This repository has been archived by the owner on Sep 18, 2024. It is now read-only.
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.8k
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
1 parent
3394f2c
commit 57924ca
Showing
32 changed files
with
1,280 additions
and
114 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ | ||
| # 使用 NNI 自动调优系统 | ||
|
|
||
| 随着计算机系统和网络变得越来越复杂,通过显式的规则和启发式的方法来手工优化已经越来越难,甚至不可能了。 下面是使用 NNI 来优化系统的两个示例。 可根据这些示例来调优自己的系统。 | ||
|
|
||
| * [在 NNI 上调优 RocksDB](../TrialExample/RocksdbExamples.md) | ||
| * [使用 NNI 调优 SPTAG (Space Partition Tree And Graph) 参数](SptagAutoTune.md) | ||
|
|
||
| 参考[论文](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3352031)了解详情: | ||
|
|
||
| Mike Liang, Chieh-Jan, et al. "The Case for Learning-and-System Co-design." ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review 53.1 (2019): 68-74. |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,51 @@ | ||
| NNI Compressor 中的 L1FilterPruner | ||
| === | ||
|
|
||
| ## 1. 介绍 | ||
|
|
||
| L1FilterPruner 是在卷积层中用来修剪过滤器的通用剪枝算法。 | ||
|
|
||
| 在 ['PRUNING FILTERS FOR EFFICIENT CONVNETS'](https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08710) 中提出,作者 Hao Li, Asim Kadav, Igor Durdanovic, Hanan Samet 以及 Hans Peter Graf。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| > L1Filter Pruner 修剪**卷积层**中的过滤器 | ||
| > | ||
| > 从第 i 个卷积层修剪 m 个过滤器的过程如下: | ||
| > | ||
| > 1. 对于每个过滤器 ,计算其绝对内核权重之和 | ||
| > 2. 将过滤器按 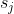 排序。 | ||
| > 3. 修剪 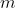 具有最小求和值及其相应特征图的筛选器。 在 下一个卷积层中,被剪除的特征图所对应的内核也被移除。 | ||
| > 4. 为第 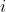 和 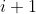 层创建新的内核举证,并保留剩余的内核 权重,并复制到新模型中。 | ||
| ## 2. 用法 | ||
|
|
||
| PyTorch 代码 | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| from nni.compression.torch import L1FilterPruner | ||
| config_list = [{ 'sparsity': 0.8, 'op_types': ['Conv2d'], 'op_names': ['conv1', 'conv2'] }] | ||
| pruner = L1FilterPruner(model, config_list) | ||
| pruner.compress() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### L1Filter Pruner 的用户配置 | ||
|
|
||
| - **sparsity:**,指定压缩的稀疏度。 | ||
| - **op_types:** 在 L1Filter Pruner 中仅支持 Conv2d。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 3. 实验 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们实现了 ['PRUNING FILTERS FOR EFFICIENT CONVNETS'](https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08710) 中的一项实验, 即论文中,在 CIFAR-10 数据集上修剪 **VGG-16** 的 **VGG-16-pruned-A**,其中大约剪除了 $64\%$ 的参数。 我们的实验结果如下: | ||
|
|
||
| | 模型 | 错误率(论文/我们的) | 参数量 | 剪除率 | | ||
| | --------------- | ----------- | -------- | ----- | | ||
| | VGG-16 | 6.75/6.49 | 1.5x10^7 | | | ||
| | VGG-16-pruned-A | 6.60/6.47 | 5.4x10^6 | 64.0% | | ||
|
|
||
| 实验代码在 [examples/model_compress](https://github.com/microsoft/nni/tree/master/examples/model_compress/) | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,23 @@ | ||
| Lottery Ticket 假设 | ||
| === | ||
|
|
||
| ## 介绍 | ||
|
|
||
| [The Lottery Ticket Hypothesis: Finding Sparse, Trainable Neural Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.03635) 是主要衡量和分析的论文,它提供了非常有意思的见解。 为了在 NNI 上支持此算法,主要实现了找到*获奖彩票*的训练方法。 | ||
|
|
||
| 本文中,作者使用叫做*迭代*修剪的方法: | ||
| > 1. 随机初始化一个神经网络 f(x;theta_0) (其中 theta_0 为 D_{theta}). | ||
| > 2. 将网络训练 j 次,得出参数 theta_j。 | ||
| > 3. 在 theta_j 修剪参数的 p%,创建掩码 m。 | ||
| > 4. 将其余参数重置为 theta_0 的值,创建获胜彩票 f(x;m*theta_0)。 | ||
| > 5. 重复步骤 2、3 和 4。 | ||
| 如果配置的最终稀疏度为 P (e.g., 0.8) 并且有 n 次修建迭代,每次迭代修剪前一轮中剩余权重的 1-(1-P)^(1/n)。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 重现结果 | ||
|
|
||
| 在重现时,在 MNIST 使用了与论文相同的配置。 [此处](https://github.com/microsoft/nni/tree/master/examples/model_compress/lottery_torch_mnist_fc.py)为实现代码。 在次实验中,修剪了10次,在每次修剪后,训练了 50 个 epoch。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 上图展示了全连接网络的结果。 `round0-sparsity-0.0` 是没有剪枝的性能。 与论文一致,修剪约 80% 也能获得与不修剪时相似的性能,收敛速度也会更快。 如果修剪过多(例如,大于 94%),则精度会降低,收敛速度会稍慢。 与本文稍有不同,论文中数据的趋势比较明显。 |
Oops, something went wrong.