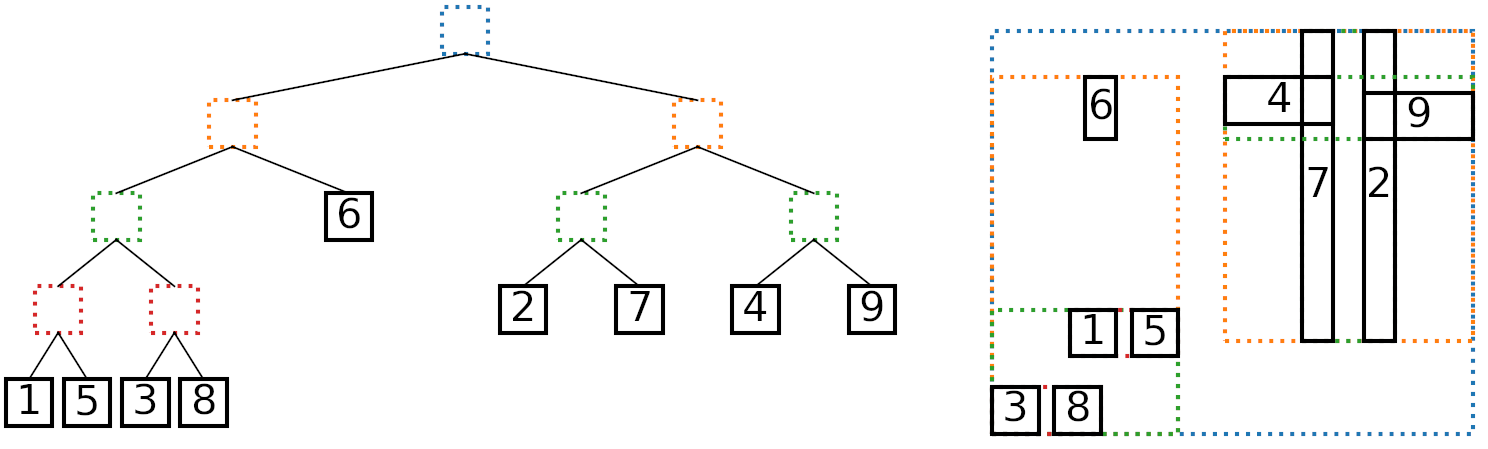
AABBTree is a pure Python implementation of a static d-dimensional axis aligned bounding box (AABB) tree. It is inspired by Introductory Guide to AABB Tree Collision Detection from Azure From The Trenches.
AABBTree is available through PyPI and can be installed by running:
pip install aabbtree
To test that the package installed properly, run:
python -c "import aabbtree"
Alternatively, the package can be installed from source by downloading the latest release from the AABBTree repository on GitHub. Extract the source and, from the top-level directory, run:
pip install -e .
The --user flag may be needed, depending on permissions.
The following example shows how to build an AABB tree and test for overlap:
>>> from aabbtree import AABB >>> from aabbtree import AABBTree >>> tree = AABBTree() >>> aabb1 = AABB([(0, 0), (0, 0)]) >>> aabb2 = AABB([(-1, 1), (-1, 1)]) >>> aabb3 = AABB([(4, 5), (2, 3)]) >>> tree.add(aabb1, 'box 1') >>> tree.does_overlap(aabb2) True >>> tree.overlap_values(aabb2) ['box 1'] >>> tree.does_overlap(aabb3) False >>> tree.add(aabb3) >>> print(tree) AABB: [(0, 5), (0, 3)] Value: None Left: AABB: [(0, 0), (0, 0)] Value: box 1 Left: None Right: None Right: AABB: [(4, 5), (2, 3)] Value: None Left: None Right: None
Documentation for the project is available at https://aabbtree.readthedocs.io.
Contributions to the project are welcome. Please visit the AABBTree repository to clone the source files, create a pull request, and submit issues.
If you use AABBTree in you work, please consider including this citation in your bibliography:
K. A. Hart and J. J. Rimoli, Generation of statistically representative microstructures with direct grain geomety control, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 370 (2020), 113242. (BibTeX) (DOI)
The incremental insertion method is discussed in section 2.2.2 of the paper.
Copyright © 2019-2023, Georgia Tech Research Corporation
AABBTree is open source and freely available under the terms of the MIT license.