TechnicPF is an Arduino library for controlling Power Functions motors.
Author: Dmitry Akulov pink0D.github@gmail.com
The example included in this library is for demonstration purposes only. The example hardware and the library itself DO NOT INCLUDE any kind of battery discharge protection. Since electric motors consume quite a lot of power, this can lead to permament damage to Li-ion/LiPo batteries if there's no such protection. For a real application please consider adding discharge control or use batteries with integrated protection curcuit.
- Supported motors
- Library istallation
- Basic Power Functions motors
- GeekServo
- Mould King Servo proportional control
- Bluetooth gamepad controller example
The library supports several types of motors:
- Original PF Motors (including proportional Servos)
- PF Simple motors (M/L/XL-motors)
- PF Servo Motors (which usually have only 3 positions: -90 / 0 / +90)
- Mould King Servo motors (which normally also have just 3 positions, however this library introduces support for fully proportional steering)
- GeekServo (Technic-compatible motors with 3-wire plug)
Copy contents of this repo to <Worspace folder>/libraries/TechnicPF
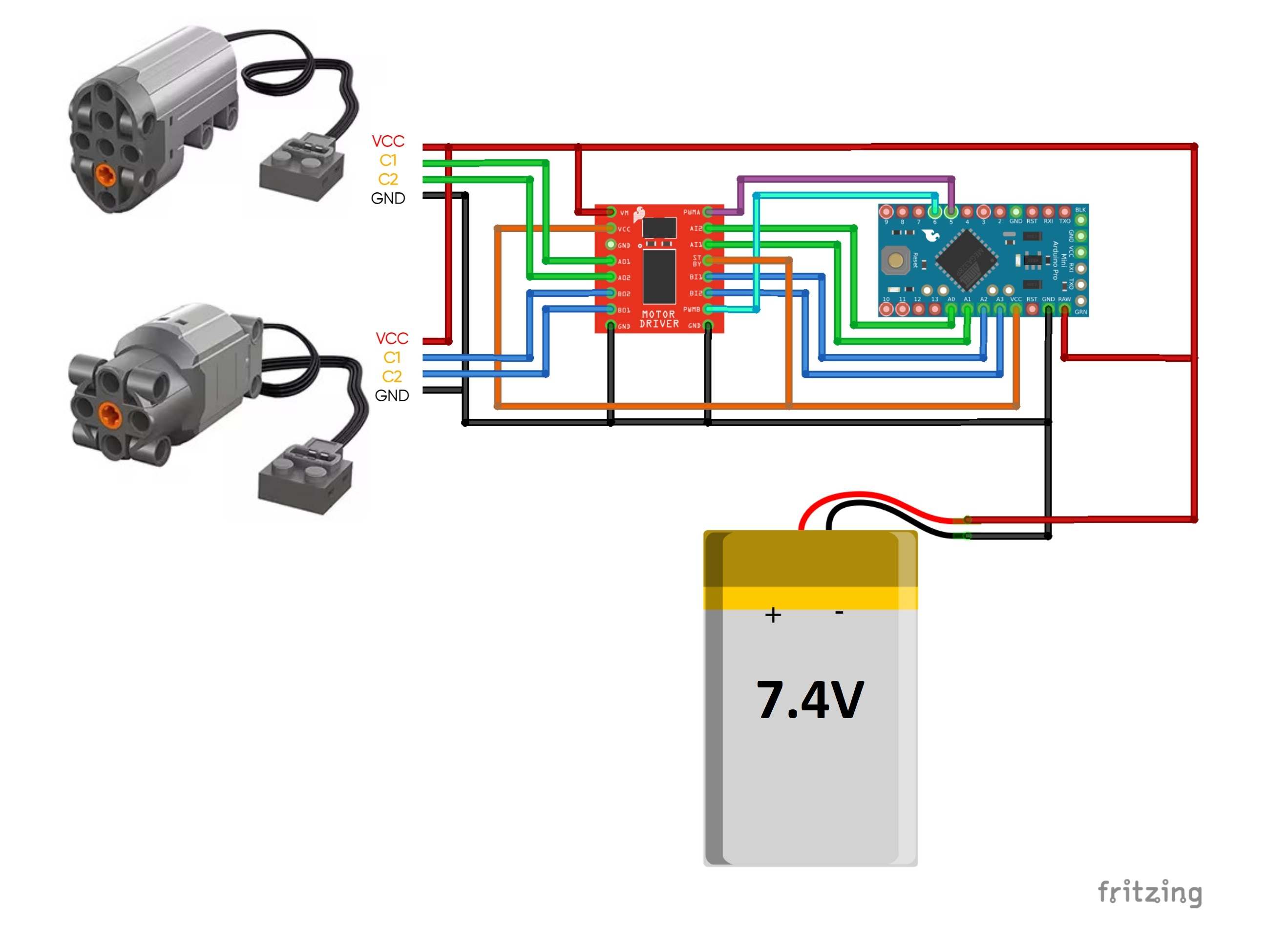
For basic use of Power Functions motors you will need:
