-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3.7k
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Color Banding #5262
Labels
Comments
ItsDoot
pushed a commit
to ItsDoot/bevy
that referenced
this issue
Feb 1, 2023
…5264) # Objective - Closes bevyengine#5262 - Fix color banding caused by quantization. ## Solution - Adds dithering to the tonemapping node from bevyengine#3425. - This is inspired by Godot's default "debanding" shader: https://gist.github.com/belzecue/ - Unlike Godot: - debanding happens after tonemapping. My understanding is that this is preferred, because we are running the debanding at the last moment before quantization (`[f32, f32, f32, f32]` -> `f32`). This ensures we aren't biasing the dithering strength by applying it in a different (linear) color space. - This code instead uses and reference the origin source, Valve at GDC 2015 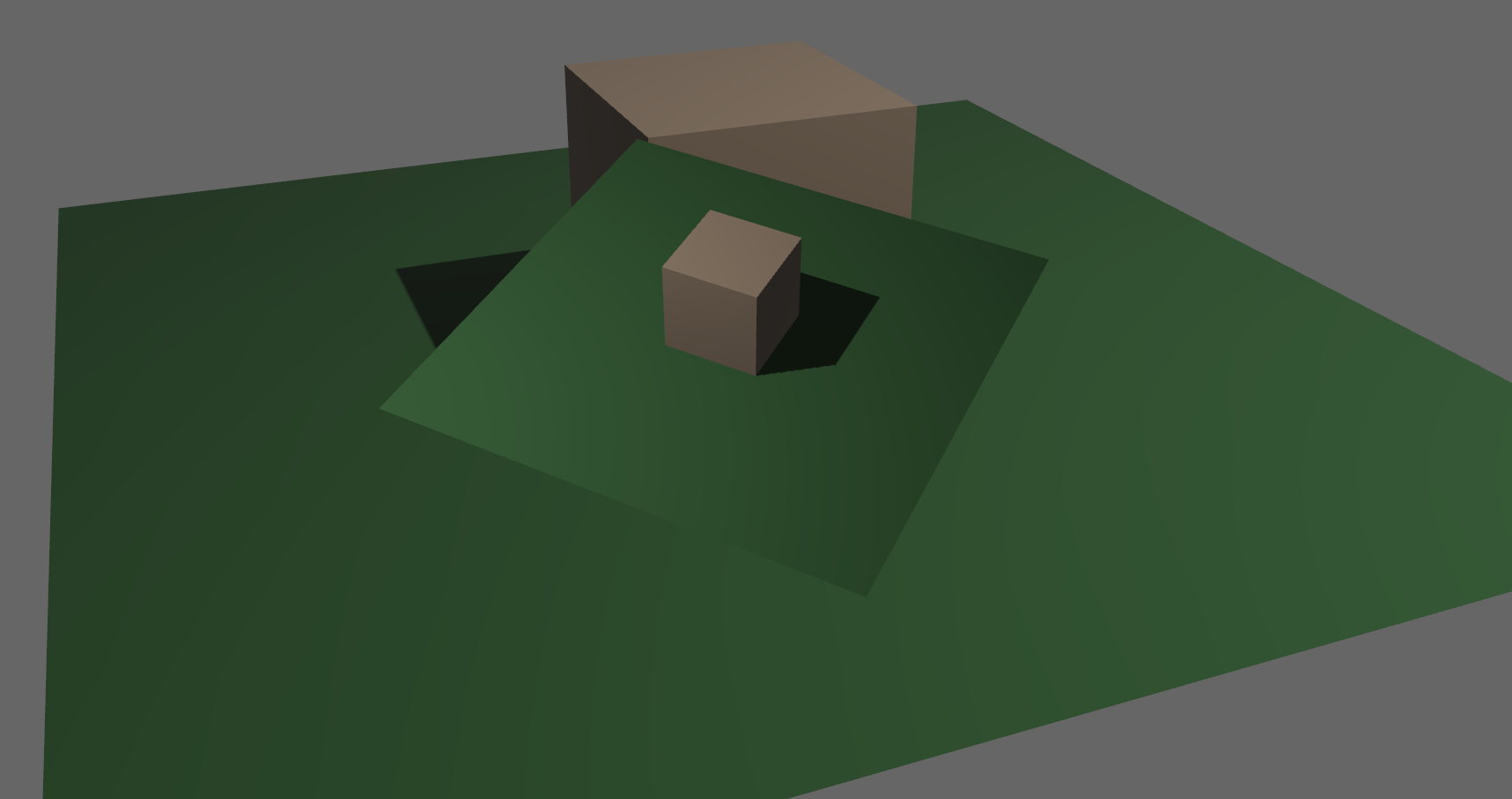  ## Additional Notes Real time rendering to standard dynamic range outputs is limited to 8 bits of depth per color channel. Internally we keep everything in full 32-bit precision (`vec4<f32>`) inside passes and 16-bit between passes until the image is ready to be displayed, at which point the GPU implicitly converts our `vec4<f32>` into a single 32bit value per pixel, with each channel (rgba) getting 8 of those 32 bits. ### The Problem 8 bits of color depth is simply not enough precision to make each step invisible - we only have 256 values per channel! Human vision can perceive steps in luma to about 14 bits of precision. When drawing a very slight gradient, the transition between steps become visible because with a gradient, neighboring pixels will all jump to the next "step" of precision at the same time. ### The Solution One solution is to simply output in HDR - more bits of color data means the transition between bands will become smaller. However, not everyone has hardware that supports 10+ bit color depth. Additionally, 10 bit color doesn't even fully solve the issue, banding will result in coherent bands on shallow gradients, but the steps will be harder to perceive. The solution in this PR adds noise to the signal before it is "quantized" or resampled from 32 to 8 bits. Done naively, it's easy to add unneeded noise to the image. To ensure dithering is correct and absolutely minimal, noise is adding *within* one step of the output color depth. When converting from the 32bit to 8bit signal, the value is rounded to the nearest 8 bit value (0 - 255). Banding occurs around the transition from one value to the next, let's say