445.《Out-of-Domain Intent Detection Considering Multi-Turn Dialogue Contexts》
444.《A Survey of Query Optimization in Large Language Models》
腾讯机器学习平台部的一个关于query优化的survey。
- query扩展。
- 内部扩展。
- 外部扩展。
- query分解。
- query消歧。
- query抽象。
443.《Conversational Recommender System and Large Language Model Are Made for Each Other in E-commerce Pre-sales Dialogue》
讨论了LLM和CRS之间的相互作用用于电商导购场景。
442.《ChatQA: Surpassing GPT-4 on Conversational QA and RAG》,投了NeurIPS 2024
文章讨论了多轮对话场景下的模型微调问题,包括如下:
(1)多轮对话作为input,通过两阶段微调一个retriever
(2)针对unanswerable的模型微调
工作不复杂,但是工作量有的。数据和prompt也给的比较足。
441.COLING2025的几个工作,用LLM做传统NLP的工作
-
《A Zero-Shot Open-Vocabulary Pipeline for Dialogue Understanding》
-
《Large Language Models as Zero-Shot Keyphrase Extractors- A Preliminary Empirical Study》
-
《Match, Compare, or Select? An Investigation of Large Language Models for Entity Matching》
-
《Retrieval Augmented Instruction Tuning for Open NER with Large Language Models》
-
《Advancing Single- and Multi-task Text Classification through Large Language Model Fine-tuning》
440.《Question-Based Retrieval using Atomic Units for Enterprise RAG》
439.《Semantic Retrieval at Walmart》
438.百度搜索中的两篇关于预训练语言模型的文章
-
《Pre-trained Language Model for Web-scale Retrieval in Baidu Search》
-
《Pre-trained Language Model based Ranking in Baidu Search》
437.好久没更新,更新一些近期的笔记。
《Enhancing Asymmetric Web Search through Question-Answer Generation and Ranking》
《FIRST: Faster Improved Listwise Reranking with Single Token Decoding》
436.《meta-chunking:learning efficient text segmentation via logical perception》
两种chuncking方法,如下:
-
margin sampling chunking:classification based on model
-
perplexity chunking: perplexity distribution
现在对这种工作不是很感兴趣。
435.《A Survey of Conversational Search》
一篇关于对话式搜索的综述文章,主要包含四个部分,分别如下:
- query reformulation(包含query改写,query扩展等问题)
- search clarification(该部分是对话式搜索部分所特有的,主要是由对话系统中的两个问题带来的:指代和省略。进一步地,是对话场景中,上下文理解的一部分。ai search的产品设计中,通过prompt可以解决部分问题)
- conversational retrieval
- response generation
整体上的思路和ai search的研发范式相似,或者是一个检索式问答系统。
434.《Late Chunking:Contextual Chunk Embeddings Using Long-Context Embedding Models》
在对于long context的文本进行切分时,在包含指代的情况下,会导致缺失被指代的对象的context信息。本质上是因为在token级做了chunk。怎么解决?那就不要在token上做chunk,而是:
(1)整个文本做embedding
(2)按照切分逻辑去切embedding
核心的motivation比较清晰简单。如下:
433.《Enhancing Asymmetric Web Search through Question-Answer Generation and Ranking》,KDD2024
其实也是自己比较早的一个想法了,思路也比较直接。相关文章:《Self-QA: Unsupervised Knowledge Guided Language Model Alignment》
insight:query去和document做匹配,是一个非对称问题。那么简单点的做法是,做成对称的问题就可以。怎么搞?从document中产生question。这个事情也不麻烦,self-instruction也搞了差不多两年了吧。。。本质上其实是给document 建立一个index结构,无非不是inverted index而已。
两个阶段,分别是offline和online阶段,如下:
offline:根据document建立qa对。整体上分为三个小步骤,(1)从document中筛选core段落(2)利用llm从core段落中生成question和answer(3)通过计算qa对和core段落的相关性做进一步的筛选
online:ranking。通过计算query和question的相关性以及和content的相关性等,做ranking。这里作者针对如何融合各路信号,基于BERT做了一些雕花的工作。
作者最后秀了一把显卡资源,酸了。

432.《Deep Bag-of-Words Model: An Efficient and Interpretable Relevance Architecture for Chinese E-Commerce》,KDD2024
淘宝搜索的工作。通过利用word weight作为query和product的表征(该工作中称DeepBoW),实现相关性的计算。因此问题转为:如何得到一个合适的word weight?类似的工作包括bge系列中的sparse weight等。
在评测数据集的构建中,谈到如下:
The first is a large-scale Human-Annotation dataset which contains queryproduct pairs sampled from the Taobao search logs. Each queryproduct pair is labeled as Good (relevant) or Bad (irrelevant) by experienced human annotators. This is a daily task running in Taobao, which has accumulated more than 8 million labeled samples.
431.《ContextCite- Attributing Model Generation to Context》
通过训练一个模型实现对cite的生成能力提升。
430.《Meta Knowledge for Retrieval Augmented Large Language Models》,AWS挂出来的一篇文章
主要思想:通过对非结构化文章做结构化来增强检索(通过arXiv的paper来验证想法)。
主要做法:
(1)通过llm给一篇文章打标签(获取metadata),根据文章和标签,利用llm生成qa对
(2)建立索引:对每一个标签,拿到数据集中所有的q,通过llm得到所有q的一个summary(concept维度),这样就建立了标签-summary的pair结构
(3)在推理时,给定一个query,拿到标签,summary可以作为query的一个增强。余下的流程同标准检索逻辑。这里有个细节,要不要用summary做增强?
(3.1)不用。给query打完标签之后,直接返回标签对应的q的集合。这样比较依赖前置环节的结构化的效果
(3.2)用。泛化能力,保留能够检索到其他q的可能性(文章选择了这种做法)。
与该做法比较相关的是,llm的self-instruct技术。进一步地,本质上是对非结构化文本建立index,将问题转化为一个标准的qa对问题。对比常用的chunking策略,从检索chunk切换为检索q。