- Arduino Board
- TB6612FNG motor driver
- 7.4V LiPo battery
- Any PF compatible motors
More details on Power Functions and PF-plug pinout are available on Philo's site:
Add the following code to your sketch:
// library includes
#include <PFMotor.h>
// default pins
#include <PinConfig.h>
// if your installation is using different pinout, copy the default config to your project and redefine pins
// #include "PinConfig.h"
// define motor instance
PFMotor motor;
void setup() {
...
motor.begin(MOTOR_A);
// when using original PF motors, this option is recommended both for Servo and M/L/XL motors
// motor.begin(MOTOR_A, PWM_FIXED_15_POSITIONS); // PF with 15-positions (almost proportional)
// when using PF-compatible servo-motor, this option is recommended to avoid fluttering and power drain issues
// motor.begin(MOTOR_A, PWM_FIXED_3_POSITIONS); // PF with 3-positions (-90 / 0 / +90)
...
}
void loop() {
...
// when needed, set motor rotation speed:
// any value in -1.0 .. +1.0 range, 1.0 = full speed, 0.5 = half speed, zero value (0.0) stops the motor
// positive/negative values set rotation direction.
// for a servo: 1.0 = 90 degree rotation, 0.5 = 45 degree rotation, 0 = zero position, -1.0 = -90 degree rotation
double speed_control = 1.0;
