-
- 2.1. 2.1 Generated images
- 2.2. 2.2 loss
- 2.3. 2.3 Likelihood
-
- 6.1. 6.1 Code structure
- 6.2. 6.2 Parameter Description
- 6.3. 6.3 Implementation details
- 6.4. 6.4 Training process
- 6.5. 6.5 Test process
- 6.6. 6.6 Evaluation on pre-trained model
This project is based on the paddlepaddle framework to reproduce Adversarial Autoencoders (AAE). This is a probabilistic autoencoder that uses a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to perform variational inference by matching the aggregate posterior of the latent variable of the autoencoder with any prior distribution. It matches the aggregate posterior with the prior distribution, ensuring that meaningful samples are generated from any part of the prior space. Therefore, AAE's Decoder learns a deep generative model, which maps the prior distribution to the corresponding data.
Paper:
[1] Makhzani A, Shlens J, Jaitly N, et al. Adversarial autoencoders[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.05644, 2015.
Reference repositories:
- https://github.com/eriklindernoren/PyTorch-GAN/blob/master/implementations/aae/aae.py
- https://github.com/fducau/AAE_pytorch/tree/master/
aistudio project:
| Epoch0 | Epoch20 | Epoch100 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
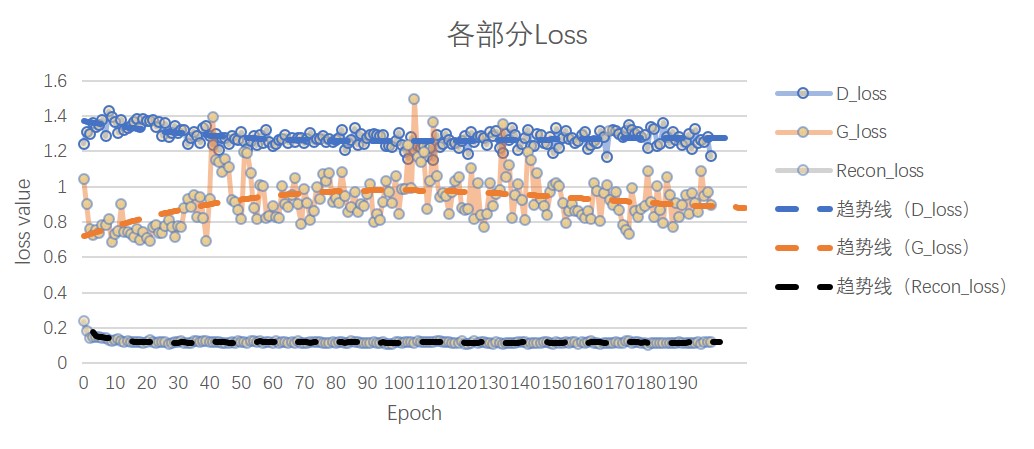
In the figure, D_loss is the loss of the discriminator, G_loss is the loss of the encoder, and recon_loss is the loss of the picture. Here, the binary cross entropy function (BCEloss) is selected.
recon loss = BCE(X_{sample}, X_{decoder})
As shown in the figure, D_loss and G_loss stabilize at around 50 epochs. The recon_loss gradually decreases and stabilizes in 20-30 rounds.
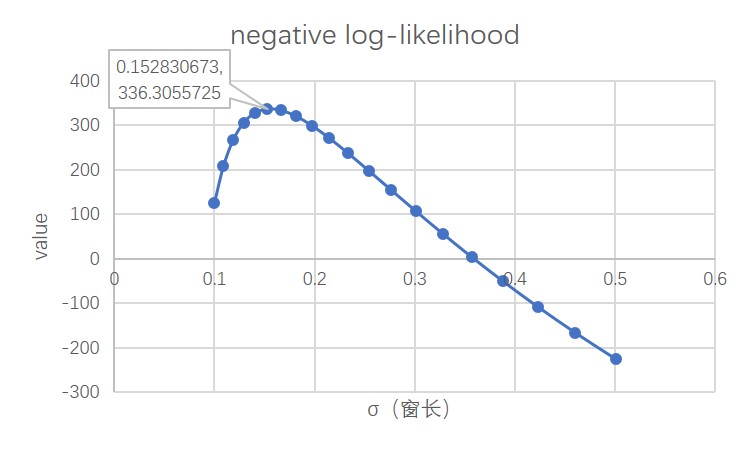
It is mentioned in the original paper that the selection of the window length σ needs to be achieved through cross-validation. This paper uses a validation set of 1000 data samples for selection, so as to obtain a window length that meets the maximum likelihood criterion.
