtokens in total).
- Token contract deployed.
- TokenSale contract deployed.
- VestingTrustee contract deployed.
- 1,000,000,000 tokens minted.
- 300,000,000 tokens on Pool account.
PRESALE_NON_VESTEDtokens distributed amongst presale non-vested buyers' accounts.PRESALE_VESTED(for presale buyers) +200,000,000tokens (for the Hey team, contributors, and advisors) controlled by the VestingTrustee contract, with a balance per vested account.- (500,000,000 -
PRESALE) of tokens controlled by the TokenSale contract, wherePRESALE=PRESALE_NON_VESTED+PRESALE_VESTED. - TokenSale contract ready to accept ETH payments against HEY tokens.
- TokenSale contract funnelling incoming ETH to Wallet account.
- TokenSale contract configured to send potential tokens remaining post-TGE to Pool account.
All actions performed below should originate from the TGEAdmin account. After deployment, this address should be kept secure, as it remains able to call pause() and finalize() on the TokenSale contract, as well as drain() on the Token contract. The deployment script is as follows:
- Deploy Token (no constructor parameters needed)
- Deploy TokenSale, with constructor parameters:
openingTime:TBCclosingTime:TBCfirstDayRate: 4400rate: 4000wallet: Wallet account addresspool: Pool account addresstoken: Token contract address (from previous step)
- Deploy VestingTrustee, with constructor parameter:
token: Token contract address (from previous step)
- Send 300,000,000 tokens to Pool account
- Send (500,000,000 -
PRESALE) tokens to the TokenSale contract address - Send
PRESALE_NON_VESTEDtokens in total to presale non-vested buyers accounts as per the distribution list (multiple transactions) - Send
PRESALE_VESTED+200,000,000tokens to the VestingTrustee contract address (from previous step) - Call the
createGrant()function on the VestingTrustee contract once for each presale vested buyer as well as for the Team account with following parameters:to: presale buyer accountvalue: presale tokens amount purchased (must include 18 decimals)start:current timecliff:TBCend:TBCrevokable: false
This deployment script is executed via a nodejs script using an HDWallet over an Infura proxy (TBC: ideally, sign transactions from Ledger hardware wallet rather than sourcing from ENV). The full deployment script code is in this file. This script and its outcome are tested in this file.
This phase will be further documented as the code review and audit progress. Initially, the tokens to be controlled by the Gateway will be stored on the Pool account. When the Gateway is deployed, it will benefit from an allowance granted by the Pool account so that The Gateway can distribute tokens on the Pool's behalf.
We allow anyone to verify the smart contracts code directly on Etherscan. For this, we use Solidity Flattener, running the following command:
./scripts/flatten.pl --contractsdir=contracts --mainsol=Token.sol --outputsol=flattened/Token.flat.sol --verbose --remapdir='contracts/openzeppelin-solidity=node_modules/openzeppelin-solidity'
This is encapsulated with the npm command npm run flatten:token. These commands output *.flat.sol files that can then be used in Etherscan. We use Solc 5.0.0 with no optimization to obtain the green checkmark.
Note that since the flattener cannot handle second-level dependencies, the EmergencyERC20Drain sol file needs to be moved to the root level of the contracts folder (and its import path modified) before running the flattener.