bool brake = false; // set to true to brake the motor (the driver shorts motor brushes which results to a fast stop)
motor.update_motor(speed_control,brake);
...
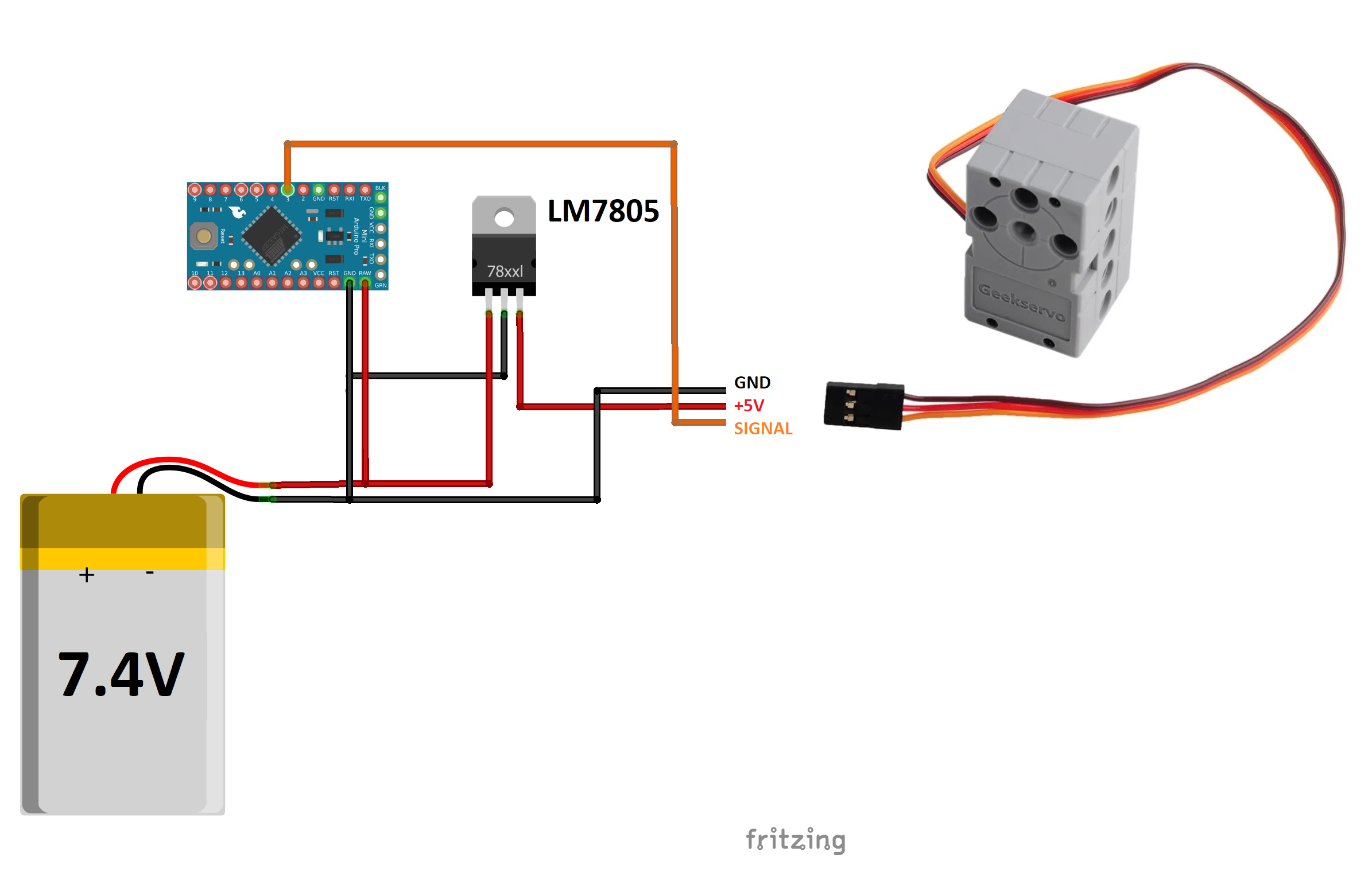
}GeekServo is a standard 3-wire Servo with Technic bricks compatible housing. By specification, GeekServo has 3.3V to 6V operating voltage, so you will need a voltage regulator. Unofficially, GeekServo can be powered directly with 2S (7.4V) LiPo battery (but use this setup at your own risk).
Code:
// library includes
#include <GeekServo.h>
// default pins
#include <PinConfig.h>
// if your installation is using different pinout, copy the default config to your project and redefine pins
// #include "PinConfig.h"
// define motor instance
GeekServo servo;
void setup() {
...
// basic setup for a servo with 1000..2000 microseconds signals for -90..+90 rotation
servo.begin(GEEK_SERVO);
// GeekServo 360 supports wider range: 500..2500 microseconds for -180..+180 rotation
// servo.begin(GEEK_SERVO,500,2500);
...
}
void loop() {
...
// any value in -1.0 .. +1.0 range
// positive/negative values set rotation direction.
// for a servo: 1.0 = maximum rotation, 0.5 = half rotation, 0 = zero position, -1.0 = maximum rotation in other direction
double rotation = 1.0;
servo.update_motor(rotation);
...