429.《A Surprisingly Simple yet Effective Multi-�Query Rewriting Method for Conversational Passage Retrieval》,SIGIR2024的文章
主要亮点:对话式文本检索场景下,用一种非常简单但是高效的方式做query扩展的方法,除此之外,没有额外的cost。
主要做法:
(1)通过微调一个generative的模型来做query rewrite,通过beam search得到multi query。
(2)怎么利用这些query呢?
对于sparse retrieval:对于多个query,拿到bow,每个term在beam score做sum&norm(一个term可能会出现在多个query中),这样就可以得到term weight了。
对于dense retrieval:对每个query进行embedding之后,做sum&norm即可。
上述的关键操做是sum&norm,与文章的核心卖点:no additional cost直接相关。
这篇文章的做法非常符合自己近期做搜索优化的思路。(1)通过数据分析,证明需要一个query扩展(2)怎么做query扩展?(3)怎么用扩展出的query?(搜索主链熵增的同时,尽量不要增加推理cost,文章中基本只有并行的资源cost)
428.《Exploring Query Understanding for Amazon Product Search》
主要包含三个工作:QU Ranking Features+Query Segment Evaluation+QU based Training
427.《Context Embeddings for Efficient Answer Generation in RAG》
新增一篇在rag场景下的context压缩的工作。
426.《Knowledge Conflicts for LLMs: A Survey》
这篇文章讨论了llm中的知识冲突问题。其实整体的脉络也可以独立推演出来,以rag为例,answer有两个来源对象,分别是llm和context,因此conficts至少包含三个方面:
(1)llm内部的知识冲突。比如,“a是b的爸爸,b是a的?”,未必是“儿子”。。
(2)context之间的冲突。典型的,retrieval阶段有不同的知识来源等。在过去的23年,和华山医院张文宏团队合作的项目中,这个问题被挑战了很多次。。
(3)llm和context之间的冲突。本质上llm内置参数化的知识,而context则是显式的知识,二者会在客观上存在冲突,以及存在冲突的时候应该怎么搞?
这篇文章不仅讨论了上述问题的原因,同时给出了可能的解决方案,具有一定的启发性。
425.《Scaling Laws For Dense Retrieval》,2024 SIGIR, Best Paper
scaling law的简单含义是,bigger more!,个人理解这篇工作是把scaling law在dense retrieval的任务上重新做了一遍,结论是:hi,你看,也符合的哦。
强调了对于optimize training processes是重要的(training dynamic)。
收获不是很多。。。
424.《RankRAG: Unifying Context Ranking with Retrieval-Augmented Generation in LLMs》
核心思想:能否通过LLM把排序和生成一起做了?部分思想其实来的都很朴素,可以回头翻最早提rag的paper。
423.《Leveraging Passage Embeddings for Efficient Listwise Reranking with Large Language Models》
PE-RANK的主要思路是:之前的各种利用LLM进行重排的方法,受限于context的长度问题。那么一种直接的思路是,能不能不要这么长?具体的做法是:比如能否给context中的每个item一个有意义的标记。将标记作为prompt的一部分?
如果沿着这个思路,和传统的方法存在一定的mismatch。标记和自然语言的差异性问题。
422.《Methods, Applications, and Directions of Learning-to-Rank in NLP Research》
2024年的一篇关于ltr的review,强调了generative model的应用+统计显著性的问题(ml领域的老问题了,大家都不怎么做严谨的test)
421.压缩retrieval context的方法:
《Compressing Context to Enhance Inference Efficiency of Large Language Models》
《Dense X Retrieval: What Retrieval Granularity Should We Use?》
420.《When to Retrieve: Teaching LLMs to Utilize Information Retrieval Effectively》
解决的方法是:通过微调一个llm来输出一个特殊标记符,来表示是否需要模型利用context来得到最终的answer,类似的做法在更早的self-rag中有体现。
419.《FlashRAG: A Modular Toolkit for Efficient Retrieval-Augmented Generation Research》
一个新的rag框架。对比了和其他rag框架的区别。
418.《Item-Language Model for Conversational Recommendation》
417.《MUVERA:Multi-Vector Retrieval via Fixed Dimensional Encodings》
从colbert开始,multi-vector model变的流行,但是multi-vector的计算cost很高。这篇文章通过将multi-vector转化为single-vector,从而实现在提升recall的同时,显著降低latency。
这里有意思的问题是:从multi vector->single vector和using single vector directly,有什么本质的区别?
416.《Crafting Interpretable Embeddings by Asking LLMs Questions》
提出了一种利用LLM产生embedding的方式,比较native,问题也比较多。但是也算是有一种方式。
415.《Overlapping Experiment Infrastructure: More, Better, Faster Experimentation》
本文是google的工作,讨论ab testing,比较久远的工作了。saas的发展,使得有机会做更多data-driven的decision making。那么如何设计一个ab实验就是一个比较有意思的问题。
414.《COLD: Towards the Next Generation of Pre-Ranking System》
广告方向中的pre-ranking,或者又称粗排。截止目前可能的主流方案仍旧是基于向量+cosine的方式,这里考虑了cross feature的问题。个人认为,本质上这个事情还是cost sensitive的,如果能够在cost的约束上放松一些,在model design上,就可以做的更重一些。
广告方向的同学把该工作称为“三塔模型”,每个塔分别是user features, ad features和cross features。
413.《Evaluation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey》
关于rag的评估体系的review
412.三篇review:
-
《From Matching to Generation: A Survey on Generative Information Retrieval》,重要!!!
-
《A Survey of Generative Search and Recommendation in the Era of Large Language Models》
-
《RAG and RAU- A Survey on Retrieval-Augmented Language Model in Natural Language Processing》
411.《RAGCache- Efficient Knowledge Caching for Retrieval-Augmented Generation》

相关工作:
- Towards Long Context RAG
- LLM Semantic Cache的两个工作:
- GPTCache
- CodeFuse-ModelCache
算法和系统系统设计的工作:
- 《PipeRAG: Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Algorithm-System Co-design》
410.《Enhancing Legal Document Retrieval: A Multi-Phrase Approach with Large Language Models》
法律文本的检索。技术思路如下:
补相关工作:
《Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Knowledge Graphs for Customer Service Question Answering》
主要内容:基于jira工单系统,回复客户问题。jira工单系统的特点是:单个工单内部有结构+工单与工单之间有结构。因此,如果利用好这种带有结构的文本就是一个有意思的问题。
相关想法:
-
财税领域政策相关的文档结构利用
-
github的repo的issue区的自动问答
-
融合llm和kg的工作包括:mindmap等。关键要思考:如何建立query和kg之间的关系?llm在主链路中如何更好的发挥作用?
补相关工作:
《From RAG to QA-RAG: Integrating Generative AI for Pharmaceutical Regulatory Compliance Process》
主要内容:围绕药物合规咨询相关的工作。主要思路其实和hyde类似,不过和传统方案做了融合。
补相关工作:
《NoteLLM: A Retrievable Large Language Model for Note Recommendation》,图画的很乱。。。大概意思是微调了一个llm用于小红书的note的hashtag&category生成,类似场景在weibo中也有挺多,不过小红书更加依赖这个场景。
409.《Fine-Tuning or Retrieval? Comparing Knowledge Injection in LLMs》
围绕llm的知识注入方式讨论。rag v.s. icl v.s. full parameters fine-tuning v.s. pre-trained
408.《LLM Evaluators Recognize and Favor Their Own Generations》
这篇文章讨论的问题和我们自己工作中得到的结论一致:使用llm打分的时候,llm更倾向于给自己的输出打更高的分。
这种现象被定义为self-perference,而self-perference的核心是self-recognition。本质上是llm能否很好的识别自己的output。文章给出的结论是:二者是线性的。
想一想各种自动化benchmarking,rewarding,constitutional ai等,影响面还是有的。
一个民科的想法:信息摄入的时候,人们多数情况下对于自己熟悉的东西摄入的更快,也更容易产生认同感。这既是优点,也是缺点。比如一篇文章,可以写70%大家熟悉的东西,30%才是真正想要传达的新的增量。。。
怎么解决?一个基本的思路:使用llm作为evaluator的时候,在早期效果优化阶段,更关心相对排序而不是绝对得分,在效果优化的后期,关注点会回到绝对得分,拉近与天花板的距离。
补充相关工作:
《How Easily do Irrelevant Inputs Skew the Responses of Large Language Models?》
关键结论如下:
-
Compared to common semantically unrelated irrelevant information, LLMs are more likely to be misled by irrelevant information that is highly semantically related.
-
With the increment of irrelevant information quantity, LLMs are less capable of identifying truly relevant information and are more easily distracted.
-
The robustness of LLMs to irrelevant information varies with the question format, with the free-form format proving to be the most robust.
-
Current strategies intended to improve LLMs’ discrimination capabilities result in only marginal, and sometimes even detrimental, enhancements in their ability to accurately identify and disregard irrelevant information.
补充相关工作:
《Evaluating Verifiability in Generative Search Engines》
补充相关工作:
《The Power of Noise Redefining Retrieval for RAG Systems》
407.《How faithful are RAG models?Quantifying the tug-of-war between RAG and LLM's internal prior?》
尝试讨论了自己很早就在思考的问题,rag体系下,retrieval和generation对最终respnonse的contribution到底是咋样的?