According to the results of a small number of samples on the validation set, the σ value that maximizes the negative log likelihood (nll) is selected as the window length
| MNIST (10K) | |
|---|---|
| original | 340 ± 2 |
| reproduced | 345 ± 1.9432 |
 |
| MNIST (10K) | |
|---|---|
| original | 340 ± 2 |
| current model | 345 ± 1.9432 |
| model in reference repository[1] | 298 ± 1.7123 |
| current model without dropout layers | 232 ± 2.0113 |
Analysis of experimental results: The results show that the current model settings can be closest to or even exceed the original nll index. This indicator measures the diversity of production data samples on the one hand, and on the other hand requires the generated data samples to be as close as possible to the samples in the data set. The model without the dropout layers is prone to overfitting, which tends to adopt conservative strategies for sample generation, and the data diversity is poor. The model in the reference repository[1] uses the LeakyReLU activation function, and the effect is improved, but it is also prone to overfitting due to the absence of dropout layers.
- Size:
- Training: 60000
- Validation: 10000
- Format: idx
- Hardware: GPU, CPU
- Framework:
- PaddlePaddle >= 2.0.0
- numpy >= 1.20.3
- matplotlib >= 3.4.2
- pandas >= 1.3.1
- step1: data generation
python data_maker.py
- step2: train
python train.py
- step3: evaluate log_likelihood
python eval.py
AAE_paddle_modified
├─ README_cn.md # readme in Chinese
├─ README.md # readme in English
├─ data # datasets and data splitted
├─ images # generated images
├─ logs # log output of the experiment
├─ model # training model
├─ utils # utilities code
├─ log.py # log output
├─ paddle_save_image.py # images output
└─ parzen_ll.py # parzen window estimation
├─ config.py # configuration file
├─ network.py # network structure
├─ data_maker.py # data segmentation
├─ train.py # training code
└─ eval.py # evaluation code
You can set training and evaluation related parameters in config.py, which are mainly divided into three categories: related to the model structure, related to the data, and related to the training and testing environment.
-
Following the original principles, Encoder uses two fully connected layers, Decoder uses two fully connected layers, and Discriminator uses two fully connected layers. Since the original text did not publish the code and related detailed parameters, the author added the Dropout layer here, and added the re-parametrization trick as described in the appendix of the original text, which is to re-parameterize the generated latent variable z into a Gaussian distribution.
-
The Gaussian prior distribution is 8-dimensional, the variance is 5, and the number of neurons is 1200. The network structure is the same as the original
run
python train.py
Output will be generated in the terminal and will be saved to ./logs/train.log
[2021-09-22 21:04:17,682][train.py][line:62][INFO] Namespace(n_epochs=200, batch_size=100, gen_lr=0.0002, reg_lr=0.0001, load=False, N=1200, img_size=28, channels=1, latent_dim=8, std=5, N_train=59000, N_valid=1000, N_test=10000, N_gen=10000, batchsize=100, load_epoch=199, sigma=None)
W0922 21:04:18.062372 50879 device_context.cc:404] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 6.1, Driver API Version: 10.1, Runtime API Version: 10.1
W0922 21:04:18.067184 50879 device_context.cc:422] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
[2021-09-22 21:04:48,115][train.py][line:174][INFO] [Epoch 0/200] [Batch 589/590] [D loss: 1.399173] [G loss: 0.836521] [recon loss: 0.201558]
[2021-09-22 21:04:48,154][train.py][line:181][INFO] images0 saved in ./images/images0.png
[2021-09-22 21:05:15,312][train.py][line:174][INFO] [Epoch 1/200] [Batch 589/590] [D loss: 1.831465] [G loss: 0.627008] [recon loss: 0.163741]
run
python eval.py
Output will be generated in the terminal and will be saved to ./logs/eval.log
[2021-09-22 22:36:11,013][eval.py][line:29][INFO] Namespace(n_epochs=200, batch_size=100, gen_lr=0.0002, reg_lr=0.0001, load=False, N=1200, img_size=28, channels=1, latent_dim=8, std=5, N_train=59000, N_valid=1000, N_test=10000, N_gen=10000, batchsize=100, load_epoch=199, sigma=None)
W0922 22:36:12.574378 66119 device_context.cc:404] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 6.1, Driver API Version: 10.1, Runtime API Version: 10.1
W0922 22:36:12.579428 66119 device_context.cc:422] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
[2021-09-22 22:36:14,076][eval.py][line:40][INFO] model/model199.pkl loaded!
[2021-09-22 22:37:04,696][parzen_ll.py][line:32][INFO] sigma = 0.10000, nll = 134.13950
[2021-09-22 22:37:53,652][parzen_ll.py][line:32][INFO] sigma = 0.10885, nll = 214.54500
The pre-trained model is saved in ./model/model199.pkl in aistudio project, which is the output result of round 199. The model can be quickly evaluated. If there is no split data set in the ./data/ folder, please run datamaker.py first to generate a split data set.
For other information about the model, you can refer to the following table:
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Publisher | Chenxi Zhong |
| Time | 2021.08 |
| Framework version | Paddle 2.1.2 |
| Application scenarios | Data dimensionality reduction |
| Support hardware | GPU, CPU |
| Download link | Pre-training model |
| Online operation | notebook |