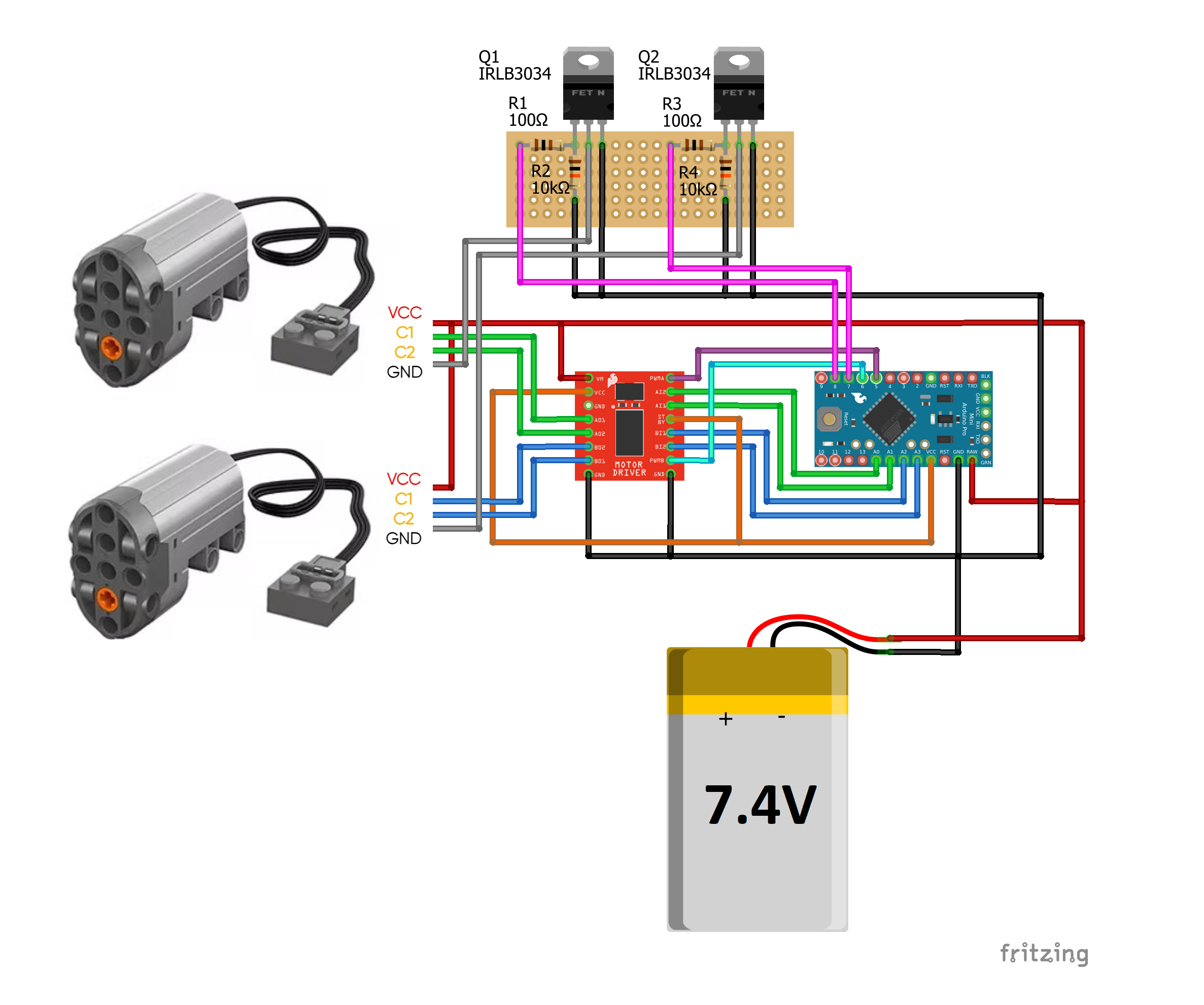
}Mould King Servos by default have only 3 fixed positions (-90, 0 and +90 rotation) when connected to control hubs. However, by sending a correct PWM signal, it is possible to make it rotate in a proportional way. There are also some side effects, including motor fluttering and hence significant power drain. This library provides a solution for proportional control of Mould King Servo Motor:
- Sending correct PWM signals to MK Servo
- Disconnecting power supply from the motor when it does not need to rotate, and connecting the power again before moving to a new position
To achive this, the hardware setup contatins N-channel MOSFETs, along with some resistors (100 Ohm and 10 kOhm). You can choose any N-channel MOSFET that can be driven by 3.3V logic. To reduce soldering time, you can use power control circuit just for one motor, and connect GND pin of the second motor directly to PCB's GND.
More details about this solution in my video on Youtube
Code:
// library includes
#include <MKServo.h>
// default pins
#include <PinConfig.h>
// if your installation is using different pinout, copy the default config to your project and redefine pins
// #include "PinConfig.h"
// define motor instance - MKServo class contain special logic for proportional control
MKServo servo;
void setup() {
...
