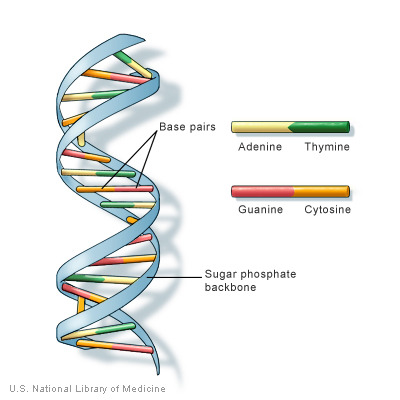
DNA is the code in which all life is written. Inside of each of our cells is a blueprint for who we are (of course, who we are also depends on our environment). Using computers to 'crack the genetic code' is one of the biggest challenges of our time, and an important field of research known as bioinformatics.
While there's a lot to learn about DNA, the quick and dirty explanation is this: Inside each cell's nucleus is DNA, which consists of two strands of chemical bases that match each other in a very particular way.
According to the National Institutes of Health:
The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to the way in which letters of the alphabet appear in a certain order to form words and sentences. DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs.
The field of bioinformatics deals with the intersection of biology and computer science. Researchers and developers write code to look for patterns and trends in huge amounts of data from genetic sequencing, in order to identify traits, ancestry, markers for diseases, and much more.
The string below consists of a small snippet of a DNA sequence. Your job is to run some basic bioinformatics analysis on the data to look for patterns and data!
"AATCGCCCAAGACAACATGGGGTTGCAGGTGTAAATCGATAAAAGAAGGGGTAGGTATCGTTCACGGGGCACACTACTAGCGGGGCTTAGATAGCAAACTAGGGGTTCTTCACGCAGCGCAAGACACATGCGCTATAAATGCTAGATCAACTGACATTATACTTATCAATGGGGAATAGGTCAGATAGATGGCACCACCATCGCACACTTATAGGCACGTCACCTGAGCCGACTCGAAATCCGCTTAGTACTGCGACAAAATCATCCGCTCGGTTGATCTAGGATCGGGACTATATCGCAGCGCCCTAGCTCATTCTCACACGTGGAGGGAGCGACGAATGCTCAGCGAGGAGTTGTTCTGACCCGTGACGGAGTACTCTTTACTATCAAGTATAGGCCAGTCTTGCCCCGATCGCTATACATTATTTGATGCCCCCATAGCCGCAGTCATTCGACAGATTAGGCCCACCACCACCTCCCCTTGAGATTGGCTGCATCTACTGTTCAGTCTAATCGCAACTAGCAACATTACGGAAGAAGGGCTACTCTAGATTGTCGCGTACAAGGTTTACCAAAGTGCATAAATCGACGGCCCCTCACGTGCGGCCGTTGGCAAGAGCAACTAAACGCCGGAAGACCCACGCCAATACAGTTCCGCGCCACGGAGGTAACTTACATGCGCGCTCCCCGGTTTACGGGTCATGCCTACCCCTCGGCATTCATGGGACTCAAACCTATCCCCGCAGCCGGAGCTTAAGAAAGAGCTAACACTTAGTTCGCATTCAAAATCGGTAAATTAATTAACATGCCGCAACGCGTCTAGACTACTCCCCGCTTTGCGTTCACCAACGTCCCGAGTTTTAACCTAGAAGCATATGTGCTGACCGTTAGCATACGGTGTTCATCACTCTCGCGATCTCGTCAACTTGGCCATCGCCATCTGGTGGACCCCGGAATCAAAGCTGCTGACTAGAGGCGTTG"
-
How long is the string?
-
How many adenine symbols ('A')?
-
How many guanine symbols ('G')?
-
How many cytosine symbols ('C')?
-
How many thiamine symbols ('T')?
-
How many times does the snippet GAT appear in the string?
-
An RNA string is a string formed from the alphabet containing 'A', 'C', 'G', and 'U'. Return a string with all 'T's replaced with 'U's (U stands for Uracil)
-
The 'complement' of a strand of DNA is what the opposing strand looks like. (Replace A with T, T with A, G with C, and C with G). For example: the complement of ATCGA is TAGCT. Find the complement to the sequence provided
-
The 'reverse complement' of DNA is the complement (see above) of a strand that is also reversed. Example: ATCGGG has a reverse complement of CCCGAT. Find the reverse complement of the string!
- A mutation is a change in the genetic sequence, when one or more base pairs are replaced by another. The 'Hamming Distance' is the number of symbols that differ between two strings.
Example: String 1: "ATCGA" String 2: "GTCGT"
Hamming distance: 2 (the first and last character are different)
Here is a string of a second sequenced section of DNA - calculate the hamming distance (number of changes) between the first and second sequences!
"AATCGCCCAAGACATCATGGGGTTGCAGGTGTAAATCGATAAAAGAAGGGGTAGGTATCGTTCACGGGGCACACTACTAGCGGGGCTTAGATAGCAAACTAGGGGTTCTTCACGCAGCGCAAGACACATGCGCTATAAATGCTAGATCAACTGACATTATACTTATCAATCGGGTATAGGTCAGATAGATGGCACCACCATCGCACACTTATAGGCACGTCACCTGAGCCGACTCGAAATCCGCTTAGTACTGCGACAAAATCATCCGCTCGGTTGATCTAGGATCGGGACTATATCGCAGCGCCCTAGCTCATTCTCACACGTGGAGGGAGCGACGAATGCTCAGCGAGGAGTTGTTCTGACCCGTGACGGAGTACTCTTTACTATCAAGTATAGGCCAGTCTTGCCCCGATCGCTATACATTATTTGATGCCCCCATAGCCGCAGTCATTCGACAGATTAGGCCCACCACCACCTCCCCTTGAGATTGGCTGCATCTACTGTTCAGTCTATTCGCAACTAGCAACATTACGGAAGAAGGGCTACTCAAGATTGTCGCGTACAAGGTTTACCAAAGTGCATAAATCGACGGCCCCTCACGTGCGGCCGTTGGCAAGAGCAACTAAACGCCGGAAGACCCACGCCAATACAGTTCCGCGCCACGGAGGTAACTTACATGCGCGCTCCCCGGTTTACGGGTCATGCATACCCCTCGGCATTCATGGGACTCAAACCTATCCCCGCAGCCGGAGCTTAAGAAAGAGCTAACACTTAGTTCGCATTCAAAATCGGTAAATTGATTAACATGCCGCAACGCGTCTAGACTACTCCCCGCTTTGCGTTCACCAACGTCCCGAGTTTTAACCTAGATGCATATGTGCTGACCGTTAGCATAGGGTGTTCATCACTCTCGCGATCTCGTCAACTTGGCCATCGCCATCTGGTGGACCCCGGAATCAAAGCTGCTGACTAGAGGCGTTG"