This repository has been archived by the owner on Sep 1, 2023. It is now read-only.
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.6k
Added anomaly detection guide #3521
Merged
Merged
Changes from all commits
Commits
Show all changes
2 commits
Select commit
Hold shift + click to select a range
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Failed to load comments.
Loading
Jump to
Jump to file
Failed to load files.
Loading
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,80 @@ | ||
| # Anomaly Detection | ||
|
|
||
| This technical note describes how the anomaly score is implemented and incorporated into the CLA (Cortical Learning Algorithm). | ||
|
|
||
| The anomaly score enables the CLA to provide a metric representing the degree to which each record is predictable. For example, if you have temporal anomaly model that is predicting the energy consumption of a building, each record will have an anomaly score between zero and one. A zero represents a completely predicted value whereas a one represents a completely anomalous value. | ||
|
|
||
| The anomaly score feature of CLA is implemented on top of the core spatial and temporal pooler, and don’t require any spatial pooler and temporal pooler algorithm changes. | ||
|
|
||
| ## TemporalAnomaly model | ||
|
|
||
| ### Description | ||
|
|
||
| The user must specify the model as a TemporalAnomaly type to have the model report the anomaly score. The anomaly score uses the temporal pooler to detect novel points in sequences. This will detect both novel input patterns (because they have not been seen in any sequence) as well as old spatial patterns that occur in a novel context. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Computation | ||
|
|
||
| A TemporalAnomaly model calculates the anomaly score based on the correctness of the previous prediction. This is calculated as the percentage of active spatial pooler columns that were incorrectly predicted by the temporal pooler. | ||
|
|
||
| The algorithm for the anomaly score is as follows: | ||
|
|
||
| 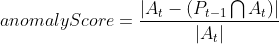 | ||
|
|
||
| 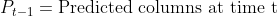 | ||
|
|
||
| 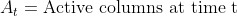 | ||
|
|
||
| __Note__: Here, a "predicted column" is a column with a non-zero confidence value. This is not exactly the same as having a cell in the predicted state. For more information, refer the "predicted cells vs. confidences" section below. | ||
|
|
||
| Thus, an anomaly score of 1 means that no predicted cells became active and represents a completely anomalous record. A score of 0 means all predicted cells became active and represents a completely predicted record. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Rationale | ||
|
|
||
| The reasoning behind this formulation of the anomaly score was that any record that is not predicted is a novel record. This holds if we have built the best predictive model possible, which we assume we have done via training/swarming. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Results | ||
|
|
||
| This anomaly score has been applied to many datasets. It is the core mechanism used in Numenta's commercial product Grok. In some cases you need to take a moving average of the anomaly score rather than just looking at the raw anomaly score. In NuPIC the example `examples/opf/clients/hotgym_anomaly` provides a good starting point to anomaly detection. See also [this set of examples](https://github.com/subutai/nupic.subutai/tree/master/swarm_examples) for swarming with anomaly detection models. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ### Confidences vs. Predicted Cells | ||
|
|
||
| #### Description | ||
|
|
||
| To compute the temporal anomaly score, the intention was to compute a normalized count of how many columns were active and not predicted. As an implementation shortcut, the set of predicted columns was computed by looking at columns with non-zero column "confidences." | ||
|
|
||
| However, it was later discovered that columns with non-zero confidences don’t necessarily have any predicted cells in them. To figure out if a cell is in the predicted state, we use the hard match count (the number of active synapses, after taking into account the permanence threshold). However, to compute the confidences for a cell, the Temporal Pooler uses the soft match count (the number of active synapses, regardless of the permanence values). Therefore, the set of columns with non-zero confidences will always be a superset of the columns containing predicted cells. | ||
|
|
||
| When this difference was discovered (~April 2013), an option was added to the CLA to compute the anomaly score based on the predicted cells rather than using confidences. | ||
|
|
||
| #### Results | ||
|
|
||
| Some experiments using the predicted cells to compute the anomaly score were run on some experiments. However, because these predictions are a subset of the columns with non-zero confidences, the results necessarily had more false positives. As of the time of writing, no change has been made to the computation of the anomaly score based on these results. The anomaly score is still computed using column confidences. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Non-Temporal Anomaly Detection | ||
|
|
||
| ### Description | ||
|
|
||
| There were also some attempts at adding anomaly detection that are "non-temporal" in nature by using the state of the spatial pooler. A non-temporal anomaly is defined as a combination of fields that doesn’t usually occur, independent of the history of the data. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Computation | ||
|
|
||
| Since NontemporalAnomaly models have no temporal pooler, the anomaly score is based on the state within the spatial pooler. | ||
|
|
||
| To compute the nontemporal anomaly score, we first compute the "match" score for each winning column after inhibition | ||
|
|
||
| 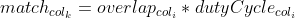 | ||
|
|
||
| Then, to get the anomaly score (how unusual the data is), we take the inverse of the total matches | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| The addition of 1 is to avoid divide by 0 errors. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Rationale | ||
|
|
||
| The purpose of this anomaly score was to detect input records that represented novel or rare input patterns (independent of the rest of the sequence). If an input pattern has a low overlap score with the winning columns, none of the columns match the input very well, indicating that the CLA has not seen a similar pattern before and this pattern is novel. Conversely, if they duty cycles for a given pattern are generally low, this indicates that a pattern has not been seen for a long time, indicating that it is rare. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Results | ||
|
|
||
| This algorithm was run on some artificial datasets. However, the results were not very promising, and this approach was abandoned. From a theoretical perspective the temporal anomaly detection technique is a superset of this technique. If a static pattern by itself is novel, by definition the temporal pooler won't make good predictions and hence the temporal anomaly score should be high. As such there was not too much interest in pursuing this route. | ||
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -7,3 +7,4 @@ Guides | |
| opf | ||
| network | ||
| swarming/index | ||
| anomaly-detection | ||
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Is there any chance we can cache and host these images ourselves?
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Yeah, good idea. I can do that with my next docs push.