// MKServo initialization
servo.begin(MOTOR_A);
...
}
void loop() {
...
// any value in -1.0 .. +1.0 range
// positive/negative values set rotation direction.
// for a servo: 1.0 = maximum rotation, 0.5 = half rotation, 0 = zero position, -1.0 = maximum rotation in other direction
double rotation = 1.0;
servo.update_motor(rotation);
...
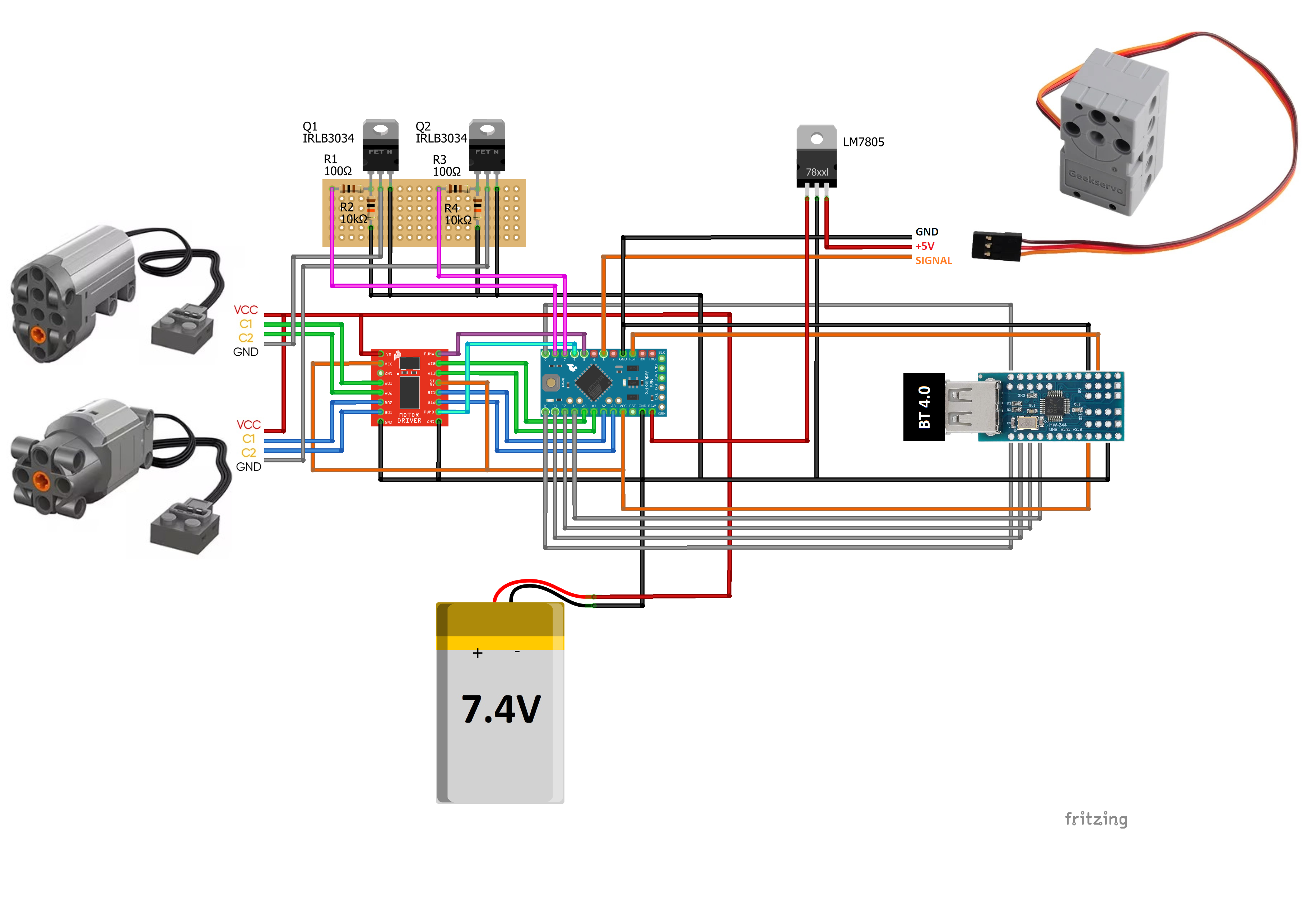
}The example project demostrates how to use the library and control Technic motors with a Bluetooth gamepad. Components required:
- Arduino Pro Mini 3.3V
- Mini USB Host Shield 3.3V
- USB Bluetooth 4.0 dongle
- Bluetooth gamepad
- TB6612FNG motor driver
- LM7805 voltage regulator (optional for GeekServo)
- IRLB3034 or similar N-channel MOSFET + 100 Ohm + 10kOhm resistors (needed only for Mould King Servo proportional control)
- 7.4V LiPo battery
To reduce soldering time, you can:
- exclude LM7805 if you do not plan to use the GeekServo (or if you will use direct 7.4V power supply for it)
- include only one power control circuit for PF motors or even connect PF motors directly to PCB's GND if you do not need proportional control fo Mould King Servos
More examples for other Bluetooth gamepads are available in USB_Host_Shield_2.0 library
//
// Copyright (c) Dmitry Akulov. All rights reserved.
//
// Repository info: https://github.com/pink0D/TechnicPF
// Contact information: pink0D.github@gmail.com
//
// Licensed under the MIT license. See LICENSE file in the project root for details.
//
#include <PS4BT.h>
#include <PFMotor.h>
#include <GeekServo.h>
#include <MKServo.h>
//
// define pins
//
#include "PinConfig.h"
//
// PlayStation style controls
//
#define INPUT_STEER LeftHatX
#define INPUT_ACCELERATOR R2
#define INPUT_BRAKE L2
#define INPUT_REVERSE TRIANGLE
#define INPUT_DEADZONE 10
#define INPUT_MAX 255
#define STEERING_MAX_ANGLE 90 // used to limit max servo rotation angle
//
// Controller setup
//
// for details about connecting Bluetooth devices to Arduino, please refer to
// examples https://github.com/felis/USB_Host_Shield_2.0
//
USB Usb;
BTD Btd(&Usb);
PS4BT controller(&Btd, PAIR); // always start in pairing mode
//PS4BT controller(&Btd); // not working...
//
// Technic motors setup
//
PFMotor motor; // Motor A - PF Large motor
GeekServo servo; // GeekServo - 3-wire servo
//MKServo servo; // Motor B - MK Servo
//PFMotor servo; // Motor B - PF Servo
bool reverse = false;
double input_to_steering(int input) {
double limit = (((double)STEERING_MAX_ANGLE) / 90.0);
if (input < INPUT_DEADZONE)
return -limit; // full left
if (input > INPUT_MAX - INPUT_DEADZONE)
return limit; // full right
if (abs(INPUT_MAX / 2 - input) < INPUT_DEADZONE)
return 0; // center
return (2.0 * ( (double) input ) / ( (double) INPUT_MAX) - 1) * limit; // calculate
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
motor.begin(MOTOR_A);
servo.begin(GEEK_SERVO);
//servo.begin(MOTOR_B); // MK Servo with proportional control
//servo.begin(MOTOR_B, PWM_FIXED_3_POSITIONS); // PF with 3-positions (-90 / 0 / +90)
//servo.begin(MOTOR_B, PWM_FIXED_15_POSITIONS); // PF with 15-positions (almost proportional)
// init Bluetooth
if (Usb.Init() == -1) {
Serial.println("Bluetooth did not start");
while (1); // halt
}
Serial.println("Startup OK");
}
void loop() {
// get updates from controller
Usb.Task();
if (controller.connected()) {
// get inputs from controller
double accelerator = ((double) controller.getAnalogButton(INPUT_ACCELERATOR)) / ((double) INPUT_MAX);
double steer = input_to_steering(controller.getAnalogHat(INPUT_STEER));
bool brake = controller.getAnalogButton(INPUT_BRAKE) > INPUT_DEADZONE;
if (controller.getButtonClick(INPUT_REVERSE))
reverse = !reverse;
if (reverse)
accelerator = -accelerator;
// update motor outputs
motor.update_motor(accelerator,brake);
servo.update_motor(steer);
}
}