from 50-51. Dithering will never add more than +/-0.5 bits of noise, so the pixels near this transition might round to 50 instead of 51 but will never round more than one step. This means that the output image won't have excess variance: - in a gradient from 49 to 51, there will be a step between each band at 49, 50, and 51. - Done correctly, the modified image of this gradient will never have a adjacent pixels more than one step (0-255) from each other. - I.e. when scanning across the gradient you should expect to see: ``` |-band-| |-band-| |-band-| Baseline: 49 49 49 50 50 50 51 51 51 Dithered: 49 50 49 50 50 51 50 51 51 Dithered (wrong): 49 50 51 49 50 51 49 51 50 ```   You can see from above how correct dithering "fuzzes" the transition between bands to reduce distinct steps in color, without adding excess noise. ### HDR The previous section (and this PR) assumes the final output is to an 8-bit texture, however this is not always the case. When Bevy adds HDR support, the dithering code will need to take the per-channel depth into account instead of assuming it to be 0-255. Edit: I talked with Rob about this and it seems like the current solution is okay. We may need to revisit once we have actual HDR final image output. --- ## Changelog ### Added - All pipelines now support deband dithering. This is enabled by default in 3D, and can be toggled in the `Tonemapping` component in camera bundles. Banding is a graphical artifact created when the rendered image is crunched from high precision (f32 per color channel) down to the final output (u8 per channel in SDR). This results in subtle gradients becoming blocky due to the reduced color precision. Deband dithering applies a small amount of noise to the signal before it is "crunched", which breaks up the hard edges of blocks (bands) of color. Note that this does not add excess noise to the image, as the amount of noise is less than a single step of a color channel - just enough to break up the transition between color blocks in a gradient. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
Labels
Bevy version
main
What you did
Run the minimal
3d_sceneexample.What went wrong
Very visible color banding:

Additional information
This is a known limitation of rendering to 8 bit color channels. A common solution appears to be a debanding shader. See here for a related section in the Godot docs. While this isn't a bug in the sense that the output is wrong, it's a bug in that it is a well known visible artifact that we can mitigate.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: