Este es un ejemplo de como crear servicios REST usando el Spring Framework 5 con Spring Boot 2 para un CRUD de Clientes
-
Es necesario tener instalado MySQL y MySQL Workbench
-
Ingresamos como root a MySQL y creamos un nuevo usuario, con las siguientes sentencias SQL:
CREATE USER 'springstudent'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'springstudent';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO 'springstudent'@'localhost';- Creamos una base de datos o schema llamada 'web_customer_tracker' y posteriormente la tabla 'customer', agregamos el siguiente código:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `web_customer_tracker` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */;
USE `web_customer_tracker`;
-- MySQL dump 10.13 Distrib 5.6.13, for osx10.6 (i386)
--
-- Host: 127.0.0.1 Database: web_customer_tracker
-- ------------------------------------------------------
-- Server version 5.6.16
/*!40101 SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT=@@CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS=@@CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_COLLATION_CONNECTION=@@COLLATION_CONNECTION */;
/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
/*!40103 SET @OLD_TIME_ZONE=@@TIME_ZONE */;
/*!40103 SET TIME_ZONE='+00:00' */;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS=@@UNIQUE_CHECKS, UNIQUE_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@@FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS, FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_SQL_MODE=@@SQL_MODE, SQL_MODE='NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO' */;
/*!40111 SET @OLD_SQL_NOTES=@@SQL_NOTES, SQL_NOTES=0 */;
--
-- Table structure for table `customer`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customer`;
/*!40101 SET @saved_cs_client = @@character_set_client */;
/*!40101 SET character_set_client = utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `customer` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
/*!40101 SET character_set_client = @saved_cs_client */;
--
-- Dumping data for table `customer`
--
LOCK TABLES `customer` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `customer` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `customer` VALUES
(1,'David','Adams','david@info.com'),
(2,'John','Doe','john@info.com'),
(3,'Ajay','Rao','ajay@info.com'),
(4,'Mary','Public','mary@info.com'),
(5,'Maxwell','Dixon','max@info.com');
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `customer` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
/*!40103 SET TIME_ZONE=@OLD_TIME_ZONE */;
/*!40101 SET SQL_MODE=@OLD_SQL_MODE */;
/*!40014 SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS */;
/*!40014 SET UNIQUE_CHECKS=@OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS */;
/*!40101 SET CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT=@OLD_CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT */;
/*!40101 SET CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS=@OLD_CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS */;
/*!40101 SET COLLATION_CONNECTION=@OLD_COLLATION_CONNECTION */;
/*!40111 SET SQL_NOTES=@OLD_SQL_NOTES */;
-- Dump completed on 2016-09-24 21:50:59
-
Descargamos el proyecto base desde el siguiente enlace: https://udlaec-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/ronald_arias_udla_edu_ec/EctAuYT1xhtPtQNRXT4Km8UBQSGrlbCUG3nb2CXvUGO1eA?e=Q7evTT
-
Abrimos Eclipse, STS, NetBeans o cualquier IDE Java que sea de su agrado para importar el proyecto descargado.
-
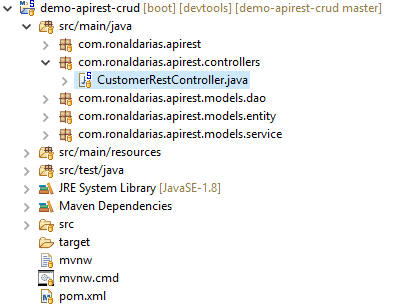
Agregamos la Clase CustomerRestController dentro del paquete controllers, como se ve en la siguiente imagen:
- Escribir el siguiente código en el controlador:
package com.ronaldarias.apirest.controllers;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.ronaldarias.apirest.models.entity.Customer;
import com.ronaldarias.apirest.models.service.CustomerService;
@CrossOrigin(origins = {"http://localhost:4200"})
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class CustomerRestController {
// injection dependency
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@GetMapping("/customers")
public List<Customer> getCustomers() {
return customerService.getCustomers();
}
@GetMapping("/customers/{customerId}")
public Customer getCustomer(@PathVariable int customerId) {
Customer customer = customerService.getCustomer(customerId);
return customer;
}
// add mapping for POST /customers - add new customer
@PostMapping("/customers")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public Customer addCustomer(@RequestBody Customer customer) {
// also just in case the pass an id in JSON ... set id to 0
// this is force a save of new item ... instead of update
customer.setId(null);
customerService.saveCustomer(customer);
return customer;
}
// add mapping for PUT /customers - update existing customer
@PutMapping("/customers")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public Customer updateCustomer(@RequestBody Customer customer) {
customerService.saveCustomer(customer);
return customer;
}
//add mapping for DELETE /customers/{customerId} - delete existing customer
@DeleteMapping("/customers/{customerId}")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT)
public void deleteCustomer(@PathVariable int customerId) {
customerService.deleteCustomer(customerId);
}
}-
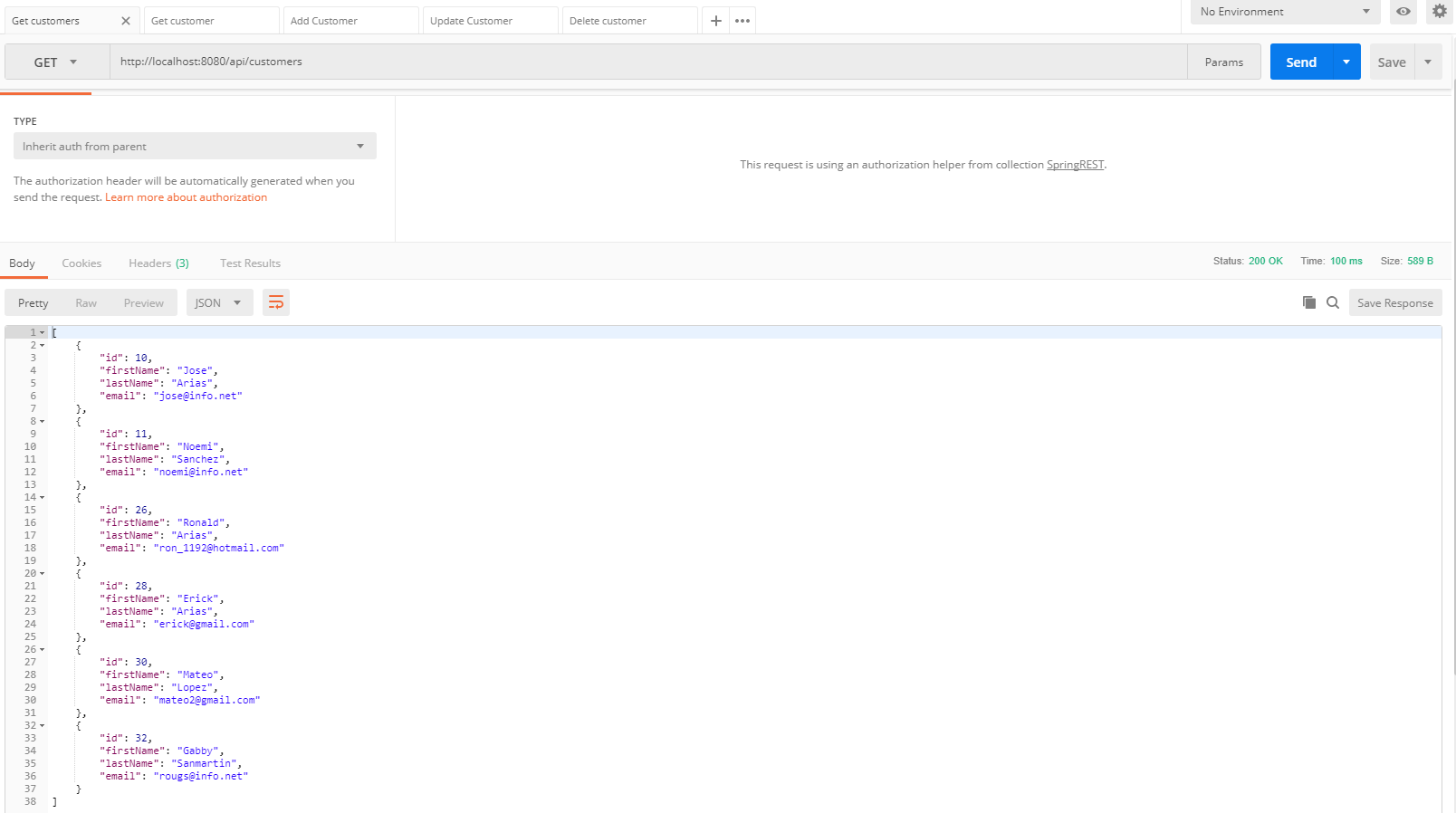
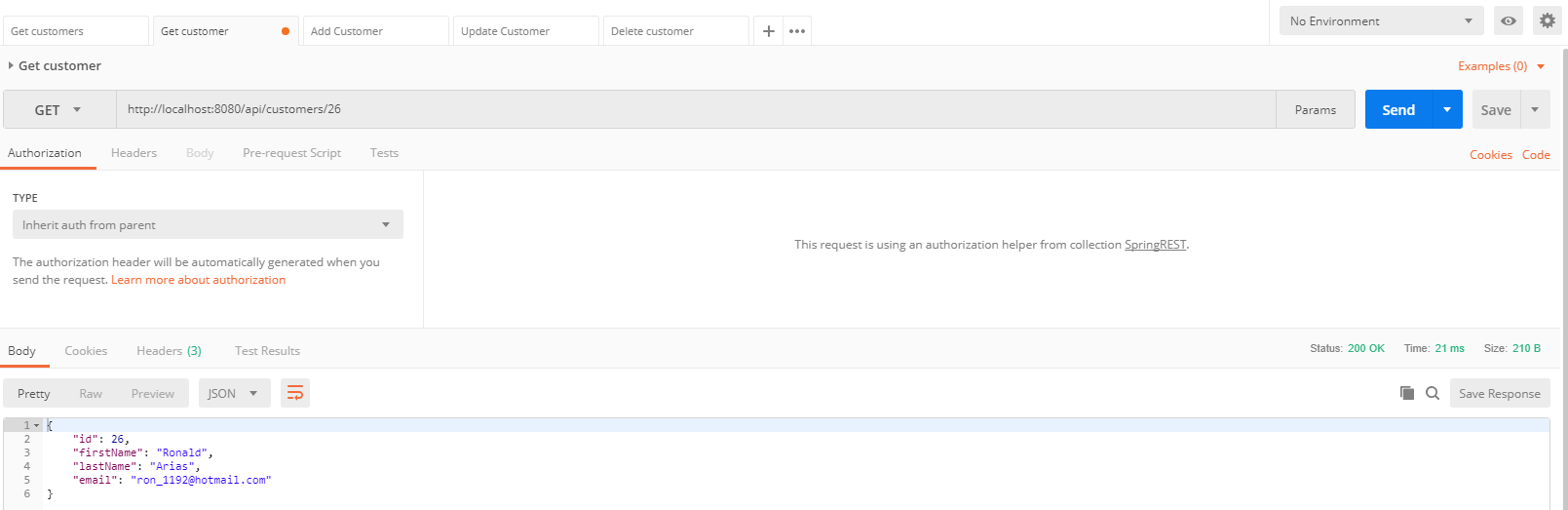
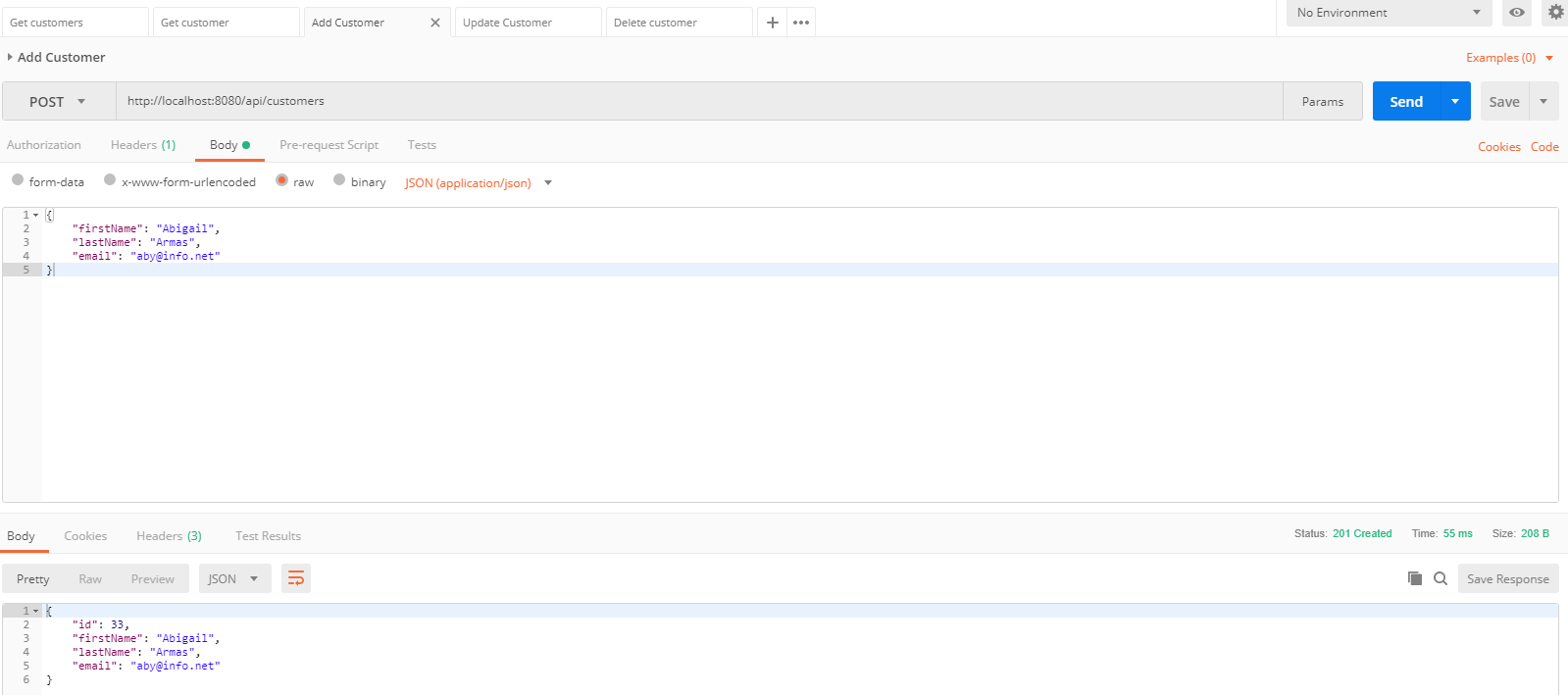
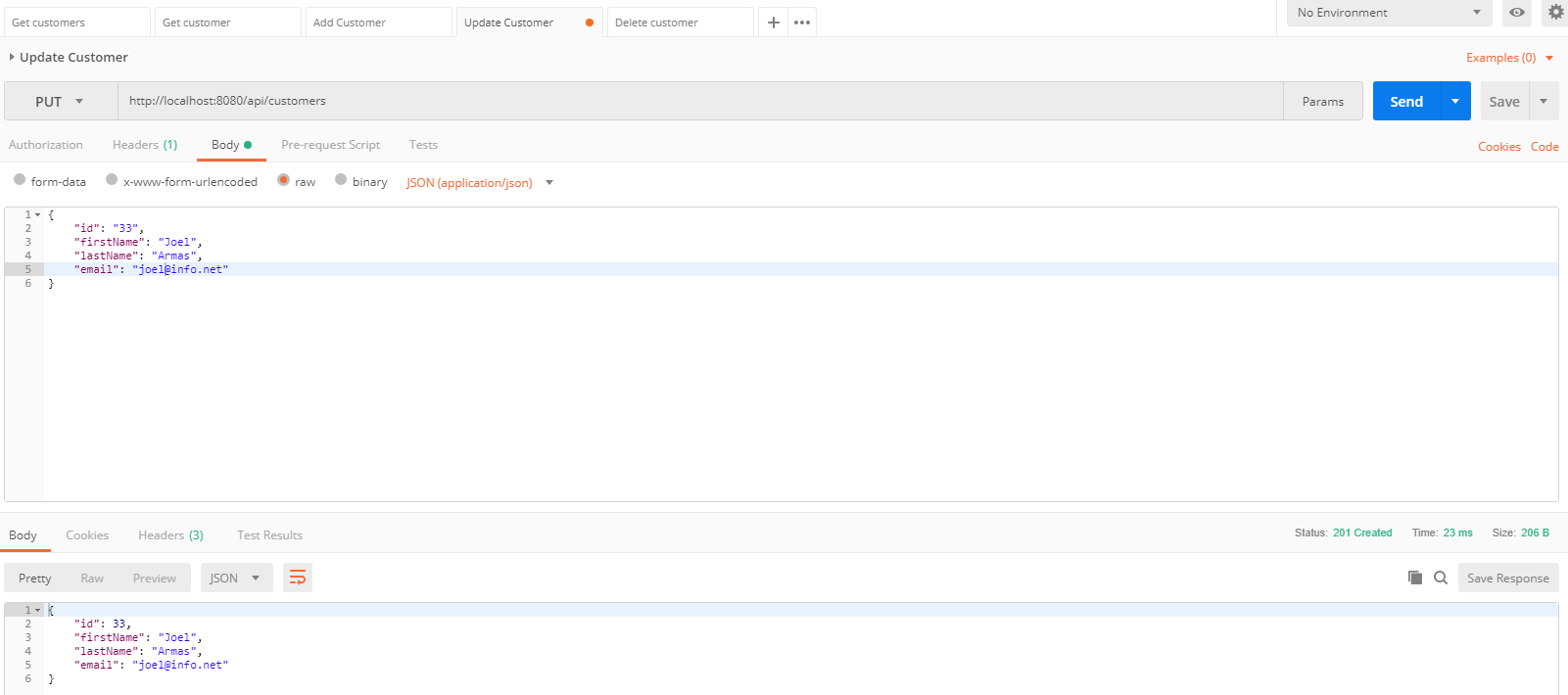
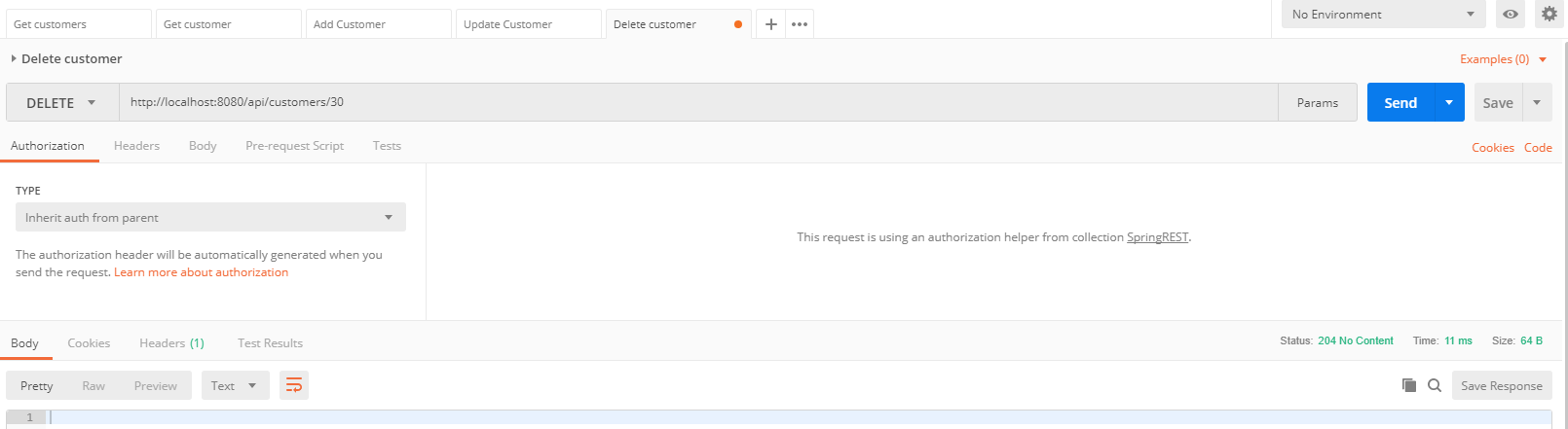
Probamos los servicios web con el programa Postman
- Como vemos, los servicios web funcionan correctamente, si lo desean, pueden descargar o clonar este proyecto.