比较有意思的是,llm-wrong+retrieval-right和llm-right+retrieval-wrong的时候,怎么办?
作者给出了两个影响因素:
(1)prompt。区别了对于retrieval信息的不同依赖程度 (2)llm的prior有多强?该工作测了gpt3.5,gpt4和mistral-7B,整体结论是:prior越强,retrieval阶段的贡献度越低。如果只是一般的prior,结果就很扑朔迷离了。。
所以,要回答这个问题,本质上还是要回答你用的llm到底是怎样的?prompt只是一个附加的外部条件且并不是很强。为了量化prior这个东西,可能的一个方式其实还是要建立domain下的测试集,对llm做系统的评估。
从我们做的医疗-发热方向的rag系统来看,gpt3.5/4/文心一言4的prior其实已经足够强,rag的增益其实并不大。
406.《Reducing Hallucination in structured outputs via Retrieval-Agumented Generation》
405.《Exploring the Impact of Table-to-Text Methods on Augmenting LLM-based Question Answering with Domain Hybrid Data》
关于表格数据处理的工作。
404.《the pitfalls of next-token prediction》
没有仔细看,大致是重新讨论了inference时采用auto-regressive和train的时候采用teacher-forcing之间存在gap的问题。
403.《大规模生成式语言模型在医疗领域的应用:机遇与挑战》
402.《Can Generalist Foundation Models Outcompete Special-Purpose Tuning? Case Study in Medicine》
在探讨一个问题:通用大模型直接用在垂直领域中,效果会弱于在垂直领域中train过的模型吗?(进一步的问题:垂直模型有没有存在的必要性?)
相关工作:graphrag
This builds upon our recent research, which points to the power of prompt augmentation when performing discovery on private datasets. Here, we define private dataset as data that the LLM is not trained on and has never seen before, such as an enterprise’s proprietary research, business documents, or communications. Baseline RAG1 was created to help solve this problem, but we observe situations where baseline RAG performs very poorly.
关于rag在什么条件下更有效?整体的结论是:rag在private的数据上更有可能有效,但是并不意味着在public的数据上无效(学过但没学好;学过但忘记了。都需要给一些提示才能回答),需要量化评估。
401.《Tag-LLM: Repurposing General-Purpose LLMs for Specialized Domains》
400.《The What, Why, and How of Context Length Extension Techniques in Large Language Models -- A Detailed Survey》
399.《MindMap: Knowledge Graph Prompting Sparks Graph of Thoughts in Large Language Models》
本质上可以看作是一个kgrag。
398.《Nomic Embed: Training a Reproducible Long Context Text Embedder》
模型的训练流程:
(1)masked language modeling pretraining. 利用bookscorpus和wikipedia,基于改造的bert架构重新训练一个支持2048长度的bert。
(2)unsupervised contrastive pretraining.基于29个数据集的,470billion的pairs,经过一致性筛选之后,得到235m的pair。(个人理解:采用弱监督的方式构建训练数据集)
https://huggingface.co/datasets/sentence-transformers/embedding-training-data
The JSON objects can come in different formats:
Pairs: ["text1", "text2"] - This is a positive pair that should be close in vector space.
Triplets: ["anchor", "positive", "negative"] - This is a triplet: The positive text should be close to the anchor, while the negative text should be distant to the anchor.
Sets: {"set": ["text1", "text2", ...]} A set of texts describing the same thing, e.g. different paraphrases of the same question, different captions for the same image. Any combination of the elements is considered as a positive pair.
Query-Pairs: {"query": "text", "pos": ["text1", "text2", ...]} A query together with a set of positive texts. Can be formed to a pair ["query", "positive"] by randomly selecting a text from pos.
Query-Triplets: {"query": "text", "pos": ["text1", "text2", ...], "neg": ["text1", "text2", ...]} A query together with a set of positive texts and negative texts. Can be formed to a triplet ["query", "positive", "negative"] by randomly selecting a text from pos and neg.
(3)supervised contrastive fine-tuning.基于高质量的数据集做监督式对比微调。
397.《Unlocking Context Constraints of LLMs: Enhancing Context Efficiency of LLMs with Self-Information-Based Content Filtering》
prompt压缩的方式
- autocompressor
- 学习一个learnable的prompt实现对prompt的摘要
- selective context
- 按照token的不确定性来选择具体丢弃哪些token(同样依赖一个causal model来给token打分)
- longllmlingual
- 对于prompt中的实体信息可能会丢失
396.《what makes good data for alignment? a comprehensive study of automatic data selection in instruction tuning》
395.《KwaiAgents: Generalized Information-seeking Agent System with Large Language Models》
几个印象中的点:
(1)整理了open_source中的几个数据工作,理论上是支持multi-lingual的
(2)有一个自动创建&筛选数据模版的方式(没仔细看)
(3)增强了qwen/baichuan的function calling的能力
问题:
(1)tools是一个closed-set的集合(update的问题;scale的问题等),当set很大的时候,能否用retrieval的方式来做?
(2)memory的问题
(3)依赖模型的理解&推理能力(能够推理多少个step?)
个人理解:agent是一个技术架构,给定目标,可以用于任务流的自动编排和实现。在此之前,low-code的方向做了一些工作,low-code解决的其实是翻译问题(业务需求->业务代码),本质上还是hard-code。基于agent,业务需求被instruction实现。从这个角度,能够自编程,其实还是有想象空间的。
相关工作包括:《ModelScope-Agent: Building Your Customizable Agent System with Open-source Large Language Models》等。
394.《Unified Demonstration Retriever for In-Context Learning》

扫了一眼《Unified Demonstration Retriever for In-Context Learning》的工作,针对单一任务,比如实体识别,可以类比在llm之前,基于检索的方案。不过在llm范式中,第一个是icl场景中,筛选相关的few-shot;第二个是利用llm的推理能力输出最终结果。
从另一个角度,想到gpt_cache和model_cache这类工作,利用semantic cache实现请求加速。
393.《large language model for generative information extraction_a survey》
392.《Wikiformer: Pre-training with Structured Information of Wikipedia for Ad-hoc Retrieval》

391.《Automated clinical coding using off-the-shelf large language models》
390.《retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive nlp task》,2020,rag的祖师爷~
389.《NEFTUNE: Noisy Embeddings Improve Instruction Finetuning》

388.《gemini: a family of highly capable multimodal models》
一大早被google的gemini刷屏了,作为一个tech report,其实也没有透漏很多的细节。整体的流程和目前已知的llm的流程类似,一个很大的区别在于multi modal的场景设定。送上一张很早画的图:
387.《can generalist foundation models outcompete special-purpose tuning?case study in medicine》
三种prompt策略:
(1)prompt的时候,选择一些相似的样本做few-shot
(2)引导模型自己生成chain of thought
(3)ensemble(适用于multi-choice类问题的融合策略)
个人观点:虽然通过prompt能够提升模型的效果,不过fine-tuning也很有用。
386.《taiyi_ A Bilingual Fine-Tuned Large Language Model for Diverse Biomedical Tasks》
主要亮点: (1)bilingual(中+英语),其中中来自cblue(相关工作promptcblue),英来自bigbio.->schema (2)two-stage sft:第一阶段没有qa和dialogue的数据;第二阶段在原来dataset的基础上添加qa和dialogue的数据 (3)验证了zero-shot的能力,此处类似flan系列(实测效果优于chatgpt)
整体工作和我们在早期做中文医疗大模型的思路比较接近,其实是flan系列的延伸和扩展。
385.《Direct Preference Optimization- Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model》
RLHF这个阶段的工作值得持续关注,比之前两个阶段,因为尚没有形成稳定的方法流程。比如引用tulu2的描述:
Early systems for RLHF were built primarily upon the proximal policy optimization (PPO) algorithm, but recent advances have seen exploration of offline RL [Snell et al., 2022], reward model data filtering called rejection sampling (RS) [Touvron et al., 2023a] or reinforced self-training (ReST) [Gulcehre et al., 2023] and direct integration of preference data [Rafailov et al., 2023].
这篇文章主要讲dpo的方式来做这个阶段的工作,实现简单,而tulu2是第一次在70b的scale上用dpo取得成功的一次实践。
384.《sira: sparse mixture of low rank adaptation》

383.《s-lora: serving thoughts of concurrent lora adapaters》
解决的核心问题:一个base model+几千个lora,怎么serving?
主要贡献: (1)unified paging,在gpu中管理lora和kv cache与variable seq len的关系,减少gpu的碎片问题,提升吞吐。依赖unified memory pool的设计
(2)tensor parallelism策略(但凡一个系统工作,不做这个,就觉得少点啥?)
(3)optimized cuda kernel(感觉同上)
题外话:
(1)slora是支持多gpu的 (2)不仅仅适用于lora,其他的adapter也是支持的 (3)vllm也支持lora serving,不过slora支持更多的lora,吞吐能做到前者的4倍(slora是在lightllm上做的,狗头。。) (4)下一步工作: (4.1)继续添加更多的adapter (4.2)强化fused kernel (4.3)multiple cuda stream的使用,提升base model+lora的计算并行度
382.《InstructExcel: A Benchmark for Natural Language Instruction in Excel》
381.《Generative Input: Towards Next-Generation Input Methods Paradigm》
科大讯飞的团队,基于文本生成的思路应用于输入法,基于prompt能够整合更多的user info,同时基于输入法的天然场景,能够获取很多的feedback(对于 其他应用场景,需要单独建设feedback的模块)
380.《JINA EMBEDDINGS 2: 8192-Token General-Purpose Text Embeddings for Long Documents》
要点: (1)MTEB的sota(comparable with text-embedding-ada-002 from openai),0.27g
(2)masked language model +alibi的训练范式
(3)在decoder端考虑long-context的同时,如何对long-context进行modeling也是一个有意义的问题。将condition推到 一个极端也是一个挖问题的好方式
379.《Qilin-Med- Multi-stage Knowledge Injection Advanced Medical Large Language Model》
多阶段知识注入的中文医疗大模型。
378.《large search model: refefining search stack in the era of llms》
按照传统的search链路,基于相同的llm,每个阶段采用不同的prompt,能否实现一个poc?

377.《StructGPT- A General Framework for Large Language Model to Reason over Structured Data》
相关分析:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/660286882
总结:怎样基于结构化数据做推理,在工业界是一个很solid的问题,这里有很多的具体问题要去解决。比如,给定一个数据库中的表(百级别),平均每个表的字段个数(百级别),能否通过llm记忆这些结构并实现推理?
类似的工作:llm->sql/llm->pandas function/llm function calling,这篇文章自定义了一些针对特定结构化数据的func(知识图谱,table,databse)
_ 376.《self-verification improves few-shot clinical information extraction》
方法:相同llm,四个prompt实现信息抽取。
prompt:original extraction->omission(in-context leanring, 哪些是少抽取的?)->evidence(in-context learning, 抽取依据是什么?找到原文本中的span)->prune(in-context learning,哪些是多抽取的?)
缺点:多次call llm+noise传递
优点:chain的方式,实现任务的逐级优化
375.《effective long-context scaling of foundation models》
our ablation experiments suggest that having abundant long texts in the pretrain dataset is not the key to achieving strong performance, and we empirically verify that long context continual pretraining is more efficient and similarly effective compared to pretraining from scratch with long sequences.
374.《Context Aware Query Rewriting for Text Rankers using LLM》
大模型用于query改写。主要的思路是:用llm基于query+doc生成data pair,再去finetuned一个小的模型做ranking->小的模型做线上的infer(这是妥妥的将大模型作为数据打标的工具了啊。)

373.《EcomGPT:instruction-tuning large language models with chain-of-task tasks for e-commerce》
flanv1/v2在电商领域的一个实践,追求cross-task的generalization能力。主要结论如下:
- scaling impact on model generalization
- more diverse domain training tasks benefit generalization capacity(追求任务的多样性,前提是如何定义这个任务的多样性?)
- excessive training instances for each task do not enhance generalization capability(每一个任务上增加更多的数据是没有用的。)
- scaling up task number takes priority over model parameter size(7b的模型在这个工作中的setting已经是够了的,scale任务数比scale模型参数的优先级更高,我们需要构建更多的数据)
372.《Making Metadata More FAIR Using Large Language Models》
利用openai的embedding的技术,实现term的cluster,用于metadata之间的alignment。

371.《Resolving Interference When Merging Models》
提出了一种多模型merge的方法。相关工作:
- https://github.com/StarRing2022/ChatGPTX-Uni
- moe的思路。为了实现这个结构,显而易见需要两部分:
(1)分发器:根据你的问题决定应该问哪些专家 (2)一群各有所长的专家:根据分发器分过来的问题做解答 (3)(可选)综合器:很多专家如果同事给出了意见,决定如何整合这些意见,这个东西某种程度上和分发器是一样的,其实就是根据问题,给各个专家分配一个权重
跳出上文所述,从系统的角度来看是:foundation model+peft module是多对多的关系。一个foundation model可以有多个head(lora,etc.),一个head被多个foundation share(这个方向还么有尝试过)。除了1对多和多对1的场景,还有多对多的场景,在该场景下,如何做routing,是个有意思的问题。
370.《Nougat: Neural Optical Understanding for Academic Documents》
langchain中采用了nougat的竞品grobid。有针对这个工作的实际测试,尚存在效果上的问题。但是这个工作还有一个核心价值是:提供了非常多的pdf处理的工具和方法。
369.《Self-Alignment with Instruction Backtranstion》,meta AI
主要分为两个阶段,分别是:
(1)self-augmentation(generating instructions),基于llama和少量的seed data来完成
(2)self-curation(selecting high-quality examples),通过iterative self-curation的方式实现对数据的层层过滤
368.《Zhongjing: Enhancing the Chinese Medical Capabilities of Large Language Model through Expert Feedback and Real-world Multi-turn Dialogue》
侧重于对话系统的能力,走完了大模型训练的全流程,包括pretrain,sft,rm和rlhf四大核心模块。
367.《Skeleton-of-Thought:Large Language Models Can Do Parallel Decoding》
366.《ArcGPT: A Large Language Model Tailored for Real-world Archival Applications》
中国电子档案大模型。
365.《Unified Language Model Pre-training for Natural Language Understanding and Generation》
seq2seq lm->prefix lm(glm的arch设计),这里主要的想法是通过attention mask实现任务范式的统一,是一个有意思的角度。比如大模型如何有效利用多轮对话的数据完成充分且高效的训练。但是进入大模型的范式,只利用seq2seq就实现了nlu和nlg任务设计上的统一,大道至简。
364.《Atlas: Few-shot Learning with Retrieval Augmented Language Models》
提供了知识增强/知识融入的一种方式。在pretrain阶段,通过mlm的方式注入,finetune阶段通过few-shot的方式注入,在每个阶段均利用检索,实现上下文的丰富完善。
363.《Challenges and Applications of Large Language Models》
这篇文章的讨论的challenges,基本就是目前llm遇到的问题,文章围绕这个部分,讨论了对应的解决方案。

362.《A Survey on Evaluation of Large Language Models》
what to evaluate + where to evaluate + how to evaluate
361.《AlpaGasus: Training A Better Alpaca With Fewer Data》
这篇文章主要证明一个问题:sft阶段instrucion的质量远比数量重要。通过将chatgpt作为一个打分器,给原来的alpaca的52k的instruction的数据打分(三元组),筛选后的数据量 52k->9k,微调时间从80mins->14mins,且效果得到显著提升。再一次证明data-centric ai的伟大,笔者自己最近做的一个工作,也基本集中在data侧,效果杠杠的。
360.《C3: Zero-shot Text-to-SQL with ChatGPT》
359.《Instruction Mining: High-Quality Instruction Data Selection for Large Language Models》
在微调阶段,如果选择高质量的指令数据,是一个关键问题。这篇文章的做法类似于做特征工程,具体的特征工程体系如下(相关文章如何自动化地挑选出大模型所需的高质量指令微调数据):
358.《Self-consistency for open-ended generations》
** Selfconsistency has emerged as an effective approach for prompts with fixed answers, selecting the answer with the highest number of votes. **
357.《SimCLS: A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Abstractive Summarization》,ACL2021
文章中提出了一个简单的框架,用于seq2seq模型框架的评估,主要的思路是:generate&evaluation。
(1)generate模型。普通的seq2seq模型,产生多个candidates
(2)evaluator模型。采用contrastive learning的方式,基于(1)中的candidates得到evaluator模型
这个思路可以用于文本生成类的比赛中,作为模型ensemble的一种方式。
356.《ChatPLUG:Open-Domain Generaative Dialogue System with Internet-Augmented Instruction Tuning for Digital Human》
达摩院的工作,围绕数字人的场景,主要讲对话系统怎么做。整体的思路在大模型之前也有类似的工作,比如LIC的,给定intent做对话中的自动意图转换等。
355.《Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models》
非常棒的文章,做了大量细节和问题的分析与讨论,需要多读几遍。
354.《A Formal Perspective on Byte-Pair Encoding》 bpe的一个改进算法,时间复杂度的优化。
353.《MidMed: Towards Mixed-Type Dialogues for Medical Consultation》
在一个医疗咨询场景中,大多数的对话系统都假定患者具有清晰的目标,包括药品咨询和手术咨询等。但是在真实场景中,由于医疗知识的缺乏,患者对于清晰的描述自己的目标(带有相关的slot)是困难的。 产出一个数据集MidMed和一个任务InsMed.
352.《ChatLaw: Open-Source Legal Large Language Model with Integrated External Knowledge Bases》
在该工作中,通过引入检索的机制实现模型幻觉现象的减少;同时,建立一个controller机制实现多specific model的路由。
Furthermore, we observed that a single general-purpose legal LLM may not perform optimally across all tasks in this domain. Therefore, we trained different models for various scenarios, such as multiple-choice questions, keyword extraction, and question-answering. To handle the selection and deployment of these models, we employed a big LLM as a controller using the methodology provided by HuggingGPT [6]. This controller model dynamically determines which specific model to invoke based on each user’s request, ensuring the most suitable model is utilized for the given task.
351.《ClinicalGPT:Large Language Models Finetuned with Diverse Medical Data and Comprehensive Evaluation》
350.《Data Selection for Language Models via Importance Resampling》

340.《Multitask Pre-training of Modular Prompt for Chinese Few-Shot Learning》
主要思想:将任务统一建模为mrc,在38个中文任务上完成得到。 相关工作:
- 《Crosslingual Generalization through Multitask Finetuning》
- 《Muppet: Massive Multi-task Representations with Pre-Finetuning》
339.《LIMA: Less Is More for Alignment》
almost all knowledge in large language models is learned during pretraining, and only limited instruction tuning data is necessary to teach models to produce high quality output.
338.《SELF-QA: Unsupervised Knowledge Guided Language Model Alignment》

337.llm在推荐系统中的应用总结
336.《Outrageously Large Neural Networks_The Sparsily-Gated Mixture-of-Experts Layer》, ICLR 2017
335.《Inference with Reference_Lossless Acceleration of Large Language Models》
方法上虽然是lossless的,但是需要reference text的参与,还是存在很多挺tricky的方法。
334.《Contrastive Search Is What You Need For Neural Text Generation》
logit的艺术。
333.《XuanYuan 2.0: A Large Chinese Financial Chat Model with Hundreds of Billions Parameters》
主要思路:基于BLOOM-175B,打散pre-train和instruction tuning两个阶段的数据。不仅能够一定程度上防止灾难性遗忘问题,同时能够实现模型的domain-specific.
332.《LLaVA-Med: Training a Large Language-and-Vision Assistant for Biomedicine in One Day》
医学多模态大模型
331.《Beyond One-Model-Fits-All: A Survey of Domain Specialization for Large Language Models》
330.《Small Language Models Improve Giants by Rewriting Their Outputs》
329.《Is GPT-4 a Good Data Analyst?》
328.《Lawyer LLaMA Technical Report》
行业垂直大模型的工作:法律领域。这个工作特别谈到了领域知识融入的问题。同时针对中文词典扩充的问题,这里也有一个观点和实验结论:
截止目前比较有代表性的行业大模型工作:
- 金融领域大模型:bloomberge
- 法律领域大模型:lawyer LaMA
- 医疗领域大模型:我们在做的...
327.《InstructIE: A Chinese Instruction-based Information Extraction Dataset》
类似的工作已经有几篇了,这里可以重点看下prompt的构建方式

326.《DoReMi: Optimizing Data Mixtures Speeds Up Language Model Pretraining》
围绕大模型的训练,在数据侧关心的三大问题: (1)数量。质量比数量重要,甚至不需要很多。 (2)质量 (3)多样性。针对“多”,如何学习到一个有效的weight呢?等weight未必是一个最佳解决方案。
325.《Rething with Retrieval:Faithful Large Language Model Inference》
324.《Large Language Models Are Reasoning Teachers》
fine-tuning CoT:本质上是面向大模型的蒸馏。
323.《GLM: General Language Model Pretraining with Autoregressive Blank Infilling》,chatglm的工作
322.《MD-VQA: Multi-Dimensional Quality Assessment for UGC Live Videos》,CVPR2023
淘宝视频质量评价工作,针对淘系UGC的质量评价。很多年前做搜索的时候,做网页质量评价;近期看到一个很有意思的事情,是用CV的方法做前端页面的测试。在之前的工作中,接触到手术质量评价的工作。
321.《Evaluation of ChatGPT as a Question Answering System for Answering Complex Questions》,漆桂林组的工作
系统评估ChatGPT在复杂QA中的应用效果。
320.《BioGPT: Generative Pre-trained Transformer for Biomedical Text Generation and Mining》,MS的工作

319.《Zero-Shot Information Extraction via Chatting with ChatGPT》,DAMO
基于ChatGPT做Zero-Shot的信息抽取的工作(拼手速,预计近期类似的工作还会有很多)
相关工作:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/PM_xgHPLitBhh6Gd5DhU7w
318.《ChatAug: Leveraging ChatGPT for Text Data Augmentation》,使用ChatGPT进行数据增强。
相关文章: (1)https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/AdcdIOEDniu-g3OigmnQ6g (2)《ChatGPT科普和应用初探》:https://redian.news/wxnews/289575,58AILab在一些具体的业务上的量化评测
317.《Visual ChatGPT: Talking, Drawing and Editing with Visual Foundation Models》,MS的工作
并不是训练了一个模型,而是多个foundation model的整合,构建了一个系统。这个系统能干啥?
(1)发送和接收文本+图片 (2)能够通过多个ai基础模型的多个步骤完成复杂的视觉问答和图片编辑指令 (3)providing feedback and asking for corrected results
这套系统尚存在的问题: (1)依赖ChatGPT和VFM (2)比较依赖prompt工程 (3)实时性差 (4)输入token限制(关于这点,印象中有一个相关工作能够一定程度上缓解) (5)安全和隐私
补充:在多模型整合上,除了各种vfms,用了langchain的工作。
316.《表格识别技术研究进展》,2022.06
三种主流技术方向:
(1)自底向上::先检测单元格,然后确定表格线
(2)自顶向下:先检测表格线,然后确定单元格之间的关系
(3)encoder-decoder:image->html/latex
相关资料:
医疗纸质文档电子档OCR识别:http://www.cips-chip.org.cn/2022/eval4
推荐个离线OCR工具bibiocr(上):https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yVnSa7m1BQ7HOHeVK3i3hA
好未来的比赛
315.federated learning的两篇文章:
《When Federated Learning Meets Blockchain:A New Distributed Learning Paradigm》,用区块链技术解决联邦学习的中心化结构问题。中心挂了,系统就会挂。
《Swarm Learning for decentralized and confidential clinical machine learning》,发表在nature上的文章。
314.《Unified Structure Generation for Universal Information Extraction》
整体上采用了encoder-decoder架构,基于transformer模型,实际中预训练模型采用了ernie3.0。用一个统一的架构实现了实体识别,关系抽取,属性抽取,观点提取,事件抽取等各个理解任务。 生成的范式具有极大的灵活性,类似的思想也有很多工作。比如《A Unified Generative Framework for Various NER Subtasks》,该工作用一个生成模型解决NER的各个子任务,在此之前需要单独建模。在中文纠错方向上,由于错误类型较多,比如包含拼写纠错,语法错误等,理论上,一个生成模型可以解决各种设定下的具体任务,而不需要多个模型设计。大概两年前,复现Magi的时候,同组同学基于预训练模型,采用生成的思路做SPO抽取,取得了比理解范式下的模型更好的结果。
313.《Clinical Prompt Learning with Frozen Language Models》
Prompt Learning 在医疗文本分类中的应用。
312.《Context Enhanced Short Text Matching using Clickthrough Data》,利用点击数据做短文本匹配的上下文增强。
311.《PLOME: Pre-training with Misspelled Knowledge for Chinese Spelling Correction》
主要的亮点有三处:
(1)预训练拼写纠错语言模型
(2)多特征融合:character(字形)+position(位置)+phonic(拼音,也许可以进一步考虑发音特征)+shape(笔画)
(3)预训练任务设计:不同于传统的mlm,只预测单个字;该工作中同时预测单字+拼音
310.《Corpora Generation for Grammatical Error Correction》
(1)通过找到维基百科的编辑历史来解决
(2)通过back translation的方式来解决
309.《Towards Unsupervised Dense Information Retrieval With Contrastive Learning》
结论:具体对比学习方法在NLP具体任务上实践,没有显著创新贡献。
数据增强方法:
(1)inverse cloze task
(2)independent cropping
(3)additional data augmentation
负例构建方法:
(1)negative pairs within a batch
(2)negative pairs across batches
308.《Improving language models by retrieving from trillions of tokens》,DeepMind
基于特殊设计的交互组件,通过检索式的方法强化PLM的训练。
307.《Document-level Relation Extraction as Semantic Segmentation》,陈华钧老师组的工作
引用前一段时间的个人微信:
大家都在聊《Pix2seq: A Language Modeling Framework for Object Detection》,发一篇多年前第一次做NER时的一个想法,刚查了下,今年1月的文章,《Named Entity Recognition in the Style of Object Detection》。
在解决问题的范式上,CV和NLP是相通的。
306.《Med-BERT: pretrained contextualized embeddings on large- scale structured electronic health records for disease prediction》
相比其他医学预训练模型,该模型的特色是对ICD编码进行表征。
305.《Named Entity Recognition for Entity Linking》,EMNLP2021
打通NER和EL的关系,核心想法是:如何利用NER得到的Type信息?
304.《Few-Shot Named Entity Recognition_A Comprehensive Study》
文章总结了三种做few-shot ner的方式,并提出了第四种self-training的方式。
具体self-training的思路如下:
303.《Learning Rule Embeddings over Knowledge Graphs: A Case Study from E-Commerce Entity Alignment》, WWW2020
相关工作:AMIE
自动化Rule Learning。
302.《Lattice-BERT: Leveraging Multi-Granularity Representations in Chinese Pre-trained Language Models》
301.ML中的数据验证想法:https://github.com/zhpmatrix/PaperReading/edit/master/README.md
300.《RadGraph: Extracting Clinical Entities and Relations from Radiology Reports》, 放射报告的结构化能力抽取
299.对比学习在NLP中的应用:
相关参考:
2.利用Contrastive Learning对抗数据噪声:对比学习在微博场景的实践
3.对比学习(Contrastive Learning):研究进展精要
298.《DiaKG: an Annotated Diabetes Dataset for Medical Knowledge Graph Construction》,CCKS2021
糖尿病知识图谱的构建。这篇文章的主要亮点:
(1)糖尿病知识图谱schema的设计:实体和关系
(2)标注流程设计。
297.《Pre-trained Language Model for Web-scale Retrieval in Baidu Search》,预训练模型在百度搜索的应用,印象中Google Blog也有一篇工作是讲述BERT在Google Search中的应用。
向量压缩和量化是工程实践中很关键的技术点。
296.《Wordcraft: a Human-AI Collaborative Editor for Story Writing》,Google Research
人机协作的Editor,一个完整的事情。
295.《A Data-driven Approach for Noise Reduction in Distantly Supervised Biomedical Relation Extraction》
multi-instance learning to noise reduction.
294.《CLINE:Contrastive Learning with Semantic Negative Examples for Natural Language Understanding》
利用对抗样本和对比样本提升PLM的鲁棒性。基于MLM,构建额外两个损失函数,预训练一个语言模型。整体上,个人收获不是很大的一个工作。
293.《AliCG: Fine-grained and Evolvable Conceptual Graph Construction for Semantic Search at Alibaba》
阿里概念图谱的工作,利用search log构建一个concept graph(基于UC Browser的log),可以用在多个应用场景中,如:
(1)text rewriting
(2)concept embedding
(3)conceptualized pretraining
在之前,阿里图谱相关的工作包括但不限于:AliCoCo(认知图谱), AliMe等。
292.《ABCD:A Graph Framework to Convert Complex Sentences to a Covering Set of Simple Sentences》
解决问题:将一个复杂的句子拆分成多个简单的句子。
方法:传统的方法是将问题建模为一个seq2seq的问题,但是在该工作中,借助graph的方式,取得不错的效果。
评价:problem setting有意思。
291.《COVID-19 Imaging Data Privacy By Federated Learning Design: A Threoretical Framework》, 联邦学习在cv领域的一个工作
290.《Large-Scale Network Embedding in Apache Spark》,KDD2021,在腾讯的两款游戏中有上线哦
289.《AliCoCo_Alibaba E-commerce Cognitive Concept Net》,短文本相关的技术
288.《A Neural Multi-Task Learning Framework to Jointly Model Medical Named Entity Recognition and Normalization》
同样的思想,基于multi-task的方式建模ner和norm两个任务。
287.《A transition-based joint model for disease named entity recognition and normalization》
老文章了。讨论的想法是医疗领域针对疾病,做实体识别和norm的联合建模。作为医疗NLP领域的三大基础任务:ner/nre/norm,采用jointly的方式,one model to rule all of them,也许是一个想法。
286.《A Survey on Complex Knowledge Base Question Answering》
主要综述两种KBQA的解决方案:分别是semantic-parsing based methods和information-retrieval based methods。
future中提到的一个有意思的观点是:要做Evolutionary KBQA,简而言之,要将用户的feedback带入到系统的优化中。
285.病历相似性(基于电子病历数据)
目前看到的主流思路是:梳理出EMR的各个维度,然后按照维度计算每个维度的相似性,每个维度都有自己的相似度计算方式,之后按照加权的方式求解。
个人想法:
(1)纯文本的方式。计算tf-idf(ES based solution)
(2)计算表征。但是由于EMR文本较多,医学文本对于精确性要求比较高,因此需要hierarchical representation fusion的思想。(不管怎样,首先需要一个好的encoder)
《Measurement and application of patient similarity in personalized predictive modeling based on electronic medical records》
284.《A Unified Generative Framework for Various NER Subtasks》,邱锡鹏老师组的工作
主要内容:用seq2seq(bart)解决三种常见ner的case(flat ner + nested ner + discontinuous ner)
想法:
(1)在之前的工作中,围绕这三种情况,有很多的paper。但是这篇文章采用seq2seq来解决,思路上之前也已经有相关工作了,但是这篇文章主要采用bart作为plm。毕竟seq2seq是万能的,哈哈。
(2)围绕bert做的中文nlp比较多,为啥?原因之一是因为bert有中文版,但是想用一下bart,就需要自己训练一个中文的bart了。每当这个时候,就不禁想到英文世界的话语权是怎么来的,到底意味着啥?
(3)技术创新个人认为谈不上:seq2seq(plm:bart)+ner(是一个体力活儿,不过还是要做很多工作的)

283.《SMedBERT: A Knowledge-Enhanced Pre-trained Language Model with Structured Semantics for Medical Text Mining》,丁香园的预训练语言模型
知识增强预训练语言模型。研究了丁香园,联合阿里和东南大学做的工作,丁香园利用5G的医疗领域中文文本+内部的知识图谱,通过巧妙的模型设计,得到的模型能够显著提升NER/NRE等上游任务的指标。我们可以利用开源爬取的数据(目前量<5G),同时结合OMAHA,做类似的工作以支持上游模型。
282.《Modeling Joint Entity and Relation Extraction with Table Representation》,EMNLP2014
人傻就要多读书,比如,在2014年的工作中,已经用table的方式解决joint问题了,如下:
四篇information extraction相关的工作:
281.《Read, Retrospect, Select: An MRC Framework to Short Text Entity Linking》
280.《Integrating Graph Contextualized Knowledge into Pre-trained Language Models》,小样本信息抽取相关的工作
279.《A novel cascade binary tagging framework for relational triple extraction》
278.《Entity-Relation Extraction as Multi-Turn Question Answering》
277.《Lifelong Learning based Disease Diagnosis on Clinical Notes》,腾讯天衍实验室的工作,TODO
276.《PRGC: Potential Relation and Global Correspondence Based Joint Relational Triple Extraction》,腾讯天衍实验室的工作,TODO
275.《MIE: A Medical Information Extractor towards Medical Dialogues》
annotate online medical consultation dialogues in a window-sliding style.
274.《A Survey of Data Augmentation Approaches for NLP》
比较新的NLP数据增强文章,按照任务类型划分增强的方式。
273.《HyperCore: Hyperbolic and Co-graph Representation for Automatic ICD Coding》, ACL2021
ICD编码映射,医疗NLP的特色任务。
ICD的特点:
(1)层次
(2)共现(因果)
主要方法:GCN的应用
272.《Few-Shot Named Entity Recognition: A Comprehensive Study》,Jiawei Han组的工作
NER中的少样本问题,三种解决方案:
(1)基于proto的few-shot learning方法(此前在研究文本分类的few-shot问题时,该方向上的工作也一直比较受欢迎)
(2)带噪音,有监督预训练
(3)伪标签,自训练
271.《Summarizing Medical Conversations via Identifying Important Utterances》,COLING2020
主要内容:从医疗问答中抽取摘要。
数据:从春雨医生爬取
方法:抽取式摘要
270.《Enquire One’s Parent and Child Before Decision_ Fully Exploit Hierarchical Structure for Self-Supervised Taxonomy Expansion》,腾讯,刘邦
分类树扩展的工作,用于腾讯的疫情问答场景。刘邦的博士论文可以一读。
269.Federated Learning
《Privacy-Preserving Technology to Help Millioins of People_Federated Prediction Model for Stroke Prevention》
FL使用传统模型,也是目前主要做的工作
《Empirical Studies of Institutional Federated Learning For Natural Language Processing》
FL使用TextCNN的经验性工作
《FedED: Federated Learning via Ensemble Distillation for Medical Relation Extraction》
内容:FL应用于医疗关系抽取
结果:实现了隐私保护,但是指标下降
核心:在通信,不在计算
科普:《Introduction to FL》,本质上还是分布式学习的一种。
结论:除非必要,否则目前在工业界推进的ROI应该不算高。不单纯是一个算法问题,还是一个架构问题。但是在医疗行业目前现状下(数据孤岛现象),仍有必要关注
268.《MedDG: A Large-scale Medical Consultation Dataset for Building Medical Dialogue System》,Xiaodan Liang等
构建了一个中文医学对话数据集,特点是:标注了每个对话可能涉及的实体。
基于该数据集,定义了两个任务:
(1)next entity prediction。文章中用multi-label classification的方式实现
(2)doctor response generation。标准的文本生成类任务+融合任务(1)中的实体信息(最简单的方式:直接concat实体)
其他:ICLR2021要基于该数据集举办一个比赛,可以关注。
想法:其实是对生成领域强化对实体信息的利用。传统做生成的同学有一些对应的方式强化对实体信息的利用。不过,文章中的建模方式更偏intent识别。
《MedDialog: Large-scale Medical Dialogue Datasets》,EMNLP2020,这篇工作也是构建了一个中文医疗对话数据集,不过没有实体信息。
267.《BioBERT:a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining》
预训练任务没有做任何改进,但是在下游的三个理解任务上均取得了提升,比较适合工业界操作的工作。
补充:《Conceptualized Representation Learning for Chinese Biomedical Text Mining》,阿里巴巴,张宁豫
266.《Building Watson:An Overview of the DeepQA Project》,2011年,IBM Watson的DeepQA项目,具体实现细节
讨论了架构和工程实现的问题,其中的特色在于对证据的重视。
265.《Strategies For Pre-training Graph Neural Networks》,ICLR2020
主要内容:预训练图的工作
motivation:node的pretrain和graph的pretrain都要;之前的一些工作只考虑node或者graph的单个类型的pretrain
训练任务:
(1)node:context graph的定义,学习context;attribute mask任务 (2)graph:supervised graph-level properties prediction + structural graph similarity prediction
基础模型: GIN
直观感受:中规中矩;目前还没看到预训练图的工作应用于电商领域等
264.《A User-Centered Concept Mining System for Query and Document Understanding at Tencent》,KDD2019
腾讯刘邦的工作,刘邦的博士论文也有share,主要做概念挖掘,偏向于工程系统的工作。相关文章
263.《Read, Retrospect, Select: An MRC Framework to Short Text Entity Linking》
和《AutoRegressive Entity Retrieval》,ICLR2021一块儿读。
262.《CRSLab:An Open-Source Toolkit for Building Conversational Recommender System》
CRS系统的设定:
261.《Open Domain Event Extraction Using Neural Latent Variable Models》
开放域的事件抽取。(个人对隐变量模型不是很了解)
260.《Billion-scale Commodity Embedding for E-commerce Recommendation in Alibaba》,KDD2018
259.《AutoRegressive Entity Retrieval》,ICLR2021
用生成的方式(seq2seq)做el,entity disambiguation, page retrieval任务。将传统分类任务转化为一个生成任务是问题解决范式的转变,很有意思的工作。在自己的博客,MRC is all you need?中讨论了将很多经典NLP任务用MRC的方式来做。
258.《Metapath-guided Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network for Intent Recommendation》,KDD2019
基于user-item-query构建的图,三种类型的边:search,click, guide,用于淘宝意图检测。
257.《Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network》,WWW2019
异构图+gat,文章写作思路很赞。目前,我们正尝试将该工作用于销量预测与归因分析。
256.《POG:Personalized Outfit Generation for Fashion Recommendation ai Alibaba iFashion》,KDD2019
阿里dida平台建设,compatibility+personality都要考察。
相关PR稿(dida也是从luban演化而来):https://hackernoon.com/finding-the-perfect-outfit-with-alibabas-dida-ai-assistant-71ba7c9e8cfa
255.《Spam Review Detection with Graph Convolutional Networks》,CIKM2018 Best Paper
重新翻开这篇文章,方法如下:
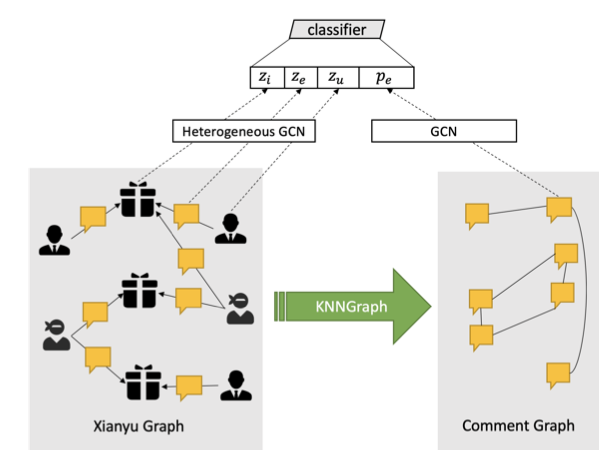
文章要解决的问题是垃圾评论检测,构建了两个图。第一个图:用户-评论-商品图,是异构图;第二个图:评论-评论图,是同构图。分别用异构GCN和GCN学到各自的表征,做节点分类工作。
整体上,文章的思路和这篇《Abusive Language Detection with Graph Convolutional Networks》非常相似,但是二者都没有互相引用。这篇文章做的是Tweet分类(三分类),分别构建两个图。第一个图:用户-用户的同构图;第二个图:用户-Tweet的异构图。针对同构图,用node2vec去学到表征(node2vec不是仅仅适用于同构图,不过效果需要考察);针对异构图,用gcn去学到表征。表征组合(embedding+n-gram)+分类器做节点分类。
对比二者,整体上的技术思路相似,不过显然后者在图构建上更加的自然。
254.《Graph Neural Networks:Taxonomy, Advances and Trends》,最新的GNN相关的综述文章
253.《Understanding Image Retrieval Re-Ranking:A Graph Neural Network Persperctive》
有意思的工作,作者提到:
(1)Re-ranking can be reformulated as a high-parallelism Graph Neural Network (GNN) function.
(2)On the Market-1501 dataset, we accelerate the re-ranking processing from 89.2s to 9.4ms with one K40m GPU.
252.《Why Are Deep Learning Models Not Consistently Winning Recommender Systems Competitions Yet?》,RecSys2020
非常棒的文章,多年以前自己就很好奇了。
251.《Enriching Pre-trained Language Model with Entity Information for Relation Classification》
250.《Diverse, Controllable, and Keyphrase-Aware: A Corpus and Method for News Multi-Headline Generation》
新闻标题生成
249.《CharBERT: Character-aware Pre-trained Language Model